Nak Diagnoses
Nak measures the number of point-to-point packets that request retransmission of point-to-point data.
Non-zero Nak values to or from a specific address usually indicates one of these problems:
|
•
|
A faulty network interface card at a specific computer. |
|
•
|
A faulty or overloaded network infrastructure component (for example, switching or router hardware). |
|
•
|
A fast sender is overwhelming a slower receiver with point-to-point packets. |
|
•
|
A sender on a fast network is overwhelming a network infrastructure component by sending point-to-point packets to a receiver on a slower network. |
Begin by checking the specific interface card, and widen the investigation to other components until you can resolve the difficulty.
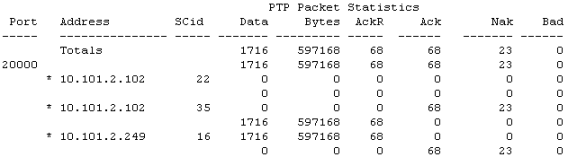
Nak Indicates Faulty Network Card or Infrastructure Component displays example output with this pattern.
|
•
|
SCid 35 at address 10.101.2.102 is sending point-to-point data to SCid 16 at 10.101.3.249. |
|
•
|
The AckR column shows that 10.101.2.249 received 68 requests for acknowledgment to 10.101.2.102. |
|
•
|
The Nak column shows that SCid 16 at 10.101.2.249 did not receive all the packets correctly, and sent 23 NAKs back to SCid 35 at 10.101.2.102. These NAKs constitute retransmission requests for the missed point-to-point packets. |
|
•
|
The Ack column shows that eventually, 10.101.2.249 did receive all 68 retransmitted packets correctly, recovering from the problem. |
|
•
|
This particular example report does not contain sufficient information to determine the locus of the problem—it could be either at the sender or the receiver. |
Figure 160: Nak Indicates Faulty Network Card or Infrastructure Component