Using a Performer Data Field or Parameter to Dynamically Define a Participant
A performer data field/parameter is a special type of data field/parameter that you can select as a participant for a user task. By assigning a value to the performer data field/parameter earlier in the process, you can dynamically define a participant for a user task. You can populate a performer data field/parameter with one or more organization entity GUIDs, or a single valid non-array RQL expression.
Using a performer field, you can deliver work dynamically to an organizational entity, so that the work items appear in managed work lists. For example:
- Dynamically deliver to a group by name (e.g. using an organization entity GUID:
bpm.process.getOrgModel().groupByName('MyGroup')) - Dynamically deliver to a position within an organization unit by name (for example:
orgunit(name='KEYTeam').position(name='AdditionalStaff') union orgunit(name='Agency').position(name='Contractor'))
You can also use non-RQL scripting to identify dynamic performers. For example:
var groups = bpm.process.getOrgModel().groupByName('MyGroup');
if (groups != null && groups.length == 1) {
// If you find the group that you want, then use its GUID as the performer field value.
data.performer = groups[0].getGuid();
} else {
// If no groups match the given name OR there is more than one group with the same name,
// then take appropriate application-specific remedial action here.
}
resource(name='tibco-admin'),
tibco-admin receives an email notification of a work item
only if the Distribution Strategy is
Allocate to One. - Procedure
- Add the performer data field/parameter as a participant to the user task, using the Properties View.
- Make sure that the process logic assigns a suitable value to the parameter before the user task is executed - for example, by using a script.
You can assign a script.
You can populate a performer field with one of the following:
- an organization entity GUID
- multiple organization entity GUIDs (using a performer array field that contains multiple GUIDs - each of the performer fields in the array contains an organization entity GUID )
- a single valid non-array RQL expression (that resolves to one or more organization entities).
- a resource GUID. For example:
var users= bpm.process.getOrgModel().resourceByName('JohnSmith'); if (users!= null && users.length == 1) { // If you find the user that you want, then use its GUID as the performer field value. data.performer = users[0].getGuid(); } else { // If no users match the given name OR there is more than one user with the same name, // then take appropriate application-specific remedial action here. }
Note: Using an organization entity GUID or multiple organization entity GUIDs means that dynamic performers allow references to specific organizational entities, so that they appear in the relevant managed work lists. You should only need to use RQL if you want to offer work based on capabilities, privileges or intersections of organization entities. In most cases, writing a script to identify the organization entity GUIDs you need and populating the performer fields with these are much more efficient than using RQL.For example, the annotated process extract below shows part of a purchasing process that contains a user task to approve a requisition. The process requires that if the requisition value is less than $50000, this task can be performed by an Accountant. If it is more than or equal to $50000, it must be performed by the Finance Manager.
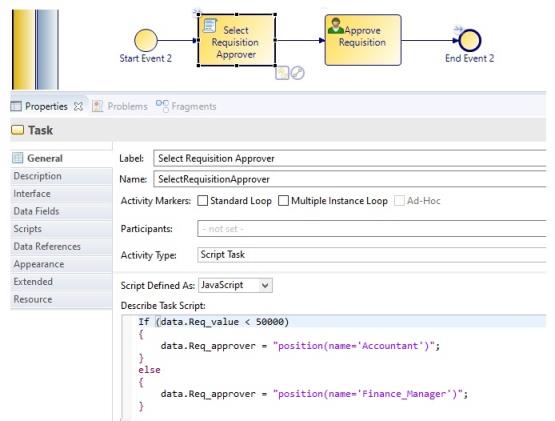
The Select Requisition Approver script task assigns a value to the Req_approver performer data field, based on the value of the requisition which is held in Req_value (and which we assume to have been defined earlier in the process).
The Approve Requisition task assigns the work item to the Req_approver performer data field - the value of which is either "Accountant" or "Finance_Manager" (both of which are also defined as participants for the process).
Using a performer field, you can deliver work dynamically to an organizational entity, so that the work items appear in managed work lists.