Pivot
This operator transforms the categorical data contained in a column of a table into columns of a new table, by means of subtotals (or other calculations) that can be defined by another column in the same list. The other calculations can be averages and counts.
![]()
Information at a Glance
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
| Category | Transform |
| Data source type | TIBCO® Data Virtualization |
| Send output to other operators | Yes |
| Data processing tool | TIBCO® DV, Apache Spark 3.2 or later |
Algorithm
For typical data entry and storage, data usually appears in flat tables such that it only consists of rows and columns. While such data contains a lot of information, it can be difficult to get the information summary. A pivot table helps quickly summarize the flat data, giving it depth, and highlighting the desired information.
The usage of a pivot table is extremely broad and depends on the situation. The first question to ask is "What am I looking for?" A pivot table usually consists of rows, columns, and data (or fact) fields. These fields allow several kinds of aggregations including sum, average, count, max, min, and so on.
The Pivot Column can only be categorical. In the output table, the Pivot Column is transformed into multiple columns, one for each category. To run this operator, you must define at least one variable with a categorical data type.
- The results are also grouped by a selected column.
- The values in the new columns are aggregates of a third column (or of the presence of the category if no aggregate column is chosen).
- The columns are listed (in the table, file, or array) in a descending order of the value of the category that they represent.
Input
An input is a single tabular data set.
Bad or Missing Values
Null values are not allowed and result in an error.
Configuration
The following table provides the configuration details for the Pivot operator.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Notes | Notes or helpful information about this operator's parameter settings. When you enter content in the Notes field, a yellow asterisk appears on the operator. |
| Pivot Column | Specify the column for pivot transformations. On database data sources, you can only select the categorical columns to pivot. |
| Group By | Specify the column to group by. |
| Aggregate Column | Specify the pivot column's value column. |
| Aggregation | Specifies the aggregate function. The following values are available:
|
| Output Schema | Specify the schema for the output table or view. |
| Output Table | Specify the table path and name where the output of the results is generated. By default, this is a unique table name based on your user ID, workflow ID, and operator. |
| Store Results | When set to Yes, the operator saves the results. If set to No, the operator does not save the results. |
Output
- Output: A table that displays the output of a data set for the succeeding operator.
Example
The following example demonstrates the Pivot operator.
Data
golf: This data set contains the following information:
- Multiple columns namely outlook, temperature, wind, humidity, and play.
- Multiple rows (14 rows).
Parameter Setting
The parameter settings for the golf data set are as follows:
-
Pivot Column: play
-
Group By: outlook
-
Aggregate Column: temperature
-
Aggregation: sum
-
Store Results: Yes
Output
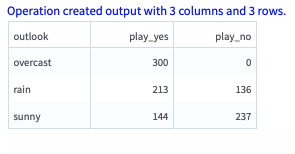
The following figure displays the output for the parameter settings for the golf data set.