Swimlanes
Swimlanes consist of Lanes and Flows.
Lanes
A lane is a subdivision of a pool that is used as a container for partitioning processes.
How you use lanes is specific to your business. A lane can be Normal or Closed. The contents of a normal lane are visible. The contents of a closed lane are not visible and are used for "black-box" processes where you do not know the details of the contained processes.
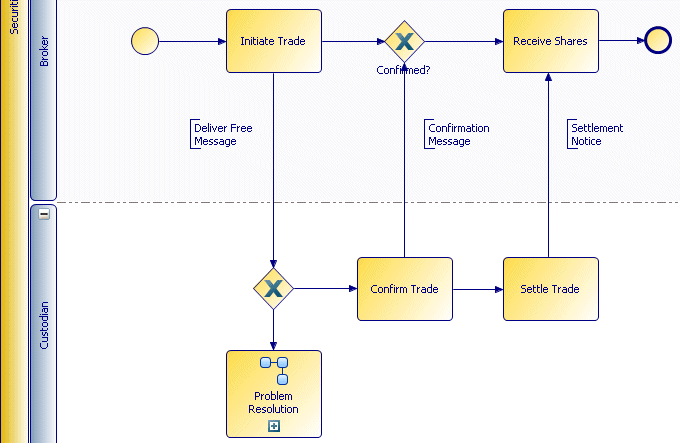
Suppose the back office of a financial institution has a process in which the Securities Reconciliations Department, the Cash Reconciliations Department, the Legal Department and a custodian are all involved. When defining this process, they can be represented by lanes within the pool:
Sequence flow can connect objects in different lanes:
The previous example shows a securities trade between a Broker and a Custodian. The same trade could be represented as follows:
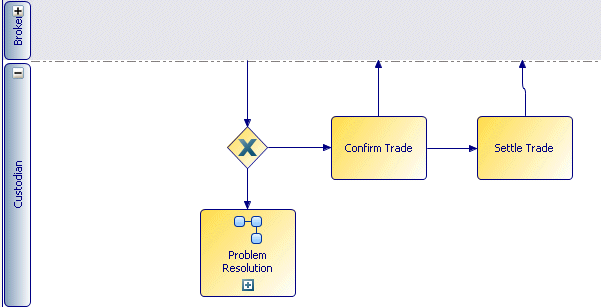
This shows the Custodian lane in a Normal state and the Broker lane in a Closed state. The trade might be represented this way because it is documenting the Custodian’s part in the trade and the Custodian has no knowledge of the internal processes of the Broker.
Pools
A pool is used as a container for partitioning processes in ways that make sense for your business.
A pool is commonly used to document a process in a self-contained system. Typically the business analyst focusses on just one system or pool, but sometimes needs to show interactions with outside systems. For example, a customer places order and does not know how it is fulfilled in the closed supplier pool, but at some point in the process the customer pool receives a fulfillment response (message).
Pools are used in conjunction with lanes and are also related to message flow, which can also be used to show message flow between objects in different pools (see Flows).