ユーザーサービスの実装
実装インターフェイス
次の表に、実装するインターフェイスのネイチャーを示します。
ネイチャー | インターフェイス |
|---|---|
Dataspace | UserService<DataspaceEntitySelection> |
Dataset | UserService<DatasetEntitySelection> |
TableView | UserService<TableViewEntitySelection> |
Record | UserService<RecordEntitySelection> |
Hierarchy | UserService<HierarchyEntitySelection> |
HierarchyNode | UserService<HierarchyNodeEntitySelection> |
Association | UserService<AssociationEntitySelection> |
AssociationRecord | UserService<AssociationRecordEntitySelection> |
ライフサイクルとスレッドモデル
ユーザーサービスの実装クラスは次のとおりです。
宣言 createUserService() メソッドを呼び出すことにより、最初のHTTPリクエストでインスタンス化されます。
現在のページがスコープ外になるか、セッションがタイムアウトすると破棄されます。
このクラスへのアクセスはTIBCO EBX®によって同期され、一度に1つのHTTPリクエストのみが処理されるようにします。したがって、クラスはスレッドセーフである必要はありません。
ユーザーサービスには属性がある場合があります。これらの属性の状態は、HTTPリクエスト間で保持されます。ただし、開発者は、EBX®サーバーに過負荷をかけないように、これらの属性でメモリなどのリソースを適度に使用する必要があることに注意する必要があります。
オブジェクトコンテキスト
オブジェクトコンテキストは、ユーザーサービスによって管理されるオブジェクトのコンテナです。このコンテキストは、ユーザーサービスによるメソッド UserService.setupObjectContext の実装によって初期化および変更されます。
オブジェクトコンテキストのオブジェクトは、オブジェクトキーによって識別されます。
ObjectKey customerKey = ObjectKey.forName("customer");
オブジェクトには、次のものがあります。
レコード
データセット
まだ持続していない新しいレコード
動的オブジェクト
オブジェクトコンテキストはHTTPリクエスト間で維持され、通常は最初のリクエスト時にのみ設定する必要があります。
永続化されると、新しいレコードオブジェクトは自動的にプレーンレコードオブジェクトに変更されます。
適応と同様に、パス式はオブジェクトのサブエレメントを参照するために使用されます。
次の例では、ペインライターがオブジェクトの属性にマップされたフォーム入力を追加します。
// Add an input field for customer's last name.
aWriter.setCurrentObject(customerKey);
aWriter.addFormRow(Path.parse("lastName"));
次の例では、イベントコールバックがオブジェクトの属性の値を取得します。
// Get value of customer's last name.
ValueContext customerValueContext = aValueContext.getValueContext(customerKey);
String lastName = customerValueContext.getValue(Path.parse("lastName"));
動的オブジェクトは、スキーマがユーザーサービス自体によって定義されるオブジェクトです。プログラムでスキーマを定義するためのAPIが提供されています。このAPIでは、インスタンスエレメント(インスタンスノード)のみを定義できます。テーブルの定義はサポートされていません。タイプ、ラベル、カスタムウィジェット、列挙型、プログラムによる制約など、標準のEBX®データモデルで利用できる他のほとんどの機能をサポートします。
次の例は、同じスキーマを持つ2つのオブジェクトを定義しています。
public class SampleService implements UserService<TableViewEntitySelection>
{
// Define an object key per object:
private static final ObjectKey _PersonObjectKey = ObjectKey.forName("person");
private static final ObjectKey _PartnerObjectKey = ObjectKey.forName("partner");
// Define a path for each property:
private static final Path _FirstName = Path.parse("firstName");
private static final Path _LastName = Path.parse("lastName");
private static final Path _BirthDate = Path.parse("birthDate");
...
// Define and register objects:
@Override
public void setupObjectContext(
UserServiceSetupObjectContext<DataspaceEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceObjectContextBuilder aBuilder)
{
if (aContext.isInitialDisplay())
{
BeanDefinition def = aBuilder.createBeanDefinition();
BeanElement firstName = def.createElement(_FirstName, SchemaTypeName.XS_STRING);
firstName.setLabel("First name");
firstName.setDescription("This is the given name");
firstName.setMinOccurs(1);
BeanElement lastName = def.createElement(_LastName, SchemaTypeName.XS_STRING);
lastName.setLabel("Last name");
lastName.setDescription("This is the familly name");
lastName.setMinOccurs(1);
BeanElement birthDate = def.createElement(_BirthDate, SchemaTypeName.XS_DATE);
birthDate.setLabel("Birth date");
birthDate.addFacetMax(new Date(), false);
aBuilder.registerBean(_PersonObjectKey, def);
aBuilder.registerBean(_PartnerObjectKey, def);
}
...
