Ranking
You might want to assign a ranking number to the values within a data column.
The ranking can be made in different ways, and the examples below illustrate some of them. For more options, see Ranking functions.
Rank() and DenseRank()
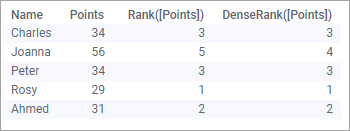
Points from a competition are listed for a number of people in the data table below. Note that two of the points are identical.
Two calculated columns are added, each of the ranking in an ascending order:
Rank([Points]) and DenseRank([Points])
When values are identical, the two functions handle the following ranking numbers differently.
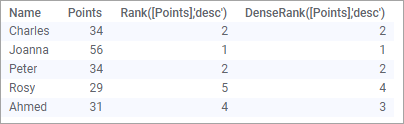
Descending ranking
By default, the ranking is ascending. You can change to a descending order by adding 'desc' to the expressions:
Rank([Points],'desc') and DenseRank([Points],'desc')
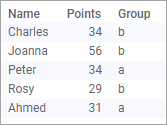
Rank groups within a column separately
Assume there are two groups represented in the competition, a and b, and they should be ranked separately.
This can be done using the expression
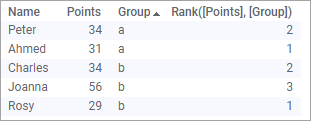
Rank([Points], [Group])
shown below. To make it easier to see the separate ranking in the groups, the 'Group' column is sorted.