Deploying a monitoring application on Kubernetes
You can deploy an monitoring application on kubernetes with an external database.
Before you begin
- Ensure that you have configured the database for application monitoring.
- Ensure that you have created the TIBCO BusinessWorks™ Container Edition base docker image. For more information about creating base docker image, see Creating TIBCO BusinessWorks Container Edition base docker image in the Application Development guide.
- Ensure that you have created the TIBCO BusinessWorks™ Container Edition application docker image. For more information about building application docker image, see Building the application docker image in the Sample guide.
- Procedure
- Tag the application docker image by running the following command:
docker tag <application_name>your_docker_container_registry/<your_project_name>/<application_name>
- Push your application image to the Docker Container Registry.
For example: To push your application docker image on Google Cloud Registry, run the following command:
gcloud docker push gcr.io/<your_project_name>/<application_name>
- Confirm that the image is present in the Docker Container Registry.
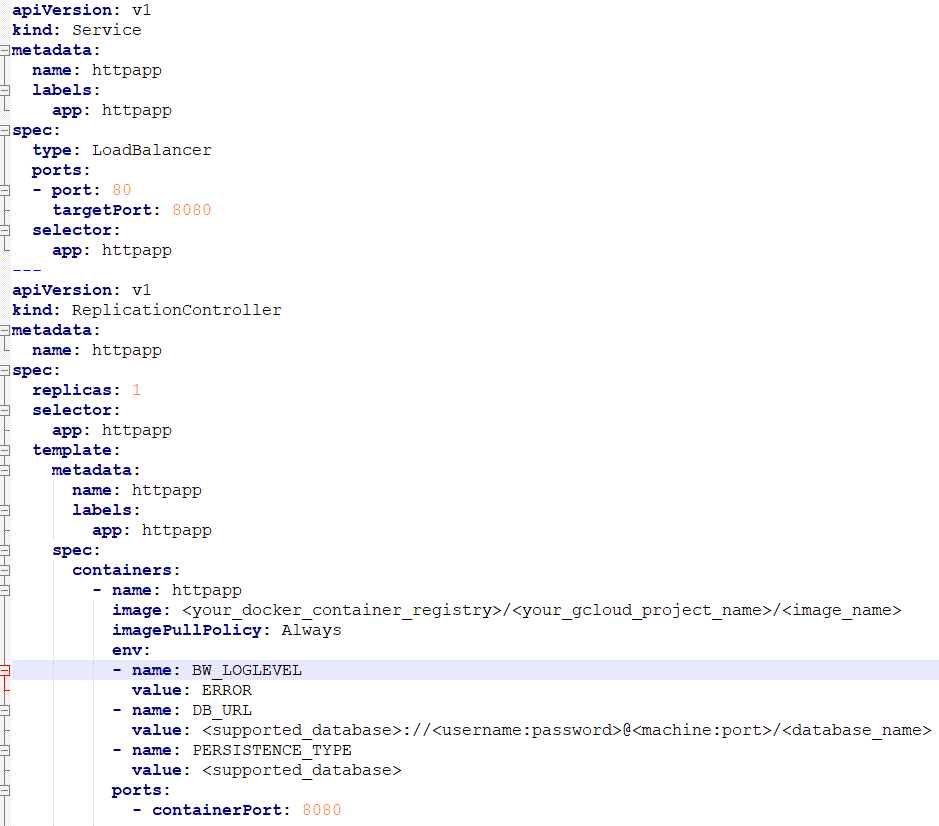
- Create the
manifest.ymlfile and update the application image name. Ensure that the image name follows the following format:<your_docker_container_registry>/<your_gcloud_project_name>/<image_name>
To configure monitoring application with external database, add the following two environment variables to the manifest file. - To create the monitoring service and replication controller, run the following command:
kubectl create -f manifest.yml
- To verify that the application has started successfully, run the following command:
kubectl logs pod-name - To get the external IP of running monitoring service, run the following command:
kubectl get svc
Access the monitoring dashboard in the browser by using the external IP.