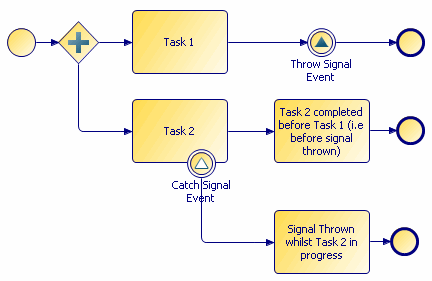
Throw and Catch Signal Events
With throw/catch signal events, an in-flow signal event broadcasts a signal, and if there is an active task with a signal event on the task boundary, that event "catches" the signal, and generally follows the exception path.
Signal events can be local or global.
Local signal events can be used for triggering event handlers, task cancellations and to halt and resume parallel flows. When attached to a user task they can be used to resend data to an outstanding work item for that task.
- You can drag and drop a global signal event onto a process to create throw / catch events.
- A catch signal event can cancel the task it is attached to or, for user tasks, can allow the task to continue. If they are set to "continue", they cannot have an outgoing flow but they can map data into the task that they are attached to and also reschedule timers attached to the same task.
A signal is transient: when it is thrown, if there is nothing to catch it at that moment, it is discarded. It is not stored for later use.
You may specify a signal name with a throw signal event. With a catch signal event, a signal name is optional:
- If a catch signal event has no signal name specified, it catches any thrown signals in the process (while the task it is attached to is active).
- If a catch signal event has a signal name specified, it only catches signal events that throw the named signal.
When you specify signal names in the Properties view for signal events, you can use content assist. This means, for example, that if you have entered SIGNAL1 for a throw signal event, when you specify the signal name for the catch signal event you can press Ctrl+Space and the available signal names are displayed from which you can select one.
A signal end event functions like any other inflow signal event, except that when one fires, if there are more tasks that need to complete as the result of an exception flow, the outstanding tasks complete; if there are no more tasks that need to be completed, the process ends.