Environments
Pipelines and data channels are deployed to Kubernetes in namespaces. Namespaces are exposed as environments.
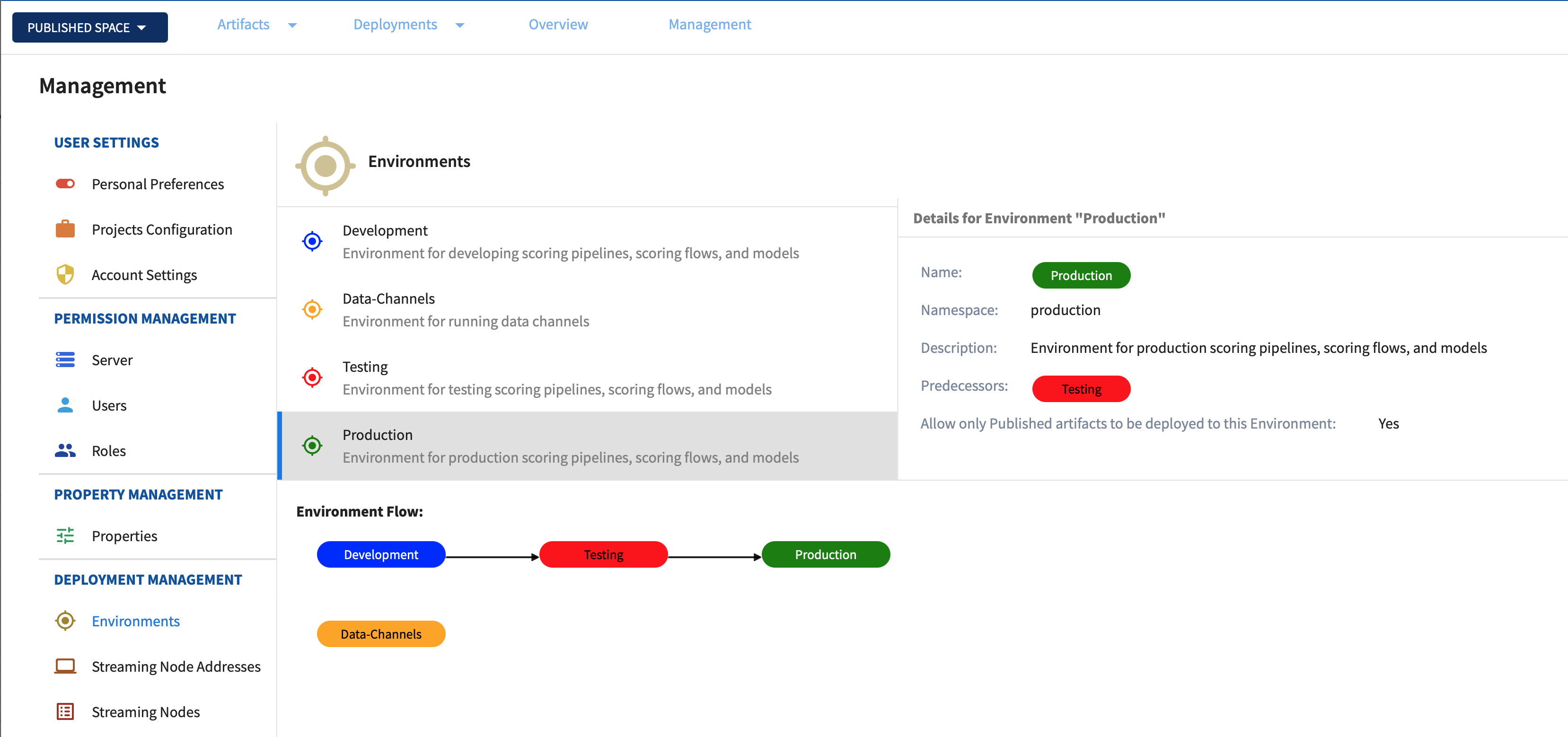
Environments are defined by adding attributes to Kubernetes namespace objects as annotations and labels to describe the environment:
- Environment Name:
label environment - Environment Description:
annotation description - Environment Color:
annotation tag - Must be Published?:
annotation publishedArtifactsOnly-trueif only published artifacts can be deployed.falseif artifacts from the sandbox space can be deployed. - Environment Predecessors:
annotation predecessors- optional JSON list of predecessors
The values specified to describe an environment have these constraints:
- The namespace
nameis restricted to characters supported by a DNS name. - The environment name is restricted to characters supported by a Kubernetes label.
- The annotation values are restricted to characters support by a Kubernetes annotation.
- The environment color
tagvalue must be a case-insensitive valid HTML color name. If an invalid color name is specified the color White is used.
Note: Visibility of environments added while ModelOps is running may be delayed for a few minutes.
Namespace
These kubectl commands are used to manage Kubernetes namespaces (see Share a Cluster with Namespaces for complete documentation):
kubectl apply --filename<file-name> - create or update a namespacekubectl describe namespace<namespace-name> - display a namespacekubectl delete namespaces<namespace-name> - remove a namespace
This example below demonstrates creating, updating, displaying, and removing a namespace custom for environment Custom.
Note: Ensure that the correct Kubernetes cluster context is set before executing kubectl commands.
kubectl config current-context
kubectl config use-context <cluster-context-name>
Example
The required kubectl commands to create the namespace associated with an
environment are:
//
// Create Custom environment
//
$ kubectl apply -f - <<!
kind: Namespace
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: custom
labels:
environment: "Custom"
annotations:
publishedArtifactsOnly: "true"
description: "Custom environment"
predecessors: '["Development"]'
tag: orange
!
//
// Display Custom environment
//
kubectl describe namespace custom
Name: custom
Labels: environment=Custom
Annotations: publishedArtifactsOnly: false
description: Custom environment
predecessors: ["Development"]
tag: orange
Status: Active
No resource quota.
No LimitRange resource.
//
// Update Custom environment (change publishedArtifactsOnly value)
//
$ kubectl apply -f - <<!
kind: Namespace
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: custom
labels:
environment: "Custom"
annotations:
publishedArtifactsOnly: "false"
description: "Custom environment"
predecessors: '["Development"]'
tag: orange
!
//
// Remove Custom environment
//
kubectl delete namespaces custom
Secrets
Any Kubernetes Secrets required by a scoring flow or data channel must be created in the new environment's namespace. All new namespaces must define these two secrets:
elasticsearch-es-elastic-user- Elasticsearch client credentialsscoring-admin- Scoring flow administration credentials
Secrets are created using this kubectl command:
kubectl create secret generic
Example
The required kubectl commands to create secrets associated with the
environment namespace are:
//
// Create elastic search user secret
//
kubectl create secret generic elasticsearch-es-elastic-user \
--from-literal=elastic=elastic \
--namespace custom \
--dry-run=client \
--output=yaml 2>/dev/null | \
kubectl apply --filename -
//
// Create scoring admin secret
//
kubectl create secret generic scoring-admin \
--from-literal=admin=admin \
--namespace custom
//
// Display secrets
//
kubectl get secret --namespace custom
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
elasticsearch-es-elastic-user Opaque 1 18s
scoring-admin Opaque 1 9s
Permissions
The namespace created for the new environment must have appropriate permissions granted. The required permissions vary based on the cloud infrastructure being used.
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
This step is required to add the required permissions for a new environment's namespace.
