K-Means Clustering
This operator implements the K-Means clustering algorithm from Spark MLLib.

Information at a Glance
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
| Category | Model |
| Data source type | TIBCO® Data Virtualization |
| Send output to other operators | Yes |
| Data processing tool | TIBCO® DV, Apache Spark 3.2 or later |
Algorithm
The objective of the K-Means algorithm is to create clusters of objects that are similar to one another and different from individuals in other clusters in terms of their attributes. To achieve this, K-Means employs a centroid-based partitioning technique that uses the centroid of a cluster to represent that cluster. Conceptually, the center point is the centroid of a cluster.
The K-Means algorithm works as follows:
- K points from the data set are chosen as the initial centroids of the K clusters according to the specified initialization method.
- K clusters are created by associating each observation to the nearest centroid.
- The new centroids are calculated for the clusters; determine whether centroid values change the coordinates.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 until convergence (when the centroid values do not change) or a specified termination criterion is met.
This operator implements the K-Means clustering algorithm from Spark MLib.
The specified columns are used to train the K-Means clustering model. You must define the initial centroids of the clusters. This operator provides two methods to define the initial centroids of the clusters such as K-Means++ and Random allocation.
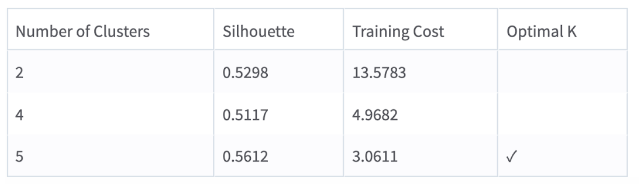
This operator uses the Silhouette value to determine the optimal number of clusters. The silhouette metric is a measure to compare the similarity of observation to its assigned cluster to other clusters. Generally, high silhouette values are preferred.
Input
An input is a single tabular data set.
Configuration
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Notes | Notes or helpful information about this operator's parameter settings. When you enter content in the Notes field, a yellow asterisk appears on the operator. |
| Use all available columns as Predictors | When set to Yes, the operator uses all the available columns as predictors and ignores the Continuous Predictors and Categorical Predictors parameters. When set to No, the user must select at least one of the Continuous or Categorical Predictors. |
| Continuous Predictors | Specify the numerical data columns for training the K-Means model. It must be numerical column. Click Select Columns to select the required columns. |
| Distance Measure | Specify the distance measure for training the K-Means model. The available options are Euclidean and Cosine. Default: Euclidean |
| Number of Clusters | The number of clusters to create during the cluster analysis process. Specify the parameter using one of the following methods.
Default: 2 |
| Initialization Method | The method for specifying the initialization cluster points. It can be either K-Means++ or Random. Default: K-Means++ |
| Normalize Features | Specify whether to normalize numerical features (Z-Transformation). Default: Yes |
| Max Iterations | Specify the maximum number of iterations performed for one run of the K-Means algorithm. Default: 100 |
| Tolerance | The smaller the value, the stricter the determination of when the analysis has converged. A smaller number results in more iterations of the algorithm, but is still capped by the iteration limit.
Default: 0.0001 |
| Random Seed | Specify the seed used for the pseudo-random row extraction.
Default: 1 |
Output
- Parameter Summary Info: Displays a list of the input parameters and their current settings.
- Training Summary: A text field that displays the training summary.
-
Silhouette: A measure to compare the similarity of observation to its assigned cluster compared to other clusters.
-
Training Cost: The sum of specified distances to the nearest centroid for all points in the training data set.
-
PRED_KM: Specifies the cluster that an observation belongs to.
-
DIST_KM: The distance between the cluster centroid and the observation.
Example
The following example builds a K-Means model and uses a Predictor operator to return the clustering result of a given data set.

- Multiple columns namely outlook, temperature, wind, humidity, and play.
- Multiple rows (14 rows).
-
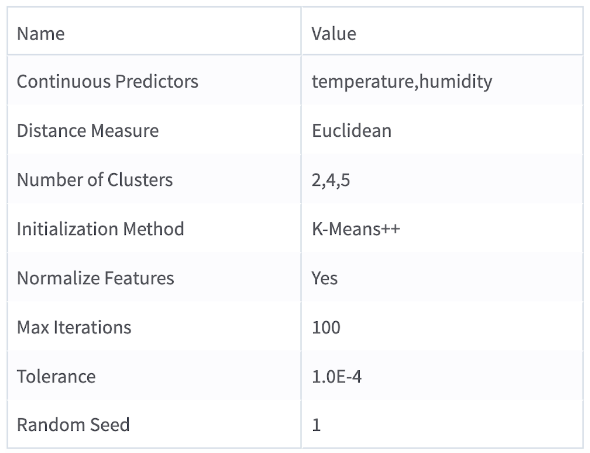
Use all available columns as Predictors:No
-
Continuous Predictors: temperature, humidity
-
Distance Measure: Euclidean
-
Number of Clusters: 2,4,5
-
Initialization Method: K-Means++
-
Normalize Features: Yes
-
Max Iterations: 100
-
Tolerance: 1.0E-4
-
Random Seed: 1