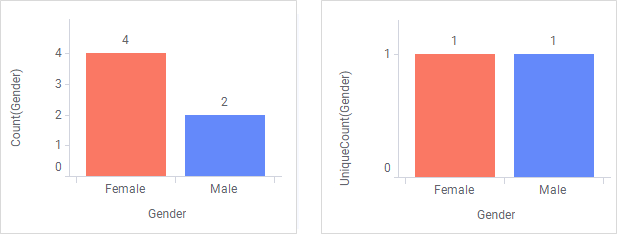
Aggregating data
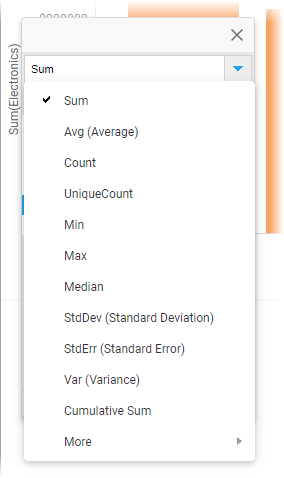
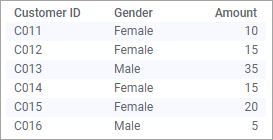
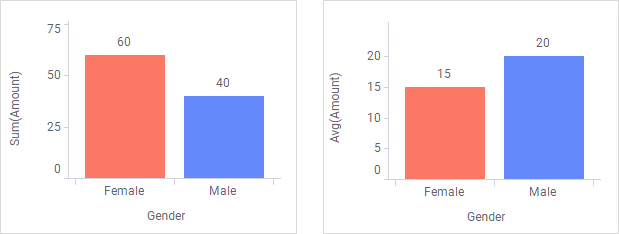
Visualizing data involves presenting aggregated values of the data you have loaded. Examples of aggregated values are sums, averages, counts of occurrences, or results from various statistical calculations. That is, they represent collections of data as single values. In most cases, the data to aggregate is numerical, but also non-numerical data can be aggregated.
The resulting values of an aggregation reflect the current data. That is, when you filter the data, a re-calculation takes place instantly, and the visualization updates.
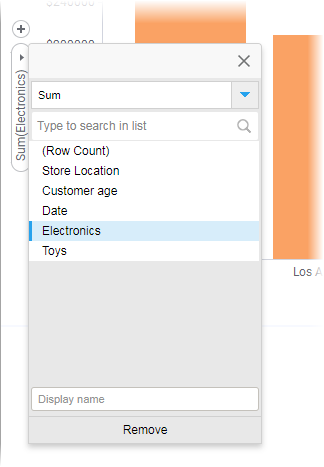
You specify which aggregation to display on the axis' column selector .
Procedure
Copyright © Cloud Software Group, Inc. All rights reserved.