}
ディスプレイの設定
表示は、ユーザーサービスによるメソッド UserService.setupDisplay の実装によって設定されます。
このメソッドはリクエストごとに呼び出され、以下を設定できます。
タイトル(デフォルトはユーザーサービス宣言で指定されたラベルです。)
コンテキストヘルプURL
階層リンク
ツールバー
下部ボタン
必要に応じて、ヘッダーと下部ボタンを非表示にすることができます。
表示設定は永続化されず、HTTPリクエストごとに、メソッド UserService.setupDisplay を呼び出す前にデフォルトにリセットされます。
下部ボタン
ボタンには、アクションと送信の2種類があります。
actionボタンは、フォームを送信せずにactionイベントをトリガーします。デフォルトでは、ユーザーは、ページを離れることにより、最後の変更が失われることを認める必要があります。この動作はカスタマイズできます。
送信ボタンは、常にフォームを送信する送信イベントをトリガーします。
イベントの詳細については、次のセクションを参照してください。
コンテンツコールバック
このコールバックは通常、インターフェイス UserServicePaneを実装して、プレーンなEBX®フォームをレンダリングします。コールバックは、タブ付きのEBX®フォームをレンダリングするための UserServiceTabbedPane のインスタンスにすることもできます。
特定のケースでは、コールバックは UserServiceRawPaneを実装できます。このインターフェイスには制限がありますが、EBX®によって管理されていないHTMLフォームを実装する場合に役立ちます。
ツールバー
ツールバーはオプションであり、2つのフレーバーがあります。
フォームスタイル:
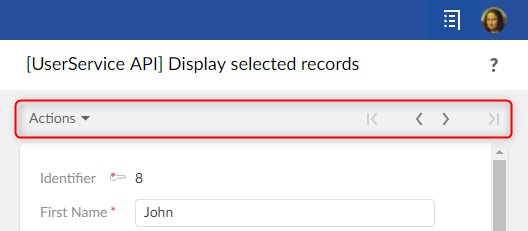
テーブルビュースタイル:
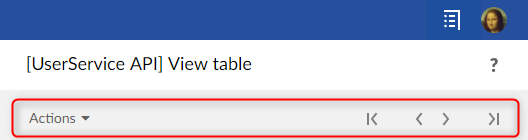
スタイルは自動的に選択されます。レコードに定義されたツールバーはフォームスタイルであり、テーブルに定義されたツールバーはテーブルビュースタイルです。
例
次の例は、データの保存が成功した場合にのみ、現在のユーザーサービスを閉じ、ユーザーを現在の選択にリダイレクトするボタンを実装しています。
public class SampleService implements UserService<...>
{
private static final ObjectKey _RecordObjectKey = ObjectKey.forName("record");
...
@Override
public void setupDisplay(
UserServiceSetupDisplayContext<RecordEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceDisplayConfigurator aConfigurator)
{
...
// Define a "save and close" button with callback onSave().
aConfigurator.setLeftButtons(aConfigurator.newSaveCloseButton(this::onSave));
}
private UserServiceEventOutcome onSave(UserServiceEventContext anEventContext)
{
ProcedureResult result = anEventContext.save(_RecordObjectKey);
if (result.hasFailed())
{
// Save has failed. Redisplay the user message.
return null;
}
// Save has succeded.Close the service.
return UserServiceNext.nextClose();
}
}
次の例は、Java6構文と互換性があります。前のコードとの違いのみが示されています。
public class SampleService implements UserService<...>
{
...
@Override
public void setupDisplay(
UserServiceSetupDisplayContext<RecordEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceDisplayConfigurator aConfigurator)
{
...
// Define a "save and close" button with callback onSave().
aConfigurator.setLeftButtons(aConfigurator.newSaveCloseButton(new UserServiceEvent() {
@Override
public UserServiceEventOutcome processEvent(UserServiceEventContext anEventContext)
{
return onSave(anEventContext);
}
}));
}
}
次の例は、サービスを閉じて現在のユーザーを別のユーザーサービスにリダイレクトするURLを実装しています。
public class SampleService implements UserService<...>
{
...
private void writePane(UserServicePaneContext aPaneContext, UserServicePaneWriter aWriter)
{
// Displays an ULR that redirect current user.
String url = aWriter.getURLForAction(this::goElsewhere);
aWriter.add("<a ");
aWriter.addSafeAttribute("href", url);
aWriter.add(">Go elsewhere</a");
}
private UserServiceEventOutcome goElsewhere(UserServiceEventContext anEventContext)
{
// Redirects current user to another user service.
ServiceKey serviceKey = ServiceKey.forModuleServiceName("CustomerModule", "CustomService");
return UserServiceNext.nextService(serviceKey);
}
}
次のコードは、メソッドUserService.processEventOutcomeの実装であり、単純なユーザーサービスには十分です。
public class HelloWordService implements UserService<...>
{
@Override
public UserServiceEventOutcome processEventOutcome(
UserServiceProcessEventOutcomeContext<DatasetEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceEventOutcome anEventOutcome)
{
// By default do not modify the outcome.
return anEventOutcome;
}
}
次の例は、3つのステップを含む、より複雑な「ウィザード」サービスであり、各ステップには独自のUserService.setupDisplayメソッドがあります。
// Custom outcome values.
public enum CustomOutcome implements UserServiceEventOutcome {
displayStep1, displayStep2, displayStep3
};
// All steps of the wizard service implement this interface.
public interface WizardStep
{
public void setupDisplay(
UserServiceSetupDisplayContext<DataspaceEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceDisplayConfigurator aConfigurator);
}
// The user service implementation.
public class WizardService implements UserService<...>
{
// Attribute for current step.
private WizardStep step = new WizardStep1();
...
@Override
public void setupDisplay(
UserServiceSetupDisplayContext<DataspaceEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceDisplayConfigurator aConfigurator)
{
...
// Display current step.
this.step.setupDisplay(aContext, aConfigurator);
}
@Override
public UserServiceEventOutcome processEventOutcome(
UserServiceProcessEventOutcomeContext<DataspaceEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceEventOutcome anEventOutcome)
{
// Custom outcome value processing.
if (anEventOutcome instanceof CustomOutcome)
{
CustomOutcome action = (CustomOutcome) anEventOutcome;
switch (action)
{
case displayStep1:
this.step = new WizardStep1();
break;
case displayStep2:
this.step = new WizardStep2();
break;
case displayStep3:
this.step = new WizardStep3();
break;
}
// Redisplay the user service.
return null;
}
// Let EBX® process the event outcome.
return anEventOutcome;
}
}
データベースの更新
イベントコールバックはデータベースを更新する場合があります。
次の例は、1つのトランザクションを使用して2つのオブジェクトを保存します。
public class MultipleObjectsSampleService implements UserService<...>
{
// This service defines a two objects having same schema.
private static final ObjectKey _Person1_ObjectKey = ObjectKey.forName("person1");
private static final ObjectKey _Person2_ObjectKey = ObjectKey.forName("person2");
...
// Save button callback.
private UserServiceEventOutcome onSave(UserServiceEventContext aContext)
{
ProcedureResult result = aContext.save(_Person1_ObjectKey, _Person2_ObjectKey);
if (result.hasFailed())
{
//Save failed. Redisplay the service.
//The user interface will automatically report error messages.
return null;
}
// Save succeeded. Close the service.
return UserServiceNext.nextClose();
}
}
次の例は、プロシージャを使用してデータベースを更新します。
import com.orchestranetworks.service.*;
import com.orchestranetworks.userservice.*;
public class MultipleObjectsSampleService implements UserService<...>
{
...
// Event callback.
private UserServiceEventOutcome onUpdateSomething(UserServiceEventContext aContext)
{
Procedure procedure = new Procedure()
{
public void execute(ProcedureContext aContext) throws Exception
{
// Code that updates database should be here.
...
}
};
UserServiceTransaction transaction = aContext.createTransaction();
transaction.add(procedure);
ProcedureResult result = transaction.execute();
if (result.hasFailed())
{
aContext.addError("Procedure failed");
}
else
{
aContext.addInfo("Procedure succeeded");
}
return null;
}
Ajax
ユーザーサービスはAjaxコールバックを実装できます。 Ajaxコールバックは、インターフェイスUserServiceAjaxRequestを実装する必要があります。
クライアントは、UserServiceResourceLocator.getURLForAjaxRequest によって生成されたURLを使用してAjaxコールバックを呼び出します。
Ajaxコンポーネントの使用を容易にするために、EBX®は、リクエストを送信して応答を処理するためのJavaScriptプロトタイプ EBX_AJAXResponseHandlerを提供します。 EBX_AJAXResponseHandlerの詳細については、UserServiceAjaxRequest を参照してください。
次の例は、部分的なHTMLを返すAjaxコールバックを実装しています。
public class AjaxSampleService implements UserService<DataspaceEntitySelection>
{
...
