Syntax: How to Calculate Running Maximum Between the Current and a Prior Value of a Field
RUNNING_MAX(field, reset_key, lower)
where:
- field
-
Numeric or an alphanumeric field that contains all numeric digits.
The field to be used in the calculation.
- reset_key
-
Identifies the point at which the running maximum restarts. Valid values are:
- The name of a sort field in the request.
- PRESET, which uses the value of the PARTITION_ON parameter, as described in Specify the Partition Size for Simplified Statistical Functions.
- TABLE, which indicates that there is no break on a sort field.
Note: The values used in the calculations depend on the sort sequence (ascending or descending) specified in the request. Be aware that displaying a date or time dimension in descending order may produce different results than those you may expect.
- lower
-
Is the starting point in the partition for the running maximum. Valid values are:
- A negative number, which identifies the offset from the current row.
- B, which specifies the beginning of the sort group.
Example: Calculating a Running Maximum
The following request calculates a running maximum for the rows from the beginning of the table to the current value of QUANTITY_SOLD, with no reset point.
TABLE FILE wf_retail_lite
SUM QUANTITY_SOLD
COMPUTE RMAX = RUNNING_MAX(QUANTITY_SOLD,TABLE,B);
BY PRODUCT_CATEGORY
BY PRODUCT_SUBCATEG
ON TABLE SET PAGE NOLEAD
ON TABLE SET STYLE *
GRID=OFF,$
ENDSTYLE
END
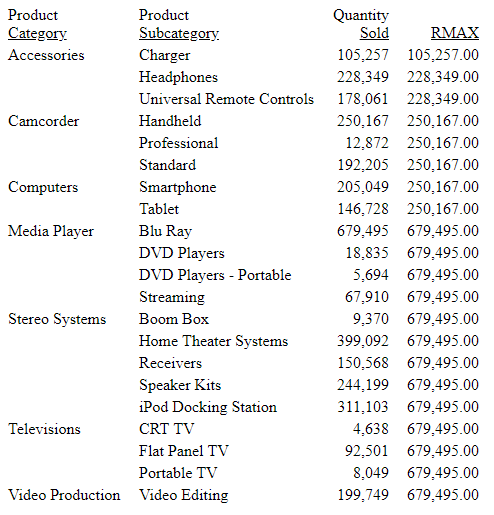
The output is shown in the following image. The first value for RMAX is the value in the Accessories category for Quantity Sold, as there is no prior value. The second value for RMAX is the value for Headphones, as that value is larger. The third value for RMAX is still the value for Headphones, as that value is larger than the Quantity Sold value in the third row. Since the maximum value in the table occurs for Blu Ray, that value is repeated on all future rows, as there is no reset point.