Migrating Design Time Libraries ( DTL) as Shared Modules
TIBCO ActiveMatrix BusinessWorks™ 5.x design time library source projects can be migrated as TIBCO BusinessWorks Container Edition shared modules.
Using the TIBCO BusinessWorks Container Edition framework, you can migrate TIBCO ActiveMatrix BusinessWorks 5.x projects where the business process uses design time libraries to define the processes, resources, subprocesses, and so on.
Procedure
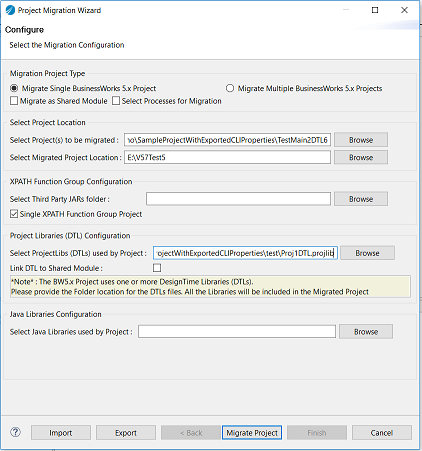
- In the Project Migration Wizard dialog box, click Migrate Single BusinessWorks 5.x Project and select the Migrate as Shared Module check box.
- Provide the Project Location details and the XPATH Function Group Configuration details if a custom XPath is used in the project.
- To browse for third party jars only if your project contains a custom XPath, click the Select Third Party JARs folder field .
- Click Migrate Project.
Result
Limitations
After migration, do not perform refactoring operations on any of the resources like the schema, TIBCO BusinessWorks Container Edition shared resources, service definitions, and so on. The properties, and naming conventions of the resources must be retained as they are. Mapping issues, if any, can be corrected, and resource specific properties of the shared resources can be changed.
- Shared module migration does not support TIBCO ActiveMatrix BusinessWorks 5.x AE schemas. AE Schemas are migrated as part of the application module.
- Custom XPath function project duplication should be managed manually by deleting the duplicate source projects.
- DTL migration does not support the Process Name Dynamic Override feature of the Call Process activity. To use this feature, add the process name manually.
Migrating Application Modules
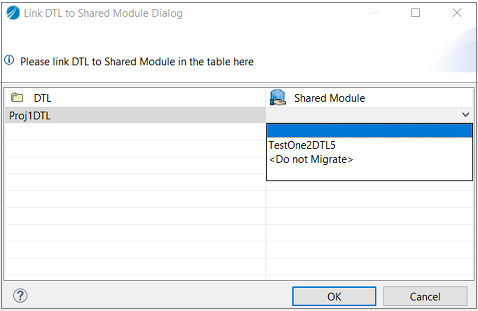
TIBCO ActiveMatrix BusinessWorks™ 5.x projects using design time libraries can be migrated as application modules by linking the corresponding shared modules to the DTL libraries.
Select the required DTL project, and click OK.
Mapping the DTL to the <Do Not Migrate> option does not link the DTL to the shared module.