@Override
public void setupDisplay(
UserServiceSetupDisplayContext<DataspaceEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceDisplayConfigurator aConfigurator)
{
aConfigurator.setLeftButtons(aConfigurator.newCloseButton());
aConfigurator.setContent(this::writePane);
}
/**
* Displays an URL that will execute the callback
* and display the returned partial HTML inside a <div> tag.
*/
private void writePane(UserServicePaneContext aPaneContext, UserServicePaneWriter aWriter)
{
// Generate the URL of the Ajax callback.
String url = aWriter.getURLForAjaxRequest(this::ajaxCallback);
// The id of the <div> that will display the partial HTML returned by the Ajax callback.
String divId = "sampleId";
aWriter.add("<div ");
aWriter.addSafeAttribute("class", UICSSClasses.CONTAINER_WITH_TEXT_PADDING);
aWriter.add(">");
// Display the URL that will execute the callback.
aWriter.add("<a ");
aWriter.addSafeAttribute("href", "javascript:sample_sendAjaxRequest('" + url + "', '"
+ divId + "')");
aWriter.add(">");
aWriter.add("Click to call a user service Ajax callback");
aWriter.add("</a>");
// Output the <div> tag that will display the partial HTML returned by the callback.
aWriter.add("<div ");
aWriter.addSafeAttribute("id", divId);
aWriter.add("></div>");
aWriter.add("</div>");
// JavaScript method that will send the Java request.
aWriter.addJS_cr();
aWriter.addJS_cr("function sample_sendAjaxRequest(url, targetDivId) {");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" var ajaxHandler = new EBX_AJAXResponseHandler();");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" ajaxHandler.handleAjaxResponseSuccess = function(responseContent) {");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" var element = document.getElementById(targetDivId);");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" element.innerHTML = responseContent;");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" };");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" ajaxHandler.handleAjaxResponseFailed = function(responseContent) {");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" var element = document.getElementById(targetDivId);");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" element.innerHTML = \"<span class='" + UICSSClasses.TEXT.ERROR
+ "'>Ajax call failed</span>\";");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" }");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" ajaxHandler.sendRequest(url);");
aWriter.addJS_cr("}");
}
/**
* The Ajax callback that returns partial HTML.
*/
private void ajaxCallback(
UserServiceAjaxContext anAjaxContext,
UserServiceAjaxResponse anAjaxResponse)
{
UserServiceWriter writer = anAjaxResponse.getWriter();
writer.add("<p style=\"color:green\">Ajax callback succeeded!</p>");
writer.add("<p>Current data and time is: ");
DateFormat format = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(
DateFormat.FULL,
DateFormat.FULL,
Locale.US);
writer.addSafeInnerHTML(format.format(new Date()));
writer.add("</p>");
}
}
RESTデータサービス
ユーザーサービスは、HTTPリクエストを介してRESTデータサービスにアクセスできます。
クライアントは、UIResourceLocator.getURLForRest によって生成されたURLを使用する必要があります。このURLには、ユーザー認証に必要な情報が含まれています。
RESTデータサービスの詳細については、ビルトイン RESTfulサービスを参照してください。
次の例は、応答がtextareaに出力されるRESTデータサービス呼び出しを実装しています。
public class RestCallSampleService implements UserService<DataspaceEntitySelection>
{
...
