Iterating Through Multiple Tables
It is often the case that an organization has multiple tables with the same structure, that is column names and data types, but with different names, in different databases or schemas or on different servers.
Now a single synonym can be used to describe a collection of tables with the same structure because the TABLENAME and CONNECTION parameters in the Access File can be specified as a variable.
Before you create and run the data flows discussed in this section, in addition to the source data, you must also create the multiple source tables. See Create Sample Procedures and Data for Iteration.
This will create five identically structured tables named dmordbos, dmorddal, dmordla, dmordorl, and dmordstl.
Create a Synonym With Parameterized Table Names
This example has instructions for creating a synonym that can be used to read or write multiple tables. You will create two variables, TTABLE and TCON that will be used for the table name and connection name.
Refer to the sample synonym, dmortmpl, for the complete example that also has titles and descriptions for each of the columns.
- In the ibi Data Migrator desktop interface,
right-click an application directory in the navigation pane, select New,
and then click Synonym (Create or Update).
The Get Data panel opens.
- Right-click the connection for the adapter where you created the sample procedures, and click Show DBMS Objects.
The Create Synonym panel opens.
- Select the
checkbox to the left of dmordbos, click in the field with the synonym name,
and change it to dmortmplx, as shown in the following image.
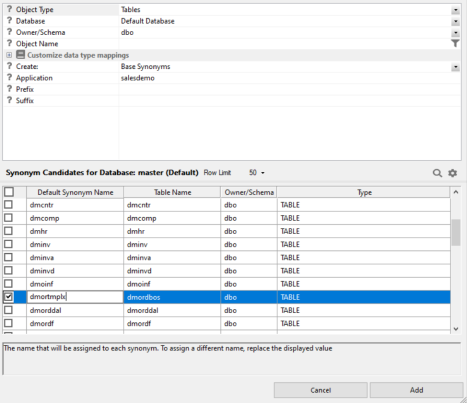
This will create a synonym that you will use as a template to access any of the six tables.
- Click Add.
- In the Navigation pane, double-click dmortmplx.
The dmortmplx synonym opens.
- If there is Business View window, click the small x to close it.
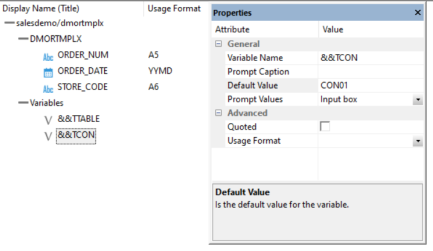
- On the ribbon, click Insert and select Variable. This adds a variable called VARIABLE1.
- Click the name and change it to TTABLE. This creates a global variable in the synonym.
- For DEFAULT, type the value dmordbos.
- Right-click the Variables folder, select Insert, then Variable.
- Click the name and change it to TCON. For the DEFAULT, type the name of your first database connection, which by the server default would be CON01.
- The names of the two variables you created are
shown.
- Click the
segment name DMORTMPLX. For TABLENAME, type
the value &&TTABLE and for CONNECTION,
type the value &&TCON.
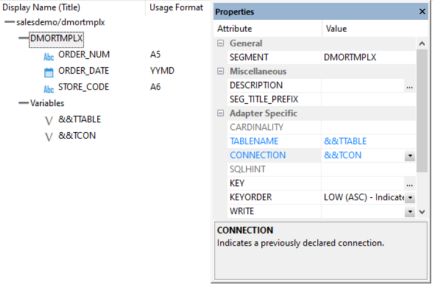
The synonym is now set up for use with multiple tables.
- Click Save from the Quick Access Toolbar to save the synonym.
View Parameter Table
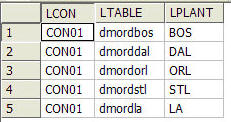
This example has instructions for viewing the parameter table used in the other examples here. The parameter table used is a delimited file, but any data source that can be described by a synonym could be used. The table has three columns: a connection name, a table name, and a plant name.
The parameter table is automatically created when you run Create Sample Procedures and Data for the iterator examples. The connection name is the name of the first connection on your server for the selected database. In this example, they are all the same, but different connection names could also be used.
- In the ibi Data Migrator desktop interface, expand the ibisamp directory in the navigation pane.
- Right-click the synonym dmplnts and
click Sample Data.
Tip: If you do not see synonyms when you expand the ibisamp directory, select Synonyms from the Filter group on the Home tab.
The Sample Data Report opens and should look like the following image.
Create a Data Flow Using a Parameterized Synonym
This example has instructions for creating a data flow that uses a synonym as a source that can be used to read multiple identically formatted tables.
Refer to the sample flow dmorsum, for the complete example.
- In the ibi Data Migrator desktop interface,
right-click an application directory in the navigation pane, select New,
and then click Flow.
