Example 5: Power Calculation in a 1-Way Repeated Measures ANOVA
In a 1-way repeated measures ANOVA, you have the choice of analyzing the data with a univariate or multivariate approach. In this example, we show how to calculate power for the univariate F-test. Suppose that a group of N = 10 subjects are observed performing a task on p = 6 different occasions. In this subjects by trials design, the degrees of freedom are p -1 and (N - 1)(p - 1). However, the noncentrality parameter δ must be adjusted, because the repeated measures are generally correlated. Estimation, a priori, of this noncentrality parameter requires that you specify a value for the RMSSE, assume a common correlation between the various trial occasions as well as a common variance, and provide an estimate of this common correlation, ρ.
The noncentrality parameter is then given by
Suppose that, in this case, the RMSSE is assumed to be .30, and the common correlation is .50. Then δ may be computed easily as
δ = (10(6 -1).302) / 1 - .50 = 4.5 / .50 = 9
Ribbon bar. Select the Statistics tab. In the Advanced/Multivariate group, click Power Analysis to display the Power Analysis and Interval Estimation Startup Panel.
Classic menus. From the Statistics menu, select Power Analysis to display the Power Analysis and Interval Estimation Startup Panel.
In the Startup Panel, select Probability Distributions and Noncentral F Distribution.
Click the OK button to display the Noncentral F Probability Calculator dialog box.
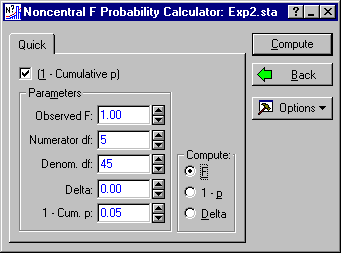
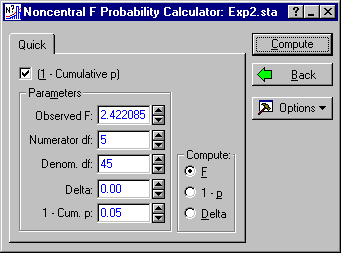
First, compute the critical value of F used for the significance test. The degrees of freedom are 5 and 45; therefore, enter 5 in the Numerator df field and 45 in the Denom. df field. Then select the (1 - Cumulative p) check box, and enter a value of .05 in the 1 - Cum. p field. This is the significance level for the F-test. Next, in the Compute group box, select the F option button as the quantity to compute. The dialog box should now look like this:
Click the Compute button to calculate the critical value of F. A value of 2.422085 is produced as the Observed F.
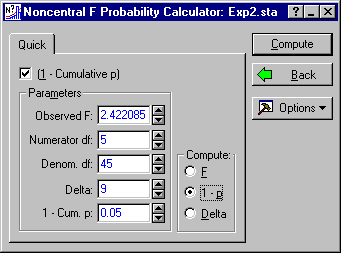
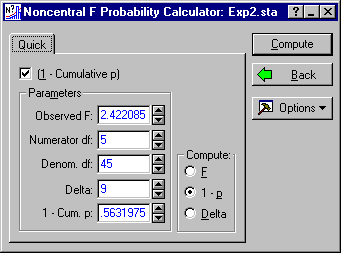
To compute power, we need to compute the probability of obtaining a value higher than the critical value of F, when the degrees of freedom are 5 and 45, and the Delta is the previously calculated value of 9. Simply enter 9 in the Delta field, and select 1 - p as the quantity to compute in the Compute group box. The dialog box should look like this:
To compute power, click the Compute button and observe the value for 1 - Cum. p.
In this case, it seems the power is somewhat less than adequate, only about .56.
See also, Power Analysis - Index.