- Patch the existing
ClusterRoleBindingnamedmodelopsto grant required API permissions for the new namespace
For example,
//
// Grant API access for the custom namespace
//
kubectl patch clusterrolebinding modelops \
--type='json' \
--patch='[{"op": "add", "path": "/subjects/5", "value": {"kind": "User", "apiGroup": "rbac.authorization.k8s.io", "name": "system:serviceaccount:custom:default"} }]'
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/modelops patched
//
// Display updated ClusterRoleBinding
//
kubectl describe clusterrolebinding modelops
Name: modelops
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=Helm
Annotations: meta.helm.sh/release-name: scheduling-server
meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: modelops
Role:
Kind: ClusterRole
Name: installer
Subjects:
Kind Name Namespace
---- ---- ---------
User system:serviceaccount:modelops:default
User system:serviceaccount:datachannels:default
User system:serviceaccount:development:default
User system:serviceaccount:production:default
User system:serviceaccount:testing:default
User system:serviceaccount:custom:default
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
This step is required to add the required permissions for a new environment's namespace.
- Patch the existing
ClusterRoleBindingnamedmodelopsto grant required API permissions for the new namespace
For example,
//
// Grant API access for the custom namespace
//
kubectl patch clusterrolebinding modelops \
--type='json' \
--patch='[{"op": "add", "path": "/subjects/5", "value": {"kind": "User", "apiGroup": "rbac.authorization.k8s.io", "name": "system:serviceaccount:custom:default"} }]'
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/modelops patched
//
// Display updated ClusterRoleBinding
//
kubectl describe clusterrolebinding modelops
Name: modelops
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=Helm
Annotations: meta.helm.sh/release-name: scheduling-server
meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: modelops
Role:
Kind: ClusterRole
Name: installer
Subjects:
Kind Name Namespace
---- ---- ---------
User system:serviceaccount:modelops:default
User system:serviceaccount:datachannels:default
User system:serviceaccount:development:default
User system:serviceaccount:production:default
User system:serviceaccount:testing:default
User system:serviceaccount:custom:default
OpenShift
These steps are required to add the required permissions for a new environment's namespace.
- Create a service account named
modelops-scoring-service-accountin new environment's namespace - Patch the existing RoleBinding named
modelops-pullerinmodelopsnamespace to allow image pulls from the new namespace - Patch the existing ClusterRoleBinding named
modelopsto update service account - Patch the existing ClusterRoleBinding named
modelops-scoring-cluster-role-bindingto grant required API permissions - Patch the existing ClusterRoleBinding named
scoring-crb-image-pullerto grant image pulling
For example,
//
// Create service account in new namespace
//
$ kubectl apply -f - <<!
kind: ServiceAccount
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: modelops-scoring-service-account
namespace: custom
!
serviceaccount/modelops-scoring-service-account created
//
// Patch RoleBinding
//
kubectl patch rolebinding modelops-puller \
--namespace modelops \
--type='json' \
--patch='[{"op": "add", "path": "/subjects/4", "value": {"kind": "ServiceAccount", "name": "default","namespace": "custom" } }]'
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/modelops-puller patched
//
// Update service account
//
kubectl patch clusterrolebinding modelops \
--type='json' \
--patch='[{"op": "add", "path": "/subjects/8", "value": {"kind": "ServiceAccount", "name": "pipeline","namespace": "custom" } }]'
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/modelops patched
kubectl patch clusterrolebinding modelops \
--type='json' \
--patch='[{"op": "add", "path": "/subjects/9", "value": {"kind": "ServiceAccount", "name": "default","namespace": "custom" } }]'
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/modelops patched
//
// Grant API permissions
//
kubectl patch clusterrolebinding modelops-scoring-cluster-role-binding \
--type='json' \
--patch='[{"op": "add", "path": "/subjects/4", "value": {"kind": "ServiceAccount", "name": "modelops-scoring-service-account","namespace": "custom" } }]'
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/modelops-scoring-cluster-role-binding patched
//
// Grant image pulling
//
kubectl patch clusterrolebinding scoring-crb-image-puller \
--type='json' \
--p='[{"op": "add", "path": "/subjects/4", "value": {"kind": "ServiceAccount", "name": "modelops-scoring-service-account","namespace": "custom" } }]'
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/scoring-crb-image-puller patched
