Logs
ISIServer provides two types of logging:
-
ISIServer Classic Logging - provides Server and Client_thread logs separately and reports every query.
-
Log4j Logging – provides logging using the standard Java logging format, including options to customize the logging output.
Logging reminders:
-
Logs can get big. Check their size frequently.
-
To improve performance, turn off logging after testing is completed.
ISIServer Classic Logging
To turn on classic logging, set Log=ON in the [Server] section of ISIserver.config.
This generates two types of logs in ISIserver’s fslog directory:
-
Server Logs – one for each time ISIserver starts.
-
Client Thread Logs – one for each time Instream or Foresight Translator runs. See Client_Thread Logs.
This example shows a listing for both types of logs.
Server Logs
Each time ISIserver starts up, it creates a new server log in the Log directory below the location of the config file. By default, this is
C:\Foresight\ISIserver\Log
The log file name is in the format ISIServer_n_log.txt.
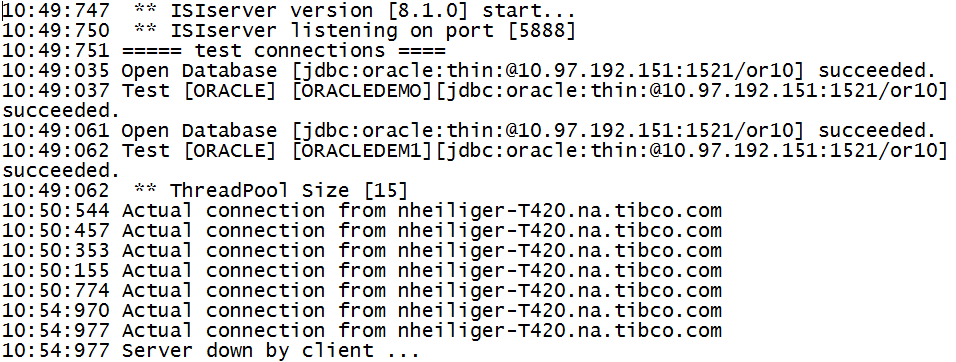
Each time Foresight Instream or Foresight Translator runs, it records connection information in this log. A line like this indicates a successful connection:
10:50:544 Actual connection from nheiliger-T420.na.tibco.com
Client_Thread Logs
Each time Foresight Instream or Foresight Translator sends a database request, ISIserver writes an entry in a log with a name that has the format ClientThread_n_n_log.txt.
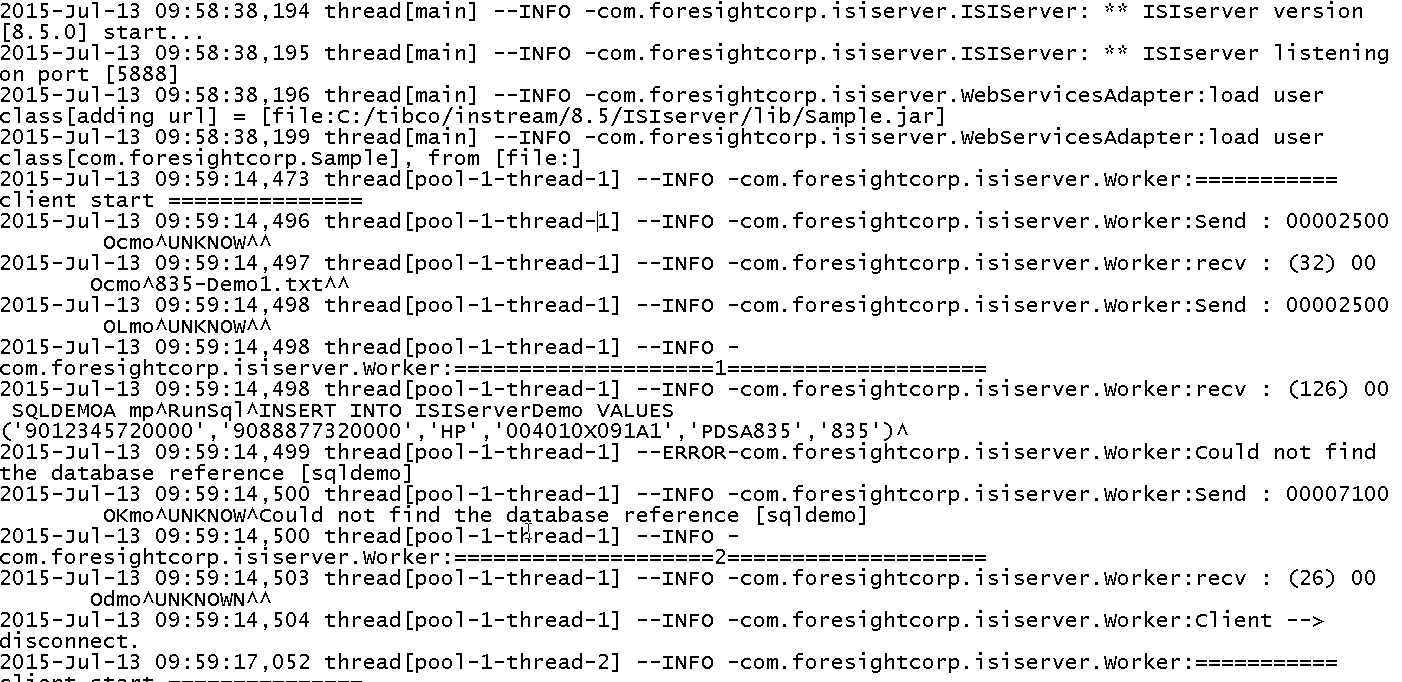
This example shows a sample log and the information it contains.
Log4j Logging
To turn on logging containing the standard Java logging “log4j” format, set Log= log4j in the [Server] section of ISIserver.config.
Properties can be set by modifying the log4j2.properties file found in the ISIserver\java directory
Sample Log
Log4j format provides one log as opposed to two (Server and Client logs) as provided with ISIServer classic logging.