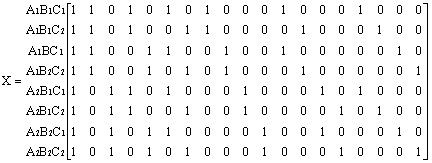GLM Introductory Overview - Factorial ANOVA
Factorial ANOVA designs contain X variables representing combinations of the levels of 2 or more categorical predictors (e.g., a study of boys and girls in four age groups, resulting in a 2 (Gender) x 4 (Age Group) design). In particular, full-factorial designs represent all possible combinations of the levels of the categorical predictors. A full-factorial design with 2 categorical predictor variables A and B each with 2 levels each would be called a 2 x 2 full-factorial design. Using the sigma-restricted coding, the X matrix for this design would be:
Several features of this X matrix deserve comment. Note that the X1 and X2 columns represent main effect contrasts for one variable, (i.e., A and B, respectively) collapsing across the levels of the other variable. The X3 column instead represents a contrast between different combinations of the levels of A and B. Note also that the values for X3 are products of the corresponding values for X1 and X2. Product variables such as X3 represent the multiplicative or interaction effects of their factors, so X3 would be said to represent the 2-way interaction of A and B. The relationship of such product variables to the dependent variables indicate the interactive influences of the factors on responses above and beyond their independent (i.e., main effect) influences on responses. Thus, factorial designs provide more information about the relationships between categorical predictor variables and responses on the dependent variables than is provided by corresponding one-way or main effect designs.
When many factors are being investigated, however, full-factorial designs sometimes require more data than reasonably can be collected to represent all possible combinations of levels of the factors, and high-order interactions between many factors can become difficult to interpret. With many factors, a useful alternative to the full-factorial design is the fractional factorial design. As an example, consider a 2 x 2 x 2 fractional factorial design to degree 2 with 3 categorical predictor variables each with 2 levels. The design would include the main effects for each variable, and all 2-way interactions between the three variables, but would not include the 3-way interaction between all three variables. Using the overparameterized model, the X matrix for this design is
The 2-way interactions are the highest degree effects included in the design. These types of designs are discussed in detail the 2(k-p) Fractional Factorial Designs section of the Introductory Overview to the Experimental Design module.
Between-subject designs
Within-subject (repeated measures) designs
Multivariate designs