Managing Essbase Metadata
When the server accesses a data source, it needs information on how to interpret the data stored there. For each data source the server will access, you create a synonym that describes the structure of the data source and the server mapping of the Essbase data type.
Creating Synonyms
Synonyms define unique names for each Essbase application.database combination that is accessible from a server. Synonyms are useful because they hide location information and the identity of the underlying data source from client applications. They also provide support for extended metadata features of the server such as virtual fields and additional security mechanisms.
Using synonyms allows an object to be moved or renamed while allowing client applications to continue functioning without modification. The only modification required is a redefinition of the synonym on the server. The result of creating a synonym is a Master File and Access File.
Create a Synonym
- Procedure
- From the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface Application page, click Get Data.
- On the
Configured Adapters section of the page, in Simple Mode, right-click an adapter
and click
Show
Connections. Right-click a connection.
Depending on the type of adapter you choose, one of the following options appears on the context menu.
- Show DBMS objects. This option opens the page for selecting synonym objects and properties.
- Create metadata objects. This option opens the page for selecting synonym objects and properties.
- Show files. This option opens a file picker. After you choose a file of the correct type, the page for selecting synonym objects and properties opens.
- Show local files. This option opens a file picker. After you choose a file of the correct type, the page for selecting synonym objects and properties opens.
- Show topics. This option opens the page for selecting synonym objects and properties for topics within the environment.
- Enter values for the parameters required by the adapter as described in the chapter for your adapter.
- After
entering the parameter values, click
Add.
This button may be labeled Next, Create Synonym, Create Base Synonyms, Create Cluster Synonym, or Update Base Synonyms.
The synonym creation process for most adapters has been consolidated so that you can enter all necessary parameters on one page. However, for some adapters such as LDAP, continue clicking Next until you get to a page that has a Create Synonym button.
The synonym is created and added under the specified application directory.
Synonym Creation Parameters for Essbase
The following list describes the parameters for which you need to supply values, and related tasks you need to complete in order to create a synonym for the adapter. These options may appear on multiple panes. To advance from pane to pane, click the buttons provided, ending with the Create Synonym button, which generates the synonym based on your entries.
Select one or more databases from the list.
Select the Make alias fields checkbox if you wish to create fields that expose the values in your alias table. The alias table can provide meaningful field values or field values in a specific language.
This option enables you to control summing on non-aggregated fields in an Essbase request.
- Choose On to enable summing on non-aggregated fields.
- Choose Off to disable summing on non-aggregated fields. For additional information and syntax, see Preventing Aggregation of Non-Consolidating Members.
This option enables you to limit the number of fields in the Master File.
- Select none to create a single data value representing the cube measures.
- Select a dimension to create a separate numeric measure field
for each member in that dimension.
Note: If you select a dimension, you can select an additional dimension for grouping the measures.
If you selected a dimension to expose the measures, you can optionally select an additional dimension for grouping those measures.
If you selected a Measure Group, you can now select specific members for which to create groups.
- Click the Select Measure Group members checkbox.
- Click Next.
A list of Scenario members displays.
- Check the members that you want to create as groups. Check the Scenario Name checkbox to create groups for all members.
Synonym field name processing options:
Select the Validate checkbox if you wish to convert all special characters to underscores and perform a name check to prevent the use of reserved names. (This is accomplished by adding numbers to the names.) This parameter ensures that names adhere to specifications. See Validation for Special Characters and Reserved Words for more information.
When the Validate option is unchecked, only the following characters are converted to underscores: '-'; ' '; ' \'; '/'; ','; '$'. No checking is performed for names.
Select the Make unique checkbox if you wish to set the scope for field and group names to the entire synonym. This ensures that no duplicate names are used, even in different segments of the synonym. When this option is unchecked, the scope is the segment.
To change the default name, type the name of the synonym.
Select an application directory. The default value is baseapp.
If you have tables with identical table names, assign a prefix or a suffix to distinguish them. For example, if you have identically named human resources and payroll tables, assign the prefix HR to distinguish the synonyms for the human resources tables. Note that the resulting synonym name cannot exceed 64 characters.
If all tables and views have unique names, leave the prefix and suffix fields blank.
To specify that this synonym should overwrite any earlier synonym with the same fully qualified name, select the Overwrite existing synonyms checkbox.
Creating a Synonym
To generate a synonym for the application Sample and database Basic, enter the following information on the Create Synonym panes of the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface or ibi Data Migrator desktop interface:
- From the displayed list, select the row that contains the Application Name Sample and the Data Base Name Basic, then click the Next button.
- Accept the default for Measure.
- Click Create Synonym. The synonym is
created and added under the specified application directory (baseapp
is the default).
A status window displays a message indicating that the synonym was created successfully.
- Open the baseapp application folder in the navigation pane and click the synonym Basic.
- Choose Edit as Text from the menu to view the generated Master File, then choose Edit Access File as Text to view the corresponding Access File.
Generated Master File
FILENAME=SAMPLE, SUFFIX=ESSBASE, $
SEGMENT=BASIC, SEGTYPE=S0, $
$ DIMENSION: Year
DIMENSION=Year, CAPTION='Year', $
HIERARCHY=Year, CAPTION='Year Levels', HRY_DIMENSION=Year,
HRY_STRUCTURE=STANDARD, $
FIELDNAME=YEAR, ALIAS=History, USAGE=A4, ACTUAL=A4,
WITHIN='*Year', PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=QUARTER, ALIAS=Quarter, USAGE=A8, ACTUAL=A8,
WITHIN=YEAR, PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=MONTH, ALIAS=Month, USAGE=A9, ACTUAL=A9,
WITHIN=QUARTER, PROPERTY=UID, $ HIERARCHY=Year2, CAPTION='Year Parent-Child', HRY_DIMENSION=Year,
HRY_STRUCTURE=RECURSIVE, $
FIELDNAME=YEAR_MEMBER, ALIAS=Year, USAGE=A4, ACTUAL=A4,
WITHIN='*Year2', PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=YEAR_CAPTION, USAGE=A9, ACTUAL=A9,
REFERENCE=YEAR_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAPTION, $
FIELDNAME=YEAR_PARENT, USAGE=A4, ACTUAL=A4,
REFERENCE=YEAR_MEMBER, PROPERTY=PARENT_OF, $
FIELDNAME=YEAR_PARENTCAP, USAGE=A9, ACTUAL=A9,
REFERENCE=YEAR_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAP_PARENT, $
FIELDNAME=YEAR_LVLNO, USAGE=I2L, ACTUAL=I4,
MISSING=ON, ACCESS_PROPERTY=(INTERNAL),
TITLE='Year_LVLNO LEVEL_NUMBER',
REFERENCE=YEAR_MEMBER, PROPERTY=LEVEL_NUMBER, $
FIELDNAME=H_T_D, ALIAS='H-T-D', USAGE=A16, ACTUAL=A16,
REFERENCE=YEAR, PROPERTY=TIMESERIES, $
FIELDNAME=Q_T_D, ALIAS='Q-T-D', USAGE=A16, ACTUAL=A16,
REFERENCE=QUARTER, PROPERTY=TIMESERIES, $
FIELDNAME=M_T_D, ALIAS='M-T-D', USAGE=A16, ACTUAL=A16,
REFERENCE=MONTH, PROPