Configuring Hawk Application Management Interface (AMI) Configuration (optional)
The TIBCO Hawk AMI Configuration page defines how the Adapter for Files Component uses TIBCO Rendezvous with TIBCO Hawk Microagents (HMA). Even when EMS is used as the primary transport, HMA still uses Rendezvous as the transport.
Procedure
-
In the TIBCO Hawk AMI Configuration window, enter values in each field.
TIBCO Hawk AMI Configuration
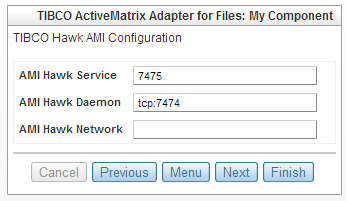
- AMI Hawk Service
- It specifies the TIBCO Hawk port number, for example, TIBCO Rendezvous will connect with TIBCO Hawk on the default port 7474. AMI Hawk Service and AMI Hawk Daemon must be set with valid values together. Setting only one of them will result in an error.
- AMI Hawk Daemon
- It specifies the location of the TIBCO Hawk Daemon. A value of "tcp:yyyy" would correspond to a local Hawk Daemon where "yyyy" would be the port number. A Hawk Daemon located elsewhere would be specified by a value of the protocol, IP address, and port number: "tcp:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:yyyy".
The AMI Hawk Service and the AMI Hawk Daemon ports may be the same or they may be different. By default, different TLMs on the same engine daemon (physical machine) are using the same RV transport (default AMI Hawk Service=7475, and default AMI Hawk Daemon=tcp:7474). This setting enables visibility of all of the deployed applications on each TLM even if some applications are NOT deployed on this particular TLM.
Note: The actual AMI Hawk Service port for the runtime component instance is incremented by an integer according to the engine instance ID. For example, if the user sets the AMI Hawk Service to 6464 and the component is instantiated to run on engine instance 1, then the service is reported in the hawkagent.cfg file as 6465. Then when the component is scaled up to other engine instances the AMI Hawk Service value will be incremented higher by the Enabler automatically.Generally, AMI Hawk Network is an empty string.
Copyright © Cloud Software Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
