Interchange
The interchange is the basic unit of electronic data transfer. It contains at least one functional group or one message and is started by either a service string advice (UNA segment) or by an interchange header (UNB segment). The interchange is identified by the interchange header and terminated by an interchange trailer (UNZ segment).
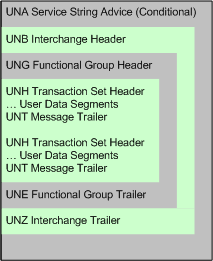
Interchange Structure depicts the structure of an interchange structure.
Figure 64: Interchange Structure
Segments starting with UN are called service segments. They constitute the envelope which groups the EDIFACT messages.
Several interchanges can be bundled into a single file for data transfer.
The following example of an EDIFACT interchange contains a BANSTA (Banking Status) message:
UNA:+.? '
UNB+UNOB:1+Interchange sender identification:1:Interchange s+Interchange recipient identificatio:1:Interchange r+009266:4372+Interchange co+Recipient refe:AA+Application re+A+1+Interchange agreement identifier+1'
UNG+BANSTA+Application sender identification:1+Application recipient identificatio:1+027900:6798+Group referenc+AA+D:98A:Associ+Application pa'
UNH+Message refere+BANSTA:D:98A:AA:Associ+Common access reference+7:C'
BGM+1:12:1:Document/message name+Document/message number:Version:Revisi+1+AA'
DTM+2:Date/time/period:2'
...
UNT+33+Message refere'
UNE+1+Group referenc'UNZ+1+Interchange co'
|
Note |
Normally all of the data in an EDIFACT interchange would be on one line. The example here has the data split across several lines to fit on the page. However, it is not unusual for EDIFACT data to be split on segment boundaries or even blocked at a particular number of characters. |