Connection Manager Data Flow
Connection Manager can work in a simple environment or two-tiered DMZ structure.
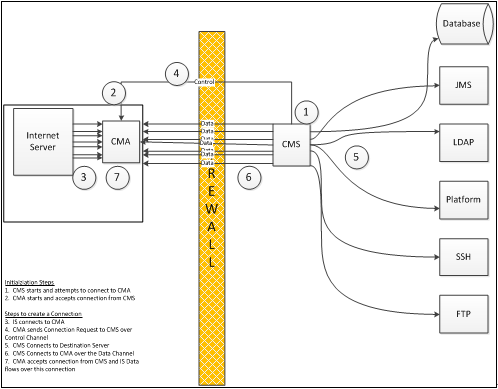
The following figure shows a simple Connection Manager data flow:
The following brief explanation shows how Connection Manager works.
- When CMS is started, it attempts to make a connection to each CMA. If the connection cannot be established, CMS waits 30 seconds and tries again. It continues retrying the connection until the connection is successfully established.
- At some point, CMA is started and listens for incoming CMS connections. CMA listens for TCP connections on the following two ports:
When CMS retries the connection to CMA control port, the connection is established successfully.
- When Internet Server needs to establish a TCP connection, it must first determine whether the connection must be routed through Connection Manager. Internet Server reviews its configuration to find a match on an IP address or IP address subnet. Assuming that the connection must be made through Connection Manager, Internet Server requests a TCP connection with CMA. It then sends a SOCKS packet to CMA indicating the destination connectivity information (IP address and IP port).
- CMA reads the Internet Server data packet and sends the request to CMS over the control connection.
- CMS reads the data from the control connection and establishes a connection with the destination server.
- CMS then establishes a TCP connection with CMA data port. CMA ties this connection together with the connection request from Internet Server.
- CMA accepts the connection from CMS and the Internet Server data begins to flow over this connection.
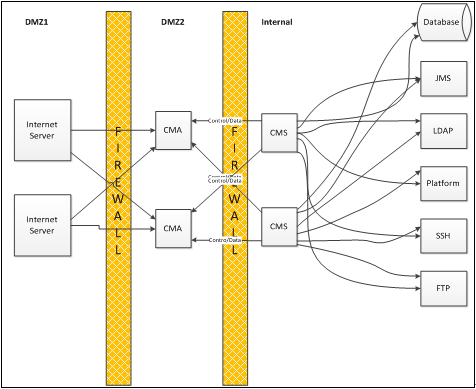
The following figure shows a two-tier DMZ architecture:
In this two-tier architecture, Internet Server is executing in DMZ1, while CMA is executing in DMZ2.
This architecture also shows the high availability capability of Connection Manager. Internet Server can connect to multiple CMA instances and CMA can accept requests from multiple CMS instances. Internet Server connects to the first CMA instance that is available and CMA requests a connection on the first active connection to a CMS instance.