Working with Context Parameters
You can retrieve a context parameter from a request or from a response, and set a context parameter in a request or a response.
Distributed File System Example
Example
A distributed file system component manages files based on the host address of the machine on which the file was created. The address is tracked in a context parameter named httpHost:
The file system component is invoked by SOAP clients through a service with a SOAP binding and by a web application component.
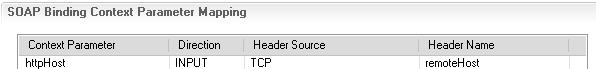
- If a request comes through the SOAP binding, the context parameter is mapped to the TCP remote host header by the SOAP binding:
- If the request originates from the web application, the parameter value is retrieved from the HTTP request and manually set by the servlet implementing the web application component:
String host = req.getRemoteHost(); MutableRequestContext mutableRequestContext = componentContext.createMutableRequestContext(); mutableRequestContext.setParameter("httpHost", String.class, host); componentContext.setRequestContext(mutableRequestContext);
The file system component retrieves the value of the context parameter as follows:
RequestContext requestContext = componentContext.getRequestContext();
String host requestContext.getParameter("httpHost", String.class);
Dynamic Binding Example
Example
Application logic can depend on the value of the application and service name. In particular, the application logic may be used to dynamically determine the target of a reference invocation (also referred to as wire by implementation) in a mediation flow. The following example illustrates how to retrieve the application and service name in a Spring component that invokes a mediation component service, and set context parameters with that data:
String appName = componentContext.getApplicationName();
String svcname = componentContext.getRequestContext().getServiceName();
MutableRequestContext mutableRequestContext =
componentContext.createMutableRequestContext();
mutableRequestContext.setParameter("ServiceName", java.lang.String.class,
svcname);
mutableRequestContext.setParameter("ApplicationName",
java.lang.String.class, appName);
componentContext.setRequestContext(mutableRequestContext);
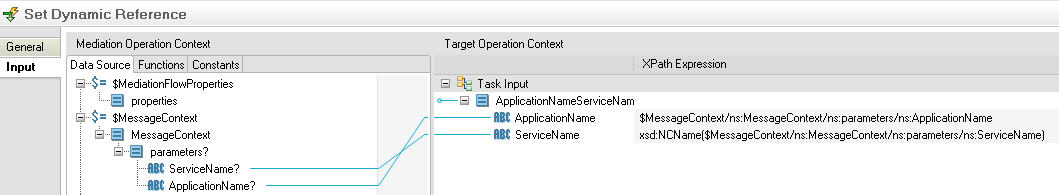
The context parameters are then mapped in the mediation flow's Set Dynamic Reference task property sheet as follows:
Copyright © 2022. Cloud Software Group, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
