Dynamic Organizations
A dynamic organization is a common organization pattern that can be referenced from a number of different organization models. It is used to represent repeating organization patterns, to avoid the need to model these individually everywhere they are required. For example, a bank might have a number of branches each containing a similar group of roles, so a dynamic organization could represent a branch and be used in different organization models.
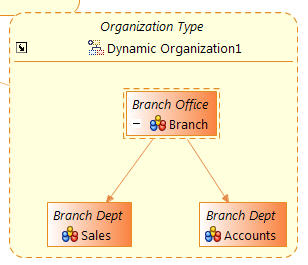
The example above shows a dynamic organization representing a Branch. Dynamic organizations are referenced from dynamic organization units within an organization. See Dynamic Organization Units.
Dynamic Organizations differ from static organizations in a number of ways:
- Only one root organization unit is allowed in a dynamic organization.
- Participants within a process (known as Dynamic Organization Participants) can be created as external references with a reference to an organization entity within a Dynamic Organization. See Dynamic Organization Participants.
- When a Dynamic Organization Participant is assigned to a task you need to identify the correct instance of the Dynamic Organization to use to resolve this participant at runtime (as there may be a number of instances generated dynamically). This is done using Dynamic Organization Identifier Mapping.
Copyright © 2021. Cloud Software Group, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
