Adding Child Tables
This section describes how to add a related child table definition for publishing data.
Data models typically contain tables that share column data through a relationship. You can configure a publishing table to include related data from another table when it publishes. Data from the related table is not copied into the publishing table, but is fetched by reference.
When rows are inserted into the publishing table, a message that includes data from the source table and related (child) table is published. On the subscriber side, a corresponding table with the same columns as the child table associated with the publishing table must be specified.
Adding child tables requires two separate procedures, one for the publisher adapter and another for the subscriber adapter. First, you add child tables for the source table, and then you add child tables for the destination table.
The database schema must be the same for all tables, but the table names can be different. If the child table associated with the publishing table and the child table associated with the destination table have different names, you must set a mapping between the child tables.
The following restrictions apply to parent and child tables:
| • | The child table in the source database and child table in the destination database must have the same columns. |
| • | When parent-child relationships are defined, a subscriber adapter must use the same repository as the publisher adapter. |
| • | When working with parent-child table relationships, it is good practice to set the ADB_OPCODE values in the parent table and child table to the same value. Or only set the value of ADB_OPCODE in the parent table and leave the child table empty. |
When you add a child table, TIBCO Designer creates a class object in the repository for the child table, and an association object for the relationship.
After adding child tables for a subscriber adapter, you create mappings between child tables on the publisher side and child tables on the subscriber side. For instructions, see Child Table Mappings Tab.
To add child tables for parent-child relationships, perform the following steps in the Publication Service Table tab:
Procedure
| 1. | Click the name of the parent table and select it, and then click the Add Child Table icon. The Add Table dialog is displayed. |
| 2. | Select the related child table from the list and click OK. |
| 3. | Repeat the previous steps to add more child tables. |
When all of the child tables are added, you can then designate a foreign key column as a key in each child table so that a relationship to the parent table can be defined.
| 4. | Select the User Key check box for the foreign key column in the child table. A key icon is displayed next to the column name. |
You must also specify the relationship between the primary column in the parent table and the foreign key column in the child table.
| 5. | Click the Join To field of the child table column, and select the name of the parent table primary key column from the drop-down list. Then click Apply. |
|
Note |
If you select the Publish to ActiveSpaces check box in the Configuration tab, child tables cannot be added. The Publish to ActiveSpaces check box is deprecated in this release. |
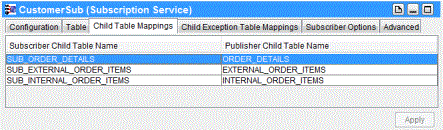
In the following example, a Publication Service service that publishes newly inserted rows into the source table is created. Publisher Options Tab explains how to configure the publisher adapter to publish data by value or by reference.
Figure 304: Publication Service: Table Tab—Add Child Table
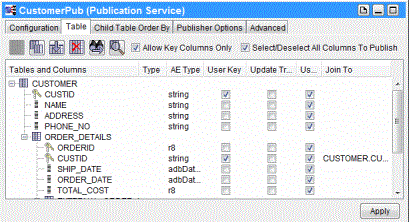
In the following example, a Subscription Service service is created. In this example, received data is inserted into the SUB_ORDER_DETAILS destination table. All three columns of the destination table are configured to receive data.
Figure 305: Subscription Service: Table Tab—Add Child Table
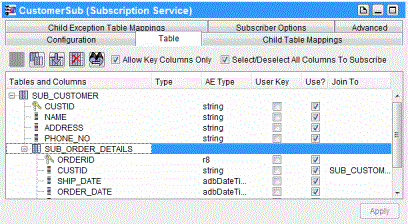
Child Table Mappings shows a child table mapping. The left column (Subscriber Child Table Name) contains the subscriber child table, and the right column (Publisher Child Table Name) contains the publisher child table.
Figure 306: Child Table Mappings