Datatype Conversion
Rendezvous software converts datatypes in two situations:
|
•
|
As it translates a message to wire format (when sending a message). |
|
•
|
As it extracts data from a message field. |
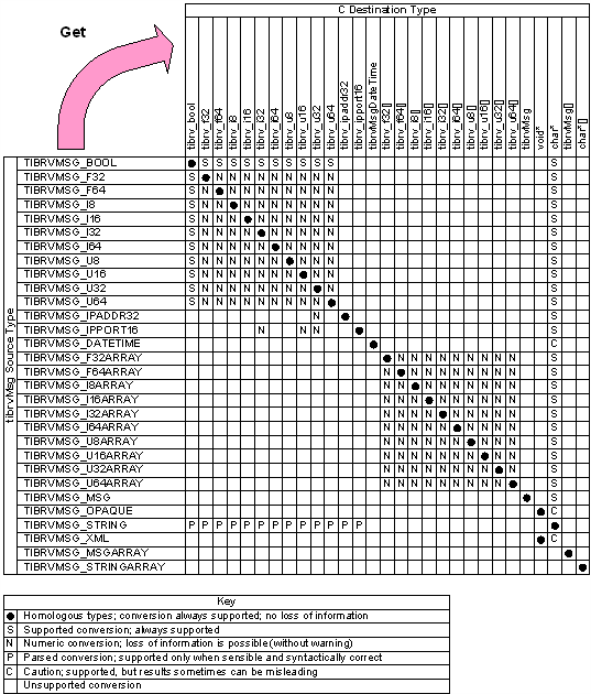
Convenience functions that extract a field from a Rendezvous message automatically decode the field’s data to a homologous C type. Wire Format to C Datatype Conversion Matrix specifies the homologous decodings as well as conversions to other types. See also, tibrvMsg_GetField()tibrvMsg_GetField().
Convenience functions that add a field to a Rendezvous message or update an existing field severely restrict type encoding. These functions encode only to homologous types (the solid dots along the diagonal of Wire Format to C Datatype Conversion Matrix indicate pairs of homologous types).
General Rules
These general rules govern most conversions.
Supported
|
•
|
All wire format types decode to the homologous C datatypes (in get calls), and all C datatypes encode to the homologous wire format types (in add and update calls). |
|
•
|
All wire format numeric scalar types convert to all C numeric scalar types. |
|
•
|
All wire format numeric array types convert to all C numeric array types. |
Caution
|
•
|
Converting a wire format opaque or XML byte sequence to a C character string creates a printable string, but the string does not capture any of the data bytes (it captures only the number of bytes). |
|
•
|
Converting a wire format signed integer to a C unsigned integer discards the sign. |
|
•
|
Converting a wire format numeric type to a C numeric type with fewer bits risks loss of precision. |
|
•
|
Converting wire format floating point numbers to C integer types discards the fractional part. |
|
•
|
Converting large (out-of-range) wire format floating point numbers to C integers results in the maximum integer of the C target size. |
Not Supported
|
•
|
Array types do not convert to scalar types. |
|
•
|
Scalar types do not convert to array types. |
|
•
|
C types do not convert to non-homologous wire format types (when adding or updating a field). |
Converting to Boolean
|
•
|
When converting a string to a boolean, all strings in which the first character is either t or T map to boolean true. All other strings map to boolean false. |
|
•
|
When converting a numeric value to a boolean, zero maps to boolean false. All non-zero numeric values map to boolean true. |
Figure 190: Wire Format to C Datatype Conversion Matrix