Using Fault Handlers
Fault handlers are used to catch faults or exceptions and create fault-handling procedures to deal with potential errors.
Fault handlers are defined at the scope level allowing you to catch faults or exceptions thrown by activities within a scope. There are two types of fault handlers: Catch Specific Fault and Catch All Faults.
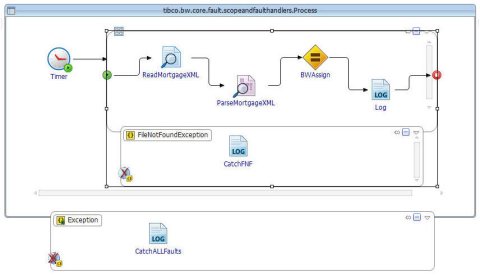
Fault handlers can be defined at the process level, or at a scope level within a process. The diagram below shows two fault handlers - one defined at the process level and the other defined at an inner scope level.
Fault Handler Attached to an Inner Scope
- Procedure
- Select the activities inside the process where the exception is expected to occur and select from the right-click menu.
- Move the cursor right underneath the scope's lower border to view the icons to create fault handlers.
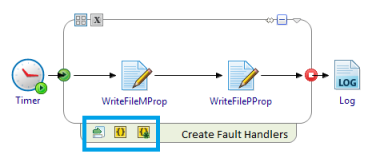
- Click one the following:
- Create Catch
 to create a fault handler for a specific exception.
to create a fault handler for a specific exception.
- Create Catch All
 to create a fault handler to catch all exceptions.
to create a fault handler to catch all exceptions.
A new fault handler is added under the scope. - Create Catch
- Add activities and configure the fault handling procedure inside the fault handler area. For example, add a Log activity inside the fault handler area to record messages from the exception.