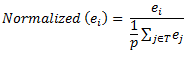
The trimmed mean for a variable is based on all values except a certain percentage of the lowest and highest values for that variable. This removes the effect of outliers during the normalization. If the trim value is set to 10% then the highest 5% of the values and the lowest 5% of the values are excluded from the calculated mean.
Assume that there are n rows with seven variables, A, B, C, D, E, F and G, in the data. We use variable E as an example in the calculations below. The remaining variables in the rows are normalized in the same way.
Without rescaling (Baseline variable = None)
The normalized value of ei for variable E in the ith row is calculated as:
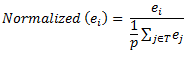
where
T = the set of rows left after trimming
p = the number of rows in T.
Rescaling by a baseline variable
If we select variable A as baseline variable, the normalized value of ei for variable E in the ith row is calculated as:
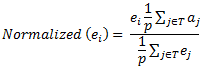
where
T = the set of rows left after trimming
p = the number of rows in T
aj = the value for variable A in the jth row.
See also: