The Global Lockout Rules section defines global lockout rules that apply to the entire system.
By setting any of the fields in the Login Failure Attempts section will require a lock action to be enabled. The administrator can set either one or both lock actions to
Yes.
Note: The Send Alert Email lock action requires you to configure the
Alert Email Address field, which is in the Global Settings section on the
System Configuration page.
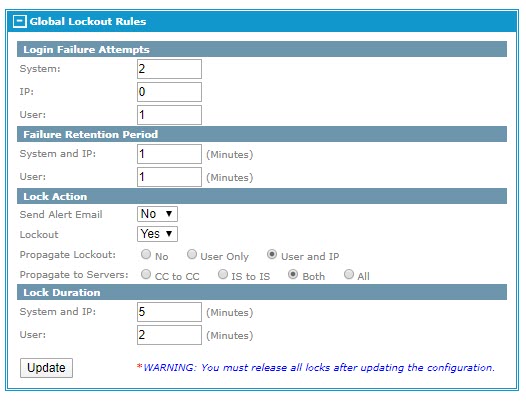
The Failure Retention Period section is reset upon a successful login for user accounts. For example, if the login failure attempts for a user is set to
3 and a user fails to login twice but on the third attempt is successful, the failed attempts will be reset to
0. This also occurs upon the lock duration time being reached. This means if a user is locked out of the system and the lock duration time has passed the failed attempts will be reset to
0. However, this action will not occur for a System or IP Retention Period. To clear the attempts for these actions requires a lockout release for the system or IP address by a super administrator account that has been configured with a restricted IP address to login. These user accounts are never locked out of the system. See the Lockout Management section for more details about releasing lock outs.
You can define the lock action to be taken when the login failure attempts thresholds are reached within the failure retention period. An alert email is sent to the email address defined in the
Alert Email Address field of the Global Settings section. The
Lockout field defines whether lockout processing is to be performed.
Note: The
Lockout field must be set to
Yes when any one value in the Login Failure Attempts section is set to a non-zero value.
The amount of time that a user, IP address, or system is locked out depends on the Lock Duration settings. You can also define whether to propagate lockout between MFT instances and also define the server instances where lockouts are propagated.
Note: Some care should be given when setting the login failure attempts for the system. An acceptable number should be based on the amount of users that can access the system. The value is reached by the accumulation of user and IP failed login attempts that are being retained. A very simple example of a system lockout occurring is if the login failure attempts for users is set to
3 and system is set to
7, the entire system will be locked when the seventh failed attempt has occurred. (The default failure retention period for user accounts is 120 minutes.) Based on the above settings all it would take is three users to fail to access the system in a 120 minute time frame due to attempting to login with bad passwords causing the failed login attempts being retained to reach the count of 7 and the system will be locked.
Copyright © 2021. Cloud Software Group, Inc. All Rights Reserved.

