TIBCO Streaming provides support for generating StreamBase Application projects with support for Kubernetes and Helm.
- Kubernetes
-
When generating a new StreamBase Application project as described in Create a StreamBase Application Project, select one extra checkbox to add support for Kubernetes:
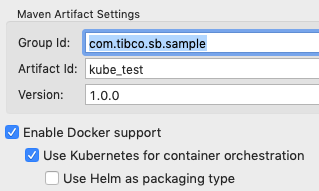
This generates an extra folder in the Studio project,
src/main/kubernetes, that contains a Kubernetes ConfigMap file in YAML format namedprojectname-app.yamlIn this
projectname-app.yamlClusterRoleBindingnamespace fromdefaultto the specific namespace on which you are deploying the StreamBase Application. Also, you can change the applicationStatefulSetdeployment file section where the Docker image is specified. You can change the Docker image name according to your container registry, such as local host or any cloud platform like Azure, AWS, or GCloud. The registry name should be added with the Docker image name. Some examples are:Kind: `localhost:5000/myimage` Azure: `myregistry.azurecr.io/myimage` AWS: `123456789012.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/myimage` GCloud: `gcr.io/myproject/myimage`
The StreamBase Application
projectname-app.yamlPrometheus, then there is no need to deploy themetrics-server.yamlfile along with the StreamBase applicationprojectname-app.yaml - OpenShift
-
To deploy the StreamBase Application on an OpenShift cluster, follow these steps:
1. Create the necessary secret for integrating with image registries on OpenShift. For example, to pull images from Azure Container Registry (ACR), you need to create a secret and integrate it with the StreamBase application as shown in this guide.
2. Similarly, to configure a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) cluster to pull images from AWS Elastic Container Registry (ECR), you need to create a secret and integrate it with the StreamBase application as shown in this guide.
Here is an example of how to create a secret for ACR:
oc create secret docker-registry acr-secret \ --docker-server=myregistry.azurecr.io \ --docker-username=myregistry \ --docker-password=mysecurepassword \ --docker-email=myuser@tibco.com \ --namespace mms3. Link the secret to the default service account for pulling images:
oc secrets link default acr-secret --for=pull -n mms4. Reference the secret in your StreamBase Application
projectname-app.yamlspec: template: spec: imagePullSecrets: - name: acr-secret5. Additionally, update the
security.conffile in the StreamBase application configuration files to add the OpenShift pod CIDR to the trusted hosts list. You can fetch the pod CIDR using the following command:oc get network.config.openshift.io cluster -o jsonpath='{.spec.clusterNetwork[0].cidr}'Here is an example of how to update the
security.conffile:TrustedHosts = { hosts = [ "${DEFAULT_ROUTE:-10.1.0.1}", "*.ocaztest.${POD_NAMESPACE:-default}.svc.cluster.local", "10.128.0.0/14" ] } - Helm
-
To generate a Docker image that uses Helm Charts to direct the creation of a Kubernetes-ready Docker image, you must have Helm installed, with the helm command in the PATH.
When generating a new StreamBase Application project as described in Create a StreamBase Application Project, select all three checkboxes to generate a Helm Chart for this project:
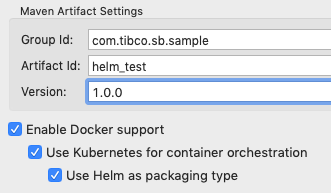
This generates an extra folder in the Studio project,
src/main/helm, that contains a folder named for the project that contains set of Helm configuration files. See Helm documentation to understand these files.The StreamBase Application
projectname-app.yamlPrometheus, then there is no need to deploy themetrics-server.yamlfile along with the StreamBase applicationprojectname-app.yaml
