GOGC
The GOGC variable sets the initial garbage collection target percentage. A collection is triggered when the ratio of freshly allocated data to live data remaining after the previous collection reaches this percentage.
Garbage collection refers to the process of managing heap memory allocation: free the memory allocations that are no longer in use and keep the memory allocations that are being used. Garbage collection significantly affects the performance of your app.
Deploying the app to your environment
Set the variable value as follows:
GOGC=150 ./<app_binary>
docker run -it -e GOGC=150 <docker-image>
The default is 100. This means that garbage collection is not triggered until the heap has grown by 100% since the previous collection. Setting the variable to a higher value (for example, GOGC=200) delays the start of a garbage collection cycle until the live heap has grown to 200% of the previous size. Setting the variable to a lower value (for example, GOGC=20) increases the frequency of garbage collection as less new data can be allocated on the heap before triggering a collection.
Case Study
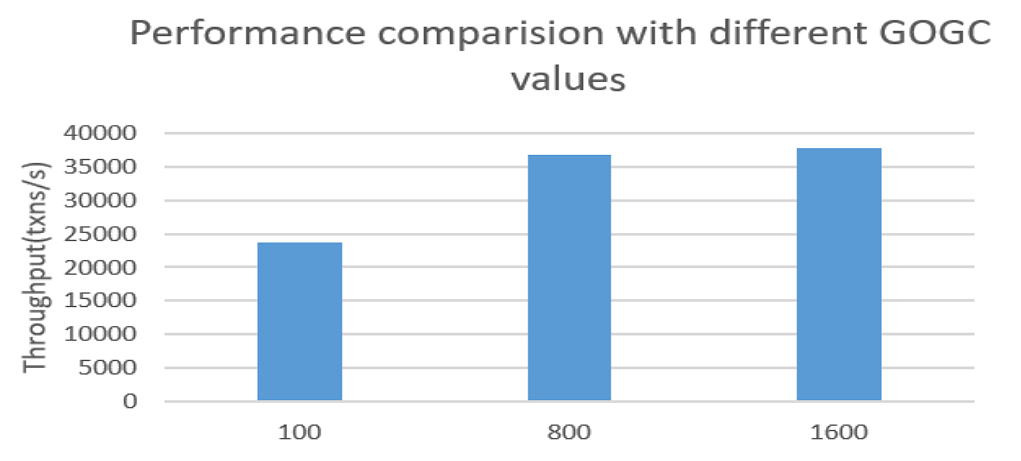
This use case illustrates the impact of the GOGC variable on performance.
Figure 21: App under test - GOGC
In this low latency scenario, you can observe significant improvement in-app performance while increasing the GOGC variable value from 100 to 1600. It is advisable to test this value for the specific scenario and understand its impact before tuning. You can get the best-suited value by running the performance test in your test environment.
GOGC value can be tuned based on the workload and available resources after validating your test environment.
Figure 22: Performance comparison with different GOGC values