Database Security
Data security is of vital importance to a business function. Database administrator in collaboration with business and security administrator, identify the sensitive and confidential data elements that need to be secure from storage and access point of view. This section will guide the user with the necessary procedure.
Procedure
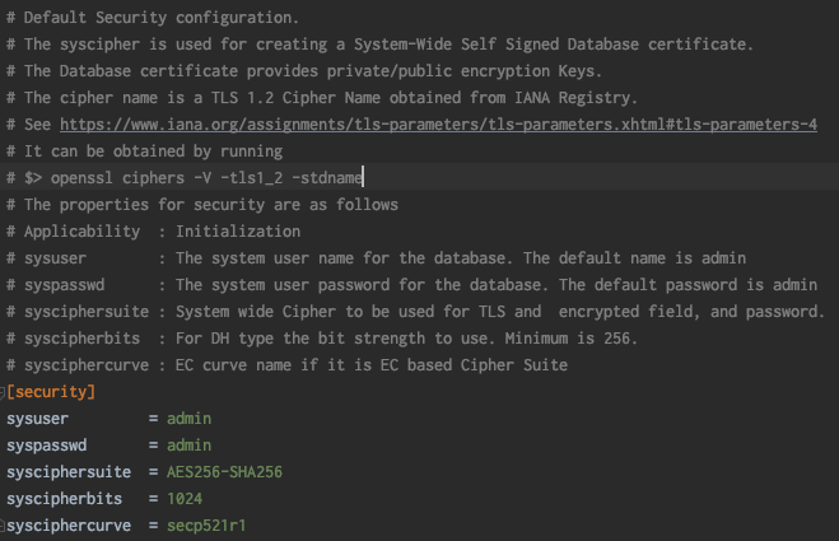
- Create/Modify a database configuration file. Under the security section, fill in the values provided by your Security Administrator. See the Figure below. Database security configuration
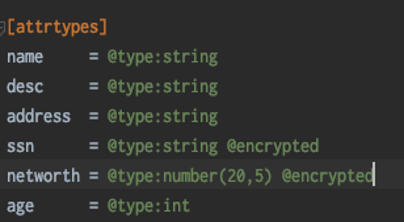
- For each field that is marked confidential or sensitive by the Business Owners, perform one of the 2 things.
- Mark the field in the configuration file as encrypted. See below.
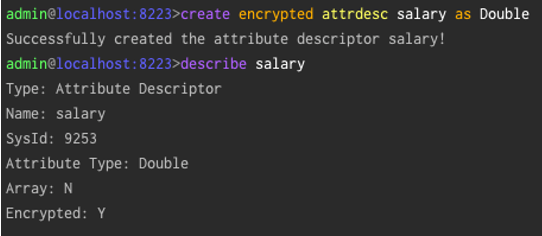
- Use the admin command to create the attribute as an encrypted attribute. Ensure you are logged in as an Administrator or as a user who has the privilege to modify the system catalogue.
- Attribute descriptor cannot be dropped from system.
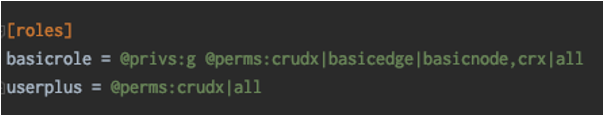
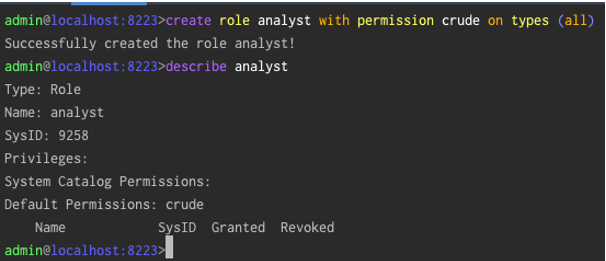
- Create Roles and grant privilege to the system catalogue objects in the database. Similar to point 2, Roles can be created either in database configuration file or from admin console.
- Create Users with specified roles and/or add Roles to an existing user. It is achieved similar to the way roles are added to the system. Skipping the screenshots for the same.
- Choose passwords for the user. The password is digested using the PBDKF2 algorithm with SHA1 digest.
- Ensure the correct user has the "Read/Update/Delete" permission on the $SYSCATALOG object. This is a system table and provides access to view/delete system objects.
- Ensure Operators who perform a backup of the database have Import/Export permissions on all objects.
- Ensure Operators who monitor and manage the server instance have "Diagnostic" permission and Operator role permission. This allows operators to perform,
- When the user leaves the organization, follow up by disabling/dropping the user, and backing up the user pertaining data.
Copyright © 2020. Cloud Software Group, Inc. All Rights Reserved.