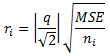
The drawing of comparison circles is a way to display whether or not the group means for all pairs are significantly different from each other. The Tukey-Kramer method is used for the calculation. Each group (each box plot) gets a circle where the center of the circle is aligned with the group mean value. The radius of the circle, ri, is calculated as follows:
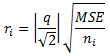
where
MSE is the mean standard error
(the pooled sample variance) for each box:
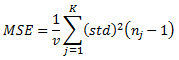
v is the degrees of freedom:
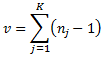
nj is the number of records in the group (count)
K is the number of groups
![]() where
q* is the critical value and q is the upper alpha quantile of the
Studentized range distribution with K groups and v degrees of freedom.
The alpha level is specified in the Visualization Properties dialog.
For details on how the quantile is calculated, see Aggregations
Overview. The value of q is calculated and updated each time the
filtering of the axis is changed.
where
q* is the critical value and q is the upper alpha quantile of the
Studentized range distribution with K groups and v degrees of freedom.
The alpha level is specified in the Visualization Properties dialog.
For details on how the quantile is calculated, see Aggregations
Overview. The value of q is calculated and updated each time the
filtering of the axis is changed.
If the circles for different groups do not overlap (or that the external angle of intersection is less than 90 degrees) the means of the two groups are generally significantly different. If the circles have a large overlap, the means are not significantly different.
The explanation to why the overlap defines whether or not group means are significant can be deduced with the Pythagorean Theorem.
Comparison circles |
Mathematical expression |
Interpretation |
|
|
The groups are significantly different. |
|
|
Borderline significantly different. |
|
|
The groups are not significantly different. |
References
http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/general/qprob
Sall, J. (1992), "Graphical Comparison of Means" Statistical Computing and Statistical Graphics Newsletter, 3, pages 27-32.
See also: