Syntax: How to Add DBA Restrictions to the Join Condition
SET DBAJOIN = {OFF|ON}
where:
- OFF
-
Treats DBA restrictions as WHERE filters in the report request. OFF is the default value.
- ON
-
Treats DBA restrictions as join conditions.
Example: Using the DBAJOIN Setting With Relational Tables
The following request creates two tables, EMPINFOSQL and EDINFOSQL:
TABLE FILE EMPLOYEE SUM LAST_NAME FIRST_NAME CURR_JOBCODE BY EMP_ID ON TABLE HOLD AS EMPINFOSQL FORMAT SQLMSS END -RUN TABLE FILE EDUCFILE SUM COURSE_CODE COURSE_NAME BY EMP_ID ON TABLE HOLD AS EDINFOSQL FORMAT SQLMSS END
Add the following DBA attributes to the end of the generated EMPINFOSQL Master File. With the restrictions listed, USER2 cannot retrieve course codes of 300 or above:
END DBA=USER1,$ USER=USER2, ACCESS = R, $ FILENAME=EDINFOSQL,$ USER=USER2, ACCESS = R, RESTRICT = VALUE, NAME=SYSTEM, VALUE=COURSE_CODE LT 300;,$
Add the following DBA attributes to the end of the generated EDINFOSQL Master File:
END DBA=USER1,DBAFILE=EMPINFOSQL,$
Issue the following request:
SET USER=USER2 SET DBAJOIN=OFF JOIN LEFT_OUTER EMP_ID IN EMPINFOSQL TO MULTIPLE EMP_ID IN EDINFOSQL AS J1 TABLE FILE EMPINFOSQL PRINT LAST_NAME FIRST_NAME COURSE_CODE COURSE_NAME ON TABLE SET PAGE NOPAGE ON TABLE SET STYLE * GRID=OFF,$ END
On the report output, all host and child rows with course codes 300 or above have been omitted, as shown in the following image:

In the generated SQL the DBA restriction has been added to the WHERE predicate in the SELECT statement:
SELECT T1."EID", T1."LN", T1."FN", T2."CC", T2."CD" FROM EMPINFOSQL T1, EDINFOSQL T2 WHERE (T2."EID" = T1."EID") AND (T2."CC" < '300;');
Rerun the request with SET DBAJOIN=ON. The output now displays all host rows, with missing values substituted for lower-level segment instances that did not satisfy the DBA restriction, as shown on the following image:
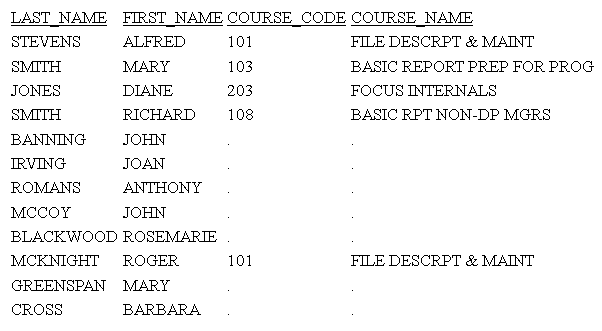
In the generated SQL, the DBA restriction has been added to the join, and there is no WHERE predicate:
SELECT
T1."EID",
T1."LN",
T1."FN",
T2."EID",
T2."CC",
T2."CD"
FROM
( EMPINFOSQL T1
LEFT OUTER JOIN EDINFOSQL T2
ON T2."EID" = T1."EID" AND
(T2."CC" < '300;') );