Like Mapping
Like mapping is useful in automatically mapping complex elements that are of different types but contain equivalent content.
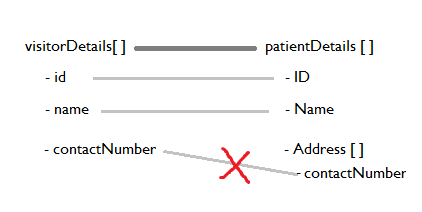
For instance, an application may have two different types VisitorDetails and PatientDetails that share some commonly named children. Performing a like mapping between these two objects is the equivalent of manually mapping all the same named simple type content from the source list to the target list.
It is possible to perform like mapping between arrays of complex types. In this case the equivalently-named child content mappings implied by the like mapping are applied to each element in the array according to the chosen array mapping strategy. If there are nested child arrays that would be like-mapped then the array mapping strategy is selected separately for each.
If there are nested child arrays that would be like-mapped then the array mapping strategy is selected separately for each array.
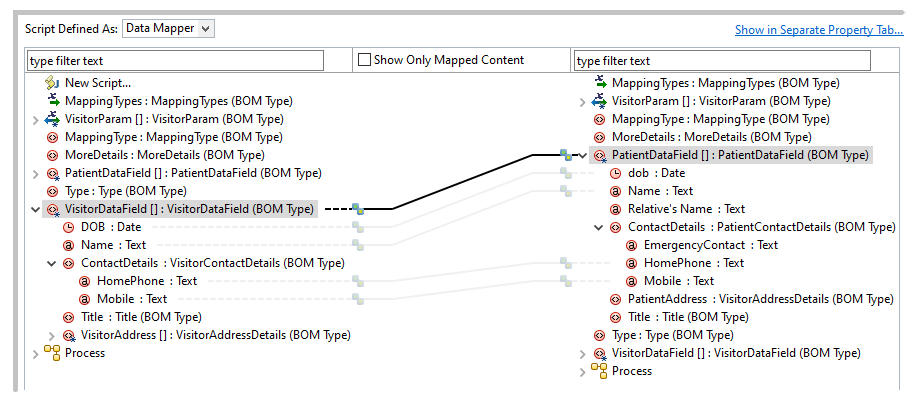
To configure a like mapping, drag an element from the source list or LHS and drop it on a corresponding element in the target list or RHS and right-click the mapping and select Map Like-Named Child Content from the context menu. The child elements with the same name and object type are automatically mapped.
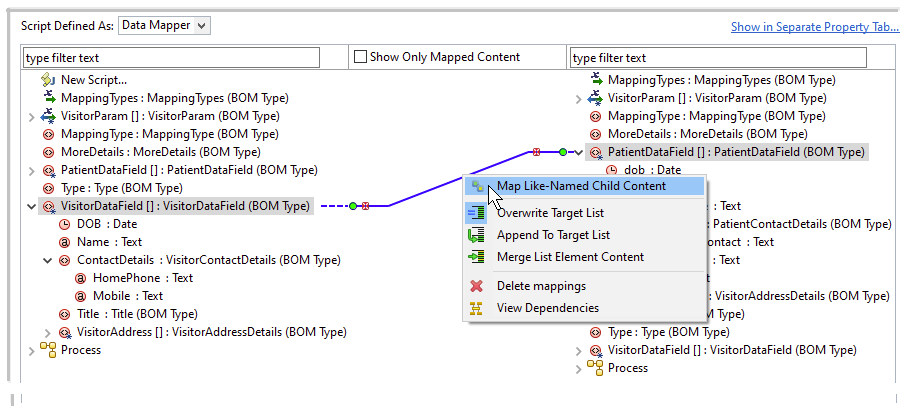
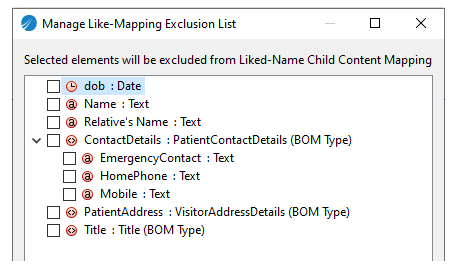
If you do not want a few child elements mapped with like-named child elements, right-click the mapping at the parent level, and select
Open Like-Mapping Exclusion List.
Manage Like-Mapping Exclusion List dialog opens, which lists all the like-mapped elements.