Deploying Flogo Apps to Red Hat OpenShift
Before you begin
- Ensure that you have a Red Hat Openshift account and the Red Hat OpenShift environment is set up to deploy the app.
- Ensure that the Red Hat OpenShift CLI is installed on your machine.
- Ensure that the image of the Flogo app is pushed to Red Hat Openshift internal registry or any other public registry such as Docker Hub.
- Procedure
- Build a docker image for your app. There are three ways to build a docker image for deployment.
Using Flogo Enterprise Web UI:
- Build the docker image from the Flogo Enterprise Web UI. See Building the App section for details.
- Tag the generated docker image from the command line:
docker tag <image-id> <app-name>:<version>The app tag must be in the format <app-name>:<app-version>
From a Linux binary:- From the
Flogo Enterprise Web UI, build a Linux binary using the
Linux/amd64option. See Building the App section for details. - Provide execute permission to the app binary:
chmod +x <app-binary> - Create a docker file. For example:
FROM <OS-version> # for example, FROM alpine:3.7 WORKDIR /app ADD <app-binary> <path-to-app-in-docker-container> # for example, ADD flogo-rest-linux_amd64 /app/flogo-rest CMD ["/app/flogo-rest"]
- Build the docker image using the docker file. Run the following command:
docker build -t <app-tag> -f <path-to-Dockerfile> .
The app tag must be in the format <app-name>:<app-version>
From the CLI:- Export your app as a JSON file (for example,
flogo-rest.json) by clicking the Export app button on the flow details page. - Build a Docker image containing the app using the builder command from the CLI. Open a command prompt and change directory to
<FLOGO_HOME>/<version>/binand run:builder-<platform>_<arch> build -f <path-to-the-.json-file> -docker -tag=<tag>
For example:builder_linux_amd64 build -f
flogo-rest.json-docker -tag=V1For more information on the builder command, refer to the section, Builder command.
- Run the docker image locally to verify that all looks good:
docker run -it -p 9999:9999 <app-tag>
- Authenticate docker with the container registry where you want to push the docker image.
- Tag the docker image. Run:
docker tag <app-tag> <CONTAINER_REGISTRY_URI>/<app-tag>
The app tag must be in the format <app-name>:<app-version> - Push the local docker image to the container registry by running the following command:
docker push <CONTAINER_REGISTRY_URI>/<app-tag>
Note: Refer to the documentation for your container registry for the exact commands to authenticate docker, tag docker image, and push it to the registry. - Login to Openshift from command line:
oc login --token=<Your token> --server=https://<host address>:<port>
For example:
oc login --token=<Your token> --server=https://api.ca-central-1.starter.openshift-online.com:6443
- Create a project in Red Hat OpenShift:
oc new-project <PROJECT_NAME>
- Deploy the app on Red Hat Openshift using an YAML file. For a sample YAML file, see
Sample YAML File: Red Hat OpenShift.
oc create -f <YAML filename>
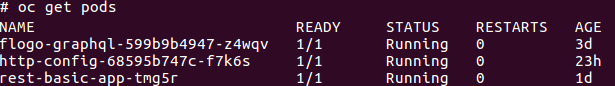
- To get information about pods, run the following command:
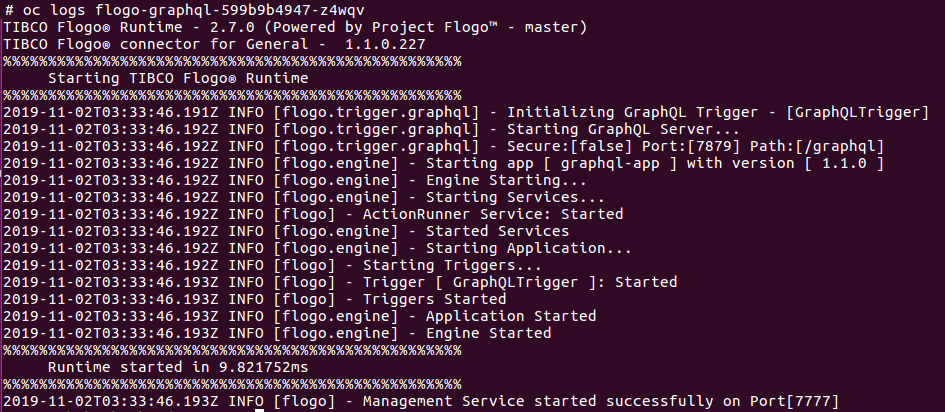
- To get the logs of a particular pod, run the following command:
- To access the endpoint of an app, run the following command:
- From the output, note the external IP and port. Access the endpoint using the following URL:
http:<external IP>:<port>/<resource_context_path>