A new flow opens.
- Drag a data source object into the data flow. If you created the synonym, dmortmplx, you can use it. Otherwise, from the ibisamp application directory, drag the synonym dmortmpl.
- Right-click
the SQL object and click Column Selection.
The Column Selection window opens.
- Select each
column in the Available Columns list, and click the arrow to move
them into the Selected Columns list. Click OK.
Tip: To select all the columns, right-click one of them and click Select All.
- Drag the target object dmorsum from the ibisamp directory into the workspace, to the right of the SQL object.
- Right-click
the dmorsum target object and click Target
Transformations.
The Transformations window opens.
- Click the Automap button.
- Under target columns, double-click PLANT to add it to the list of expressions below.
- For the PLANT expression, enter '&LPLANT' with quotes as shown. Click OK to close the expression editor and OK to close the Transformations window.
- Click the Process Flow tab.
- Right-click the arrow between Start and Data flow and click Delete.
- On the Flow tab, in the Insert group, click Set Variables and drag it onto the workflow between the Start and Data Flow icons. Then, right-click the Start icon and drag it to Set Variables and release it. Finally, right-click Set Variables and drag the arrow to Data Flow and release.
- Right-click Set
Variables and click Properties.
In the Value area for List, click the ellipsis button.
The Global Parameter Editor window opens.
- Click the Add
Parameter button.
The Global Variables calculator opens.
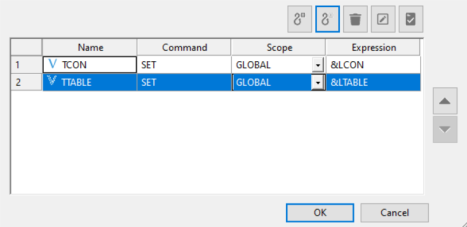
- Type over the default name VAR1 with TCON. In the expression entry area, type &LCON and then click OK.
- Repeat to
set the global variable, TTABLE, to value <ABLE.
When you are done, the Global Parameter Editor window should look
like the following image.
- Click OK.
- Click Save from the Quick Access Toolbar to save the flow. Type dmorsumx as the flow name.
Create a Process Flow to Use Parameterized Data Flow
This example has instructions for creating a process flow that runs a data flow repeatedly, using as a source, a collection of identically formatted tables.
Refer to the sample flow dmorsump for the complete example.
- In the ibi Data Migrator desktop interface,
right-click an application directory in the navigation pane, select New,
and then click Flow.
A new flow opens.
- Click the Process Flow tab.
- From the directory where you saved dmorsumx, drag the flow into the workflow area.
- Right-click the Start icon, drag the arrow to dmorsumx and release.
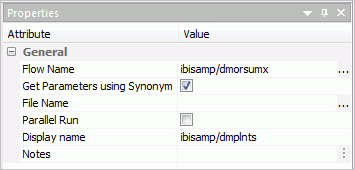
- Right-click dmorsumx and click Properties.
- Check the checkbox labeled Get Parameters using Synonym.
- Click the
ellipsis button
in the File Name entry area. In the ibisamp directory, select dmplnts.
The properties for the flow should look like the following image.
- Click Save on the Quick Access Toolbar to save the flow. Type dmorsumpx as the flow name.
- To create the target table, in the ibisamp directory located in the navigation pane, right-click the table named dmorsum, select Data Management, and then click Recreate DBMS table.
- On the Flow
tab, in the Run group, click Run and select Submit.
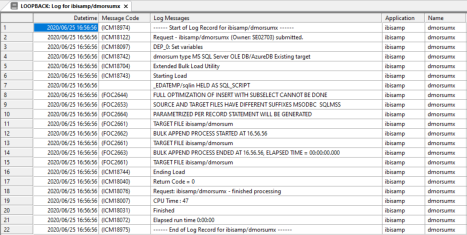
When the flow completes, you should see a message in the console log:
DM: (ICM18763) Request ibisamp/dmorsumpx complete
View Logs for a Parameterized Data Flow
When a process flow calls a data flow using the iterator, multiple logs are generated. This example shows how to view the logs.
- With the
dmorsumpx process flow open, on the Flow tab, in the Reports group, click View
Last Log.
The process flow log opens.
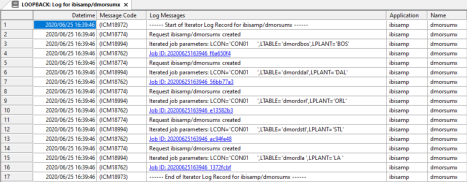
- Click the
blue line with the Job ID.
The iterator log opens. Note that the Parameters line show the values of each parameter for each run.
- Click one
of the blue lines with Job IDs. The log for an individual run of
the data flow opens.