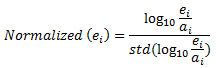
Assume that there are n rows with k variables, A, B, C, D, E, F and G, in the data. We use variable E as an example in the calculations below. All target variables are normalized in the same way.
If we select A as baseline variable the normalized value of ei for variable E in the ith row is calculated as:
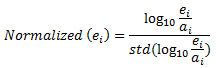
where
std = the standard deviation
ai = the value for variable A in the ith row.
See also: