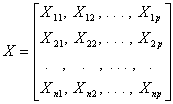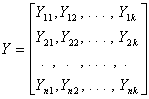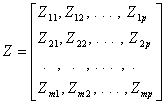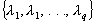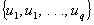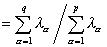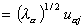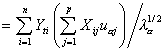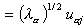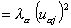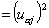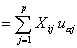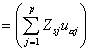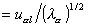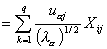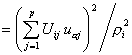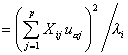Principal Components and Classification Analysis - Computational Details
This section provides the computational details and the formulas that were used in the implementation of the Advanced Principal Components Analysis in this module.
where Xij represents the value of the j th variable for the i th case, standardized or centered about their respective means. Similarly, the data pertaining to the supplementary variables can be arranged in the matrix Y of n rows and k columns:
where Yit is the value of the t th supplementary variable for the i th case, standardized or centered about their respective means. The data pertaining to m supplementary cases can be arranged in the matrix Z of m rows and p columns:
where Zls is the value of the s th variable for the l th case, standardized or centered about their respective means.
Contributions of variables.
Relative contribution of the j th variable to the variance of the a-factor axis:
Cosine2of cases. Cosine square of the i th case for the a th factor:
where pi2 is the normalizing constant, obtained by summing all the factor coordinates of the i th case. The element Uij comes from the X or Z data matrix, depending upon whether the case is active or supplementary.