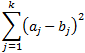
The Square Euclidean distance between two points, a and b, with k dimensions is calculated as
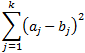
The Half Square Euclidean distance between two points, a and b, with k dimensions is calculated as
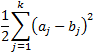
The half square Euclidean distance is always greater than or equal to zero. The measurement would be zero for identical points and high for points that show little similarity.
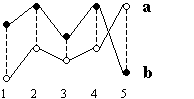
The figure below shows an example of two points called a and b. Each point is described by five values. The dotted lines in the figure are the distances (a1-b1), (a2-b2), (a3-b3), (a4-b4) and (a5-b5) which are entered in the equation above.
See also: