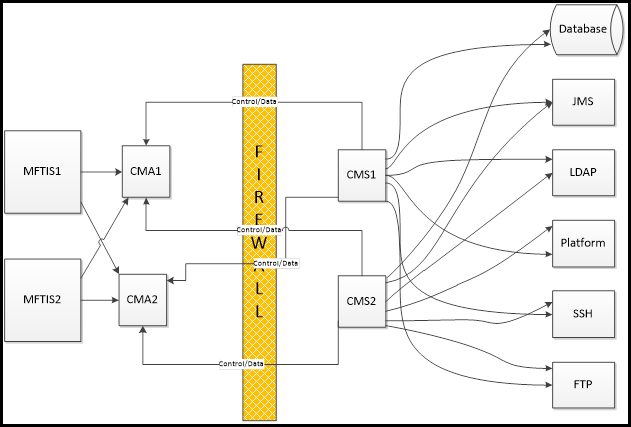
Connection Manager High Availability
The following figure shows how high availability can be configured.
Connection Manager operates in an Active/Passive mode. Requests are sent to the first available component. If the connection to that component fails or is not available, Connection Manager attempts the request to the next component.
High Availability Example (See the figure provided in this section.)
MFTIS1 needs to connect to a Platform Server in the internal network.
- At startup, CMS1 and CMS2 both attempt to establish connections to CMA1 and CMA2. If any connection requests fail, CMS1 and CMS2 continue to connect to the CMA every 30 seconds until the Connection Request is successful.
- MFTIS1attempts to connect to CMA1 to perform this connection. Assume that CMA1 is not available; then MFTIS1 connects to CMA2.
- CMA2 looks for an active Control Connection from the CMS. If CMA has an active control connection with CMS1, it will initiate the request to CMS1. Assume there is no active control connection to CMS1; CMA2 initiates the request to CMS2 over an active Control Connection.
- After CMA2 makes an active connection to the CMS2, CMS2 connects to the target Platform Server.
- CMS2 then connects back to CMA2 over the data connection port (48001).
-
CMA2 then completes the connection with MFTIS1. Data begins to flow over the connection:
- CMA2 issues “heartbeat” requests to the CMS2 every 45 seconds. If a response is not received within 30 seconds, CMA2 breaks the connection and waits for the CMS2 to initiate a new connection.
- CMS2 waits for heartbeat requests from CMA2. If a heartbeat request is not received within 90 seconds, CMS2 closes the connection to CMA2 and attempts to re-establish the connection to CMA2. If this fails, CMS attempts to connect to CMS2 every 30 seconds.
Copyright © 2022. Cloud Software Group, Inc. All Rights Reserved.