TIBCO® Metadata Agent Framework
Overview and purpose
TIBCO® Metadata Agent Framework allows customers to implement support for the specific data source types within TIBCO® Metadata Agent through specific adapters.
An adapter is a separate Java application that ensures one or several of EBX® Metadata Management capabilities for a given data source type(s):
Data source management
Metadata harvesting
Data sampling
Metadata provisioning
Lineage extraction.
TIBCO® Metadata Agent Framework includes following elements:
Java based interfaces that must be implemented in order to customize a given metadata management capability for a given data source type
Java annotations that must be used to indicate that a capability is implemented
Properties allowing to activate an adapter and define relationship between this adapter and supported data source types/EBX® Metadata Management capabilities
Extensible exception and error codes to properly raise an internationalized error from the adapter to the agent.
Extending metadata extraction capabilities
To extend existing metadata extraction capabilities you need to implement an adapter using Java programming language in respect with defined interfaces contract.
The adapter must respect following rules:
be compiled as a Java application (jar) file
provide mandatory registration data to the agent by implementing
addAdapterInfos()method of the registration serviceimplement at least one metadata extraction service respecting the interface contract and mandatory annotations
be registered in the agent properties file.
Metadata Agent leverages Spring Boot 2.5.4 framework. The adapter implementation must include Spring annotations for services (org.springframework.stereotype.Service).
Recommended adapter project structure
The adapter can be developed in any way that is comfortable for the responsible development team. Below is a recommended structure based on Maven dependencies management and architecture best practices for Java projects.

The main project contains three module projects and one configuration project:
Module name | Description |
|---|---|
tcmd-agent-example-bundle | Bundle project that defines how to assemble your adapter into one jar file and allows to manage dependencies in a simple way. |
tcmd-agent-example-common | Common library code for your adapter. Typically this would host error management framework and some common properties and utilities as well as i18n resources. |
tcmd-agent-example-conf | Project folder that hosts properties and configuration files for your adapter. |
tcmd-agent-example-service | Code implementing agent services inside your adapter. |
Register adapter in TIBCO® Metadata Agent Framework
In order to register an adapter in TIBCO® Metadata Agent Framework you must follow these steps:
1. Implement the registration service
The registration service for your adapter must implement the dedicated Agent interface com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.adapter.service.AdapterRegistrationService service and its main method addAdapterInfos().
This method allows you to create an adapter information object com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.shared.agent.dto.AdapterDTO where you must provide the following information about your adapter:
Property | Description |
|---|---|
name | Technical name of the adapter. It must match the value you’ll use for the implementation annotations and for the Agent’s property |
version | Implementation version for your adapter. |
provider | Your company name. |
productVersion | Corresponding version of the supported metadata provider. |
description | Adapter description that will be shown in EBX®. |
2. Provide suitable annotations
In order to be recognized by TIBCO® Metadata Agent Framework each service class that you consider implemented must be annotated with com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.common.annotation.MetadataAdapterProfile having as value your adapter technical name (provided in the Agent’s property agent-adapter.active-profiles and in the attribute name of the Adapter information object).
Each operation in the service that you consider implemented must be annotated with com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.common.annotation.MetadataOperationImplemented.
3. Add adapter name and properties to main agent’s properties
Following properties must be modified to indicate that the Agent should load your adapter:
#Comma-separated list of packages to scan for adapters classes agent-adapter.base.package=com.tibco.ca.tabula.agent.tdv, com.mycompany.agent #Comma separated list of profiles (corresponding to adapter technical names) agent-adapter.active-profiles=tdv,myadapter
4. Add adapter name to the active profiles
Edit your Java launch configuration for the Agent to add your adapter name as profile:
-Dspring.profiles.active=tdv,myadapter
5. Add adapter jar and optionally properties to the Agent’s CLASSPATH.
Deploy your adapter jar and optionally any properties/configuration files that are required by your code on Agent’s CLASSPATH.
Activate your adapter for the suitable data source types in application-datasources.properties file as described in Installing the TIBCO® Metadata Agent.
Implementing main capabilities
The following metadata capabilities can be implemented by an adapter:
Data source management
Metadata harvesting
Data profiling
Data sampling
Metadata provisioning
Lineage extraction.
