Motivation
Deploy secure daemons when clients must connect securely over a non-secure network. This section illustrates example situations involving remote clients.
rvsd
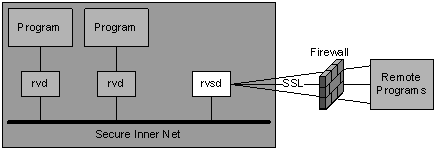
rvsd—Secure Connections across Single Firewall depicts a hub and spoke architecture. An rvsd hub runs on a firewall computer, and remote programs access the hub through secure TLS connections. This arrangement lets trusted remote programs communicate with servers and other programs inside the secure inner network. rvsd bars untrusted programs from connecting to it.
Figure 117: rvsd—Secure Connections across Single Firewall
rvsrd
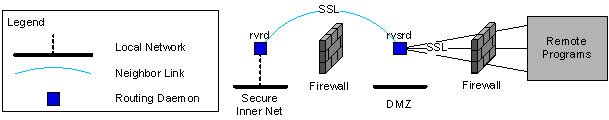
Figure 118: rvsrd—Secure Connections across Double Firewall
rvsrd—Secure Connections across Double Firewall depicts a situation with two Rendezvous routing daemons configured to cross a double firewall. Remote programs initiate secure TLS connections to a secure routing daemon hub (rvsrd) within the outer firewall (DMZ network). A secure TLS neighbor link connects that secure routing daemon with an ordinary routing daemon (rvrd) in the secure inner network.
To configure secure neighbor links, see SSL Connection with Compression.
To prevent rvsrd from multicasting client messages within the DMZ network, start rvsrd with the -no-multicast option. For background information, see Disabling Multicast.
|
|
|