2D Categorized Box Plots - Advanced Tab
Select the Advanced tab of the 2D Categorized Box Plots Startup Panel to access the options described here.
If more than one dependent variable is selected, a sequence of graphs (one for each dependent variable) will be produced using the same set of grouping variables. Note that the selected grouping variables do not have to be categorical variables (e.g., contain codes); you can use one of the methods of categorization (below) to categorize continuous variables. The selection of grouping variables is not necessary if the categories are defined via the Multiple subsets method.
Middle point. The options in this group box control the type of value and appearance of the middle point.
Style. Use the Style box to control how the middle point is represented (by a Line or Point).
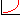
spooled2 = 1/(n-k) * [s12 *(n1 -1) + ... + sk2 *(nk -1)]
In this equation, k refers to the k groups in the plot, s12, refers to the variance in the i'th category or group, n1 refers to number of valid observations in the i'th category or group, and n is the overall number of valid observations in the plot.
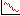
The standard error of the mean for the i'th group is then computed as:
s.e.(mean) = spooled /square root(ni)
Box. If you select Median as the middle point, the range (box) can be represented by Percentiles or the Min-Max values of the selected variable, or a specified Constant value (when you want a fixed size box around the medians).
If you select Mean as the mid-point, the range (box) can be defined in terms of standard deviations (Std. Dev), standard errors (Std. Error), Min-Max values of the selected variable, or a specified Constant value (when you want a fixed size box around the means).
You can also specify a Coefficient by which the selected range value is multiplied (by default, the Coefficient is 1). Note that, except for unusual applications, the default value of the coefficient (1) should not be changed if the box Value is Min-Max.
If you select Mean as the mid-point, the range (whiskers) can be defined in terms of standard deviations (Std. Dev), standard errors (Std. Error), or Min-Max values of the selected variable, or Non-Outlier Range.
If you select Non-Outlier Range, Statistica determines which points in the data set are outliers (see Outliers and Extremes), and then uses the highest and lowest data points which are closest to the outliers (but are not outliers) as the whiskers in the plot.
You can also specify a Coefficient by which the selected range value will be multiplied (by default, the Coefficient is 1). In most typical applications the coefficient should be set to 1 when the value of the whisker is Min-Max or Non-Outlier Range.