General implementation rules
Each custom service that implements main metadata capabilities must comply with following rules:
Each service class that you consider implemented must be annotated with
com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.common.annotation.MetadataAdapterProfilehaving as value your adapter technical name (provided in the Agent’s propertyagent-adapter.active-profilesand in the attributenameof the Adapter information object).Each service class must be annotated with Spring
org.springframework.stereotype.Serviceannotation.Each operation in the service that you consider implemented must be annotated with
com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.common.annotation.MetadataOperationImplemented.For each object of type
com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.shared.agent.landing.dto.MetadataExchangeDTOcreated by the adapter, you must populate at leastsourceId,sourceType,datasourceTypeandnameattributes.
Data source management
Data source management capability covers following operations with data sources in the metadata provider system:
read all available data sources
create a new data source
delete an existing data source
check availability of an existing data source.
This capability can be extended by implementing the com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.adapter.service.AdapterDatasourceManagementService service.
Metadata harvesting
Metadata harvesting capability covers following operations for data sources and underlying resources in the metadata provider system:
create a new data source and get all metadata for it
get metadata for a resource/data source or a list of resources/data sources
get list of children resources for a root resource/data source.
This capability can be extended by implementing the com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.adapter.service.AdapterHarvestingService service.
Data profiling
Data profiling information can be added to a metadata exchange object.
This capability can be extended by implementing the com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.adapter.service.AdapterHarvestingService service, method addProfilingToAsset.
Data sampling
Sample data can be requested from a source system for a given data source/resource.
This capability can be extended by implementing the com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.adapter.service.AdapterSamplingService service.
Metadata provisioning
Metadata provisioning capability covers operations that are for goal to provide some existing data sources/resources to a public space on the metadata provider system.
This capability also allows to create a new data source/resource based on several existing ones.
Following operations are supported:
provision metadata (create a new public source and publish resources in there)
modify already provisioned metadata resources
delete already provisioned metadata resources
check that a resource has already be provisioned
check whether a given resource is supported to be source of provisioned resource.
This capability can be extended by implementing the com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.adapter.service.AdapterProvisioningService service.
Lineage extraction
Lineage information can be extracted from the source system if the source system supports this. This information can also be added to the Metadata exchange objects and pushed through TIBCO® Metadata Agent to {{ site.PRODUCT_NAME_R }} and stored as technical flows.
This capability can be extended by implementing the com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.adapter.service.AdapterLineageService service.
Exceptions management
A specific exceptions management framework is provided as part of TIBCO® Metadata Agent Framework.
This framework includes the following elements:
com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.common.adapter.exception.MetadataAdapterException: internationalized exception class that you should implement to throw specific exceptions from your code to TIBCO® Metadata Agent and {{ site.PRODUCT_NAME_R }} to handle.com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.common.exception.MetadataExceptionReason: an interface to be implemented by enumeration classes to define custom exception reasons.
To implement your specific exception, you need to extend the generic exception class with suitable constructors and override getErrorBundle() method to return the name of your error messages file. This file is expected to be available inside src/main/resources folder with following naming convention:
<error bundle name>_<language 2 letters code>.properties
Language code is optional, if not indicated the bundle will be considered applicable for English language.
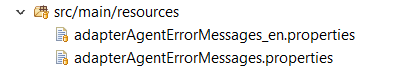
To add specific error reasons for your exception(s), you need to create an enum in your project that implements MetadataExceptionReason interface and define your error messages keys into it.
public enum MyMetadataExceptionReason implements MetadataExceptionReason {
AGENT_ADAPTER_ERROR("agent.adapter.error");
private MyMetadataExceptionReason(final String ckey) {
this.key = ckey;
}
private String key;
@Override
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
}
If you don’t wish to define specific exceptions, you can use generic technical exception provided by TIBCO® Metadata Agent Framework represented by the class 'com.tibco.ebx.ca.tabula.agent.common.adapter.exception.MetadataAdapterTechnicalException'
This exception can be instantiated using a string message or a Throwable object.
Logging
No specific logging framework is provided as of today.
TIBCO Metadata Agent leverages slf4j logging framework to write functional messages in suitable log files.
For consistency, we recommend you using the same framework for your adapter and avoid using System.out.print/println to write messages.