Matching with business objects
Overview
In some business use cases, data deduplication is performed on the data that defines a business concept or object. Often, multiple tables are used to create or model a business object and define its attributes. In these cases, matching needs to be performed in a more holistic fashion to determine whether two objects represent the same entity.
Merging and golden record creation should also take into account the object as a whole. To meet these requirements, the TIBCO EBX® Match and Merge Add-on allows you to configure and run matching and merging operations on EBX® Business Objects.
Note
The add-on supports matching up to a depth of 3 levels (parent, child, grandchild) on business objects. However, to avoid performance issues, it is recommended to configure a maximum of 2 levels for matching.
In essence, a business object is comprised of one main table, and all of its related tables. See the TIBCO EBX® documentation for more details on business objects.
Note
The current relationship depth that is supported for merging is the grandchild level. In other words, two relationships away from the main business object table.
Business object example
A common use case for business objects is that of representing a customer. For instance, a main customer table that represents an individual or business. It is possible that many tables are related to this main table and together they comprise the customer entity, for example address, contact, and billing information. From a data deduplication standpoint, two business objects might be considered as representing the same entity when a match is found in the:
Main business object table.
Business object's related tables.
Main and related tables of the business object.
If a match is found, the add-on maintains any relationships. For example:
When a new golden record is created in the main table, new golden records are also created in the related tables and linked to the new main golden.
If a record in the main table is determined to be golden, and no conflicting policies are applied to the related tables, all linked records in related tables are also considered golden.
Since a merge operation will only result in the creation of new golden records, merged records from the main and related tables remain unchanged.
Configuring matching on business objects
Before setting up a matching configuration for a business object, the business object must be created in the DMA and published. Once these steps are complete, you configure matching for a business object much in the same way as for a normal table.
Note
A table cannot be activated for a business object that is already used in a single table matching configuration.
The main differences in business object matching configuration are:
You start from the Business object activation and settings in the Administration pane and register a business object with the add-on instead of a table. Note that the Advanced settings tab is located at this level.
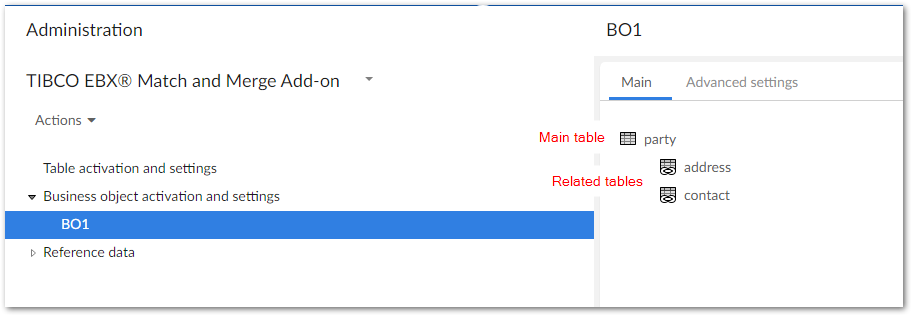
You have the option of creating one configuration for the main table, or configuring each table in the business object.
When you want to match and automatically merge records in the business object's related tables, you must configure matching and merging on the main table and related tables. Specifically, each related table must have a default matching policy that specifies a merge policy.
The option to automatically trigger matching operations is available for business objects. Only the After submission option is available to use with business objects, either On creation or On update.
Configure this option on the matching policy for the business object's main table (the option is not available on related tables). When users create records in tables related to the business object's main table, the On update property setting is used.
When configuring decision trees, you can select fields to compare from all tables that make up the business object.
Matching operations are only available to run from the main table in the business object.
The following limitations are in place for business object matching:
When configuring the decision tree for related tables, there is no Suspect node.
Only automatic foreign key alignment is available.
Automatic golden creation for business objects
When configuring automatic creation of golden records in a merge policy for a business object, you can choose from the following options:
Duplicates and Singletons (available for business object parent and child entities): The add-on automatically creates a new golden record when it identifies a positive match between records, or when a record doesn't have any match. This property is only applied in the case of record creation, modification, merge or matching operations.
Only duplicates (available for a business object parent entity only): A new golden record is automatically created only when the add-on identifies a positive match between records. With this option selected, child entities must use the On duplicate parent option described below.
Any duplicates (available for child entities only): In a Business Object if the parent has positive matches, a new golden is created for the parent and its children. If matches are found for children of the same parent, but not the parent, a new golden is created for the child only.