@Override
public void setupDisplay(
UserServiceSetupDisplayContext<DataspaceEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceDisplayConfigurator aConfigurator)
{
aConfigurator.setLeftButtons(aConfigurator.newCloseButton());
aConfigurator.setContent(this::writePane);
}
private void writePane(UserServicePaneContext aPaneContext, UserServicePaneWriter aWriter)
{
// Generates the URL for REST data service call without additional parameters
final String url = aWriter.getURLForRest("/ebx-dataservices/rest/{specificPath}", null);
final String resultAreaId = "restResult";
// Displays a link for REST data service call
aWriter.add("<div ");
aWriter.addSafeAttribute("class", UICSSClasses.CONTAINER_WITH_TEXT_PADDING);
aWriter.add(">");
aWriter.add("<p>This link will display the response after making a REST call</p>");
aWriter.add("<a ");
aWriter.addSafeAttribute("href",
"javascript:sendRestRequest('" + url + "', '" + resultAreaId + "')");
aWriter.add(">");
aWriter.add("Make the call.");
aWriter.add("</a>");
aWriter.add("<textarea ");
aWriter.addSafeAttribute("id", resultAreaId);
aWriter.add(" readonly=\"readonly\" style=\"width: 100%;\" ></textarea>");
aWriter.add("</div>");
// JavaScript method that will send the HTTP REST request
aWriter.addJS_cr("function sendRestRequest(url, targetId) {");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" xhttp.open('GET', url, true);");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" xhttp.setRequestHeader('Content-type', 'application/json');");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" xhttp.send();");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" var element = document.getElementById(targetId);");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" xhttp.onreadystatechange = function() {");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" if (xhttp.readyState == 4)");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" element.innerHTML = xhttp.responseText;");
aWriter.addJS_cr(" }");
aWriter.addJS_cr("}");
}
}
ファイルのアップロード
ユーザーサービスは、ファイル入力フィールドを使用してフォームを表示できます。
次の例は、タイトルとファイルの2つの入力フィールドを持つフォームを表示します。
public class FileUploadService implements UserService<...>
{
// This service defines a single object named "file".
private static final ObjectKey _File_ObjectKey = ObjectKey.forName("file");
// Paths for the "file" object.
public static final Path _Title = Path.parse("title");
public static final Path _File = Path.parse("file");
...
@Override
public void setupObjectContext(
UserServiceSetupObjectContext<DataspaceEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceObjectContextBuilder aBuilder)
{
if (aContext.isInitialDisplay())
{
// Create a definition for the "model" object.
BeanDefinition def = aBuilder.createBeanDefinition();
aBuilder.registerBean(_File_ObjectKey, def);
BeanElement element;
element = def.createElement(_Title, SchemaTypeName.XS_STRING);
element.setLabel("Title");
element.setMinOccurs(1);
// Type for a file must be BeanDefinition.OSD_FILE_UPLOAD.
element = def.createElement(_File, BeanDefinition.OSD_FILE_UPLOAD);
element.setLabel("File");
element.setMinOccurs(1);
}
}
@Override
public void setupDisplay(
UserServiceSetupDisplayContext<DataspaceEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceDisplayConfigurator aConfigurator)
{
aConfigurator.setTitle("File upload service");
aConfigurator.setLeftButtons(aConfigurator.newSubmitButton("Upload", this::onUpload), aConfigurator.newCancelButton());
// IMPORTANT: Following method must be called to enable file upload.
// This will set form encryption type to "multipart/form-data".
aConfigurator.setFileUploadEnabled(true);
aConfigurator.setContent(this::writePane);
}
private void writePane(UserServicePaneContext aContext, UserServicePaneWriter aWriter)
{
final UIWidgetFileUploadFactory fileUploadFactory = new UIWidgetFileUploadFactory();
aWriter.setCurrentObject(_File_ObjectKey);
aWriter.startTableFormRow();
// Title input.
aWriter.addFormRow(_Title);
// File upload input.
UIWidgetFileUpload widget = aWriter.newCustomWidget(_File, fileUploadFactory);
// Default filter for file names.
widget.setAccept(".txt");
aWriter.addFormRow(widget);
aWriter.endTableFormRow();
}
private UserServiceEventOutcome onUpload(UserServiceEventContext anEventContext)
{
ValueContextForInputValidation valueContext = anEventContext.getValueContext(_File_ObjectKey);
String title = (String) valueContext.getValue(_Title);
UploadedFile file = (UploadedFile) valueContext.getValue(_File);
InputStream in;
try
{
in = file.getInputStream();
}
catch (IOException e)
{
// Should not happen.
anEventContext.addError("Cannot read file.");
return null;
}
// Do something with title and the input stream.
return UserServiceNext.nextClose();
}
}
詳細については、UIWidgetFileUploadを参照してください。
ファイルのダウンロード
ユーザーサービスは、ファイルをダウンロードするためのURLまたはボタンを表示できます。ファイルの実際のダウンロードは、ユーザーサービスの制御下にあります。
次の例は、ファイルをダウンロードするためのURLを表示します。
public class FileDownloadService implements UserService<DataspaceEntitySelection>
{
...
@Override
public void setupDisplay(
UserServiceSetupDisplayContext<DataspaceEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceDisplayConfigurator aConfigurator)
{
aConfigurator.setLeftButtons(aConfigurator.newCloseButton());
aConfigurator.setContent(this::writePane);
}
private void writePane(UserServicePaneContext aContext, UserServicePaneWriter aWriter)
{
aWriter.add("<div ");
aWriter.addSafeAttribute("class", UICSSClasses.CONTAINER_WITH_TEXT_PADDING);
aWriter.add(">");
// Generate and display the URL for the download.
String downloadURL = aWriter.getURLForGetRequest(this::processDownloadRequest);
aWriter.add("<a ");
aWriter.addSafeAttribute("href", downloadURL);
aWriter.add(">Click here to download a sample file</a>");
aWriter.add("</div>");
}
private void processDownloadRequest(
UserServiceGetContext aContext,
UserServiceGetResponse aResponse)
{
// The file is plain text.
aResponse.setContentType("text/plain;charset=UTF-8");
// Remove the following statement to display the file directly in the browser.
aResponse.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=\"sample.txt\"");
// Write a text file using UTF-8 encoding.
PrintWriter out;
try
{
out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(aResponse.getOutputStream(), "UTF-8"));
}
catch (IOException ex)
{
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
DateFormat format = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(
DateFormat.FULL,
DateFormat.MEDIUM,
Locale.US);
Date now = new Date();
out.println("Hello !");
out.println("This is a sample text file downloaded on " + format.format(now)
+ ", from EBX®.");
out.close();
}
}
表示なしのユーザーサービス
ユーザーサービスは、表示せずにタスクを実行して前の画面に戻るか、ユーザーを別の画面にリダイレクトするように設計されている場合があります。
このタイプのサービスは、インターフェイス UserServiceExtended とメソッド UserServiceExtended.initializeを実装する必要があります。
次の例は、現在のテーブルビューで選択したレコードを削除します。
public class DeleteRecordsService implements UserServiceExtended<TableViewEntitySelection>
{
...
@Override
public UserServiceEventOutcome initialize(
UserServiceInitializeContext<TableViewEntitySelection> aContext)
{
final List<AdaptationName> records = new ArrayList<>();
// Deletes all selected rows in a single transaction.
RequestResult requestResult = aContext.getEntitySelection().getSelectedRecords().execute();
try
{
for (Adaptation record = requestResult.nextAdaptation(); record != null; record = requestResult.nextAdaptation())
{
records.add(record.getAdaptationName());
}
}
finally
{
requestResult.close();
}
Procedure deleteProcedure = new Procedure()
{
@Override
public void execute(ProcedureContext aContext) throws Exception
{
for (AdaptationName record : records)
{
aContext.doDelete(record, false);
}
}
};
UserServiceTransaction transaction = aContext.createTransaction();
transaction.add(deleteProcedure);
// Adds an information messages for current user.
ProcedureResult procedureResult = transaction.execute(true);
if (!procedureResult.hasFailed())
{
if (records.size() <= 1)
{
aContext.addInfo(records.size() + " record was deleted.");
}
else
{
aContext.addInfo(records.size() + " records were deleted.");
}
}
// Do not display the user service and return to current view.
return UserServiceNext.nextClose();
}
@Override
public void setupObjectContext(
UserServiceSetupObjectContext<TableViewEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceObjectContextBuilder aBuilder)
{
//Do nothing.
}
@Override
public void setupDisplay(
UserServiceSetupDisplayContext<TableViewEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceDisplayConfigurator aConfigurator)
{
//Do nothing.
}
@Override
public void validate(UserServiceValidateContext<TableViewEntitySelection> aContext)
{
//Do nothing.
}
@Override
public UserServiceEventOutcome processEventOutcome(
UserServiceProcessEventOutcomeContext<TableViewEntitySelection> aContext,
UserServiceEventOutcome anEventOutcome)
{
return anEventOutcome;
}
}
既知の制限事項
このようなサービスがWebコンポーネント、関連付け、パースペクティブアクション、または階層ノードのコンテキストで呼び出された場合、サービスは起動、初期化、および閉じられますが、サービスのターゲットエンティティは引き続き表示されます。