TibrvMsg.get()
Method
Declaration
java.lang.Objectget(
java.lang.String fieldName)
throws TibrvException
java.lang.Objectget(
int fieldId)
throws TibrvException
java.lang.Objectget(
java.lang.String fieldName,
int fieldId)
throws TibrvException
Purpose
Get the value of a specified field from a message.
Remarks
Programs specify the field to retrieve using the fieldName and fieldId parameters.
The method returns a snapshot of the field value.
When a program gets fields with the datatypes listed here, this method (and convenience methods) return a reference to the actual value in the message—not a copy. Use caution when modifying values of these types: TibrvMsg.MSG, TibrvMsg.DATETIME, TibrvMsg.IPPORT16, TibrvMsg.IPADDR32, TibrvMsg.OPAQUE (extracted as a byte array), TibrvMsg.XML (extracted as a byte array), and all array types.
Programs can use a related method to loop through all the fields of a message; to retrieve each field by its integer index number, see TibrvMsg.getFieldByIndex().
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
|
Get a field with this name. |
|
|
Get the field with this identifier. |
Field Search Algorithm
This method, and related methods that get message fields, all use this algorithm to find a field within a message, as specified by a field identifier and a field name.
Procedure
| 1. | If the program supplied zero as the identifier, or omitted any identifier, then begin at step 3. |
If the program supplied a non-zero field identifier, then search for the field with that identifier.
If the search succeeds, return the field.
On failure, continue to step 2.
| 2. | If the identifier search (in step 1) fails, and the program supplied a non-null field name, then search for a field with that name. |
If the name search succeeds, and the identifier in the field is null, return the field.
If the name search succeeds, but the actual identifier in the field is non-null (so it does not match the identifier supplied) then throw an exception with the status code TibrvStatus.ID_CONFLICT.
On failure, or if the program supplied null as the field name, return null.
| 3. | When the program supplied zero as the identifier, or omitted any identifier, then begin here. |
Search for a field with the specified name—even if that name is null.
If the search succeeds, return the field.
On failure, return null.
If a message contains several fields with the same name, searching by name finds the first instance of the field with that name.
Extracting Fields from a Nested Message
Earlier releases of Rendezvous software allowed programs to get fields from a nested submessage by concatenating field names. Starting with release 6, Rendezvous software no longer supports this special case convenience. Instead, programs must separately extract the nested submessage using TibrvMsg.get() (or a related method), and then get the desired fields from the submessage.
Method Forms
With only a field name, find the field by name. If the field name is not present in the message, return null. If several fields with that name are present in the message, this method returns the first one that it finds.
With only a field identifier, find the field with that identifier (since identifiers are unique, the message can contain at most one such field). If the identifier is not present in the message, return null.
With both a field name and a field identifier, search first by identifier, and then by field name. If neither are present in the message, return null. If identifier search succeeds, return the field value. If the name search succeeds, but the actual identifier in the field is non-zero (so it does not match the identifier supplied) then throw a TibrvException with status code TibrvStatus.ID_CONFLICT.
Decoding and Type Conversion
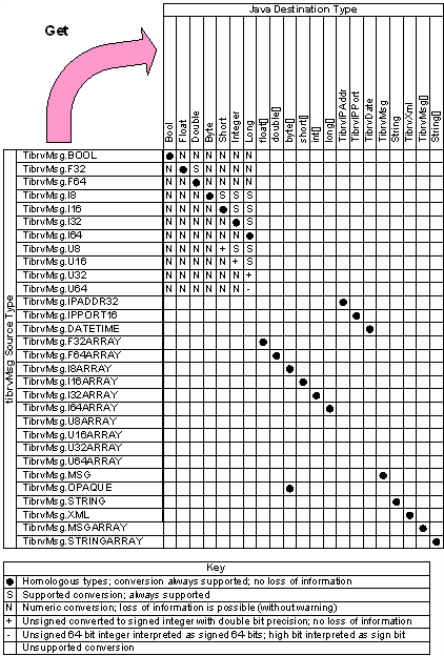
This method automatically decodes the extracted field data from its Rendezvous wire format type to a corresponding Java type. In Wire Format to Java Datatype Conversion Matrix, filled circles (as well as + and - symbols) specify default decodings between homologous types; for some types you can override the default decoding by using convenience calls that force specific types (see Get Scalar).
Java does not admit unsigned integers. When extracting an unsigned integer from an inbound message field, this method automatically promotes the value to the corresponding Java type that is large enough to contain it (Wire Format to Java Datatype Conversion Matrix indicates this with +). When extracting an unsigned 64-bit integer, Java does not have a type that can contain a number that uses all 64 bits; this method decodes it to a Java long, interpreting the high bit as a sign bit (Wire Format to Java Datatype Conversion Matrix indicates this with -).
After extracting the XML document into a byte array, explicitly convert it to a string using the encoding that corresponds to your locale (file encoding system property). For more information, see Encoding XML.
Figure 236: Wire Format to Java Datatype Conversion Matrix