Click Files
and data ![]() .
.
In the Files and data flyout, click Connect to.
In the list of connectors, click Microsoft SQL Server.
In the Microsoft SQL Server flyout, click New connection
This dialog is used to configure a connection to a Microsoft SQL Server database. You can choose whether to analyze data in-database or to import it into your analysis. You do not have to install a driver on your computer to get access to the Microsoft SQL Server connector. See Getting Started with Connectors if you need help accessing the connector.
With the Microsoft SQL Server connector, you can also connect to Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics databases. You can access both serverless and dedicated SQL pools from within Spotfire. To do so, you do not need to install any additional drivers or programs.
Note: When establishing a connection using the Spotfire connector for Microsoft SQL Server, the TIBCO Spotfire application name and version number are added to the connection string as a telemetry tag.
To add a new Microsoft SQL Server connection to the library:
On the menu bar, select Data > Manage Data Connections.
Click Add New > Data Connection and select Microsoft SQL Server.
To add a new Microsoft SQL Server connection to an analysis:
Click Files
and data ![]() .
.
In the Files and data flyout, click Connect to.
In the list of connectors, click Microsoft SQL Server.
In the Microsoft SQL Server flyout, click New connection
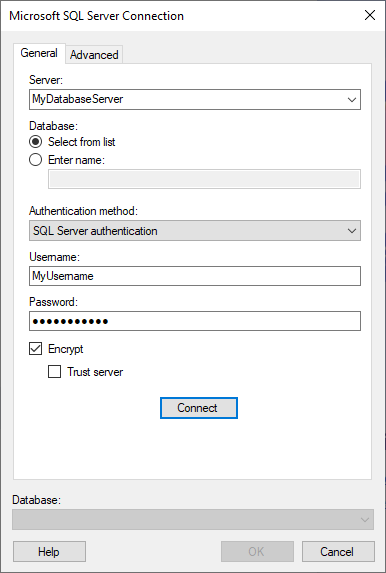
General
Option |
Description |
Server |
The name of the server where your data is located. To include a port number, add it directly after the name preceded by comma. To include an instance name, add it directly after the server name preceded by backslash. Example with port number: Example with instance name: |
Database |
Determines how you select which database to access. Select from list Select from a list of all available databases in the Database drop-down menu. The Database drop-down menu is populated after you click Connect. Note: To use the Select from list option, you must have access to the default database in the data source. The default database is often called ‘master’. Enter name Manually enter the name of the database that you want to access. |
Authentication
method |
The authentication method to use when logging into the database. Windows authentication When using Windows authentication, e.g., Kerberos, the access token of the logged in user will be used. Users that have been given the appropriate access rights to SQL Server will be able to connect and read data. Domain credentials are not stored in the analysis file. SQL Server authentication With database authentication the authentication is done using a database user. Database credentials can be stored, unencrypted, as part of the analysis file, using a setting in the Data Source Settings dialog. If credentials are found in the analysis file they will be used to automatically authenticate against the database. If no credentials or credentials profiles are found in the analysis file all who open the file will be prompted for database credentials. Note that there will be no prompting for credentials if the credentials embedded in the analysis file fail. Active Directory - Integrated [This authentication method is not supported if you open the data connection in a Spotfire web client that is running on a Linux system.] If you are using Active Directory and your domain is federated with Azure Active Directory, you can connect to Microsoft Azure SQL Database and authenticate with your logged in Azure Active Directory credentials. Select the authentication method Active Directory - Integrated. With this authentication method, credentials cannot be saved in the analysis file. Active Directory - Password Enter your Azure Active Directory principal user name and password for authentication with Microsoft Azure SQL Database. Use Active Directory - Password authentication only to connect to Microsoft Azure SQL Database. |
Username |
The username you wish to use when logging into the SQL Server database. |
Password |
The password for the specified username. |
Encrypt |
Select this check box to require that encryption is used when connecting to the SQL Server. Note: By default, Encrypt is selected. |
Trust server
|
[Only applicable when Encrypt is selected.] If you want use encryption to connect to an SQL Server which does not have a verifiable server certificate (for example if it is using a self-signed certificate), you can select this check box to trust the server and connect without validation of the server certificate. |
Connect |
Connects you to the specified server and populates the list of available databases below. |
Database |
Select the database of interest from the drop-down list. |
Advanced
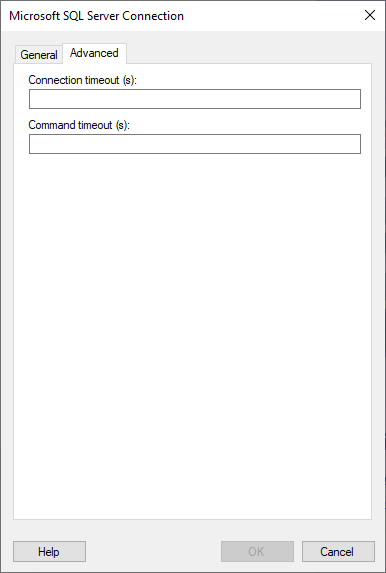
Note: For more information about the settings on the Advanced tab, see the official documentation from Microsoft about the .NET data provider for SQL Server.
Option |
Description |
Connection timeout (s) |
The maximum time, in seconds, allowed for a connection to the database to be established.
You can also set this timeout as a preference in the Administration Manager, which will be used if you don’t set a timeout in the connection dialog. If you set a timeout in the connection dialog this value overrides the settings in the Administration Manager preference. If you specify a timeout neither in the connection dialog nor in the preference, the default value of 120 seconds will be used. Note: If you set the connection timeout to zero, it will be interpreted as no timeout. This means that there will be no upper limit for trying to execute the command. This is generally not recommended. |
Command timeout (s) |
The maximum time, in seconds, allowed for a command to be executed.
You can also set this timeout as a preference in the Administration Manager, which will be used if you don’t set a timeout in the connection dialog. If you set a timeout in the connection dialog this value overrides the settings in the Administration Manager preference. If you specify a timeout neither in the connection dialog nor in the preference, the default value of 1800 seconds will be used. Note: If you set the command timeout to zero, it will be interpreted as no timeout. This means that there will be no upper limit for trying to execute the command. This is generally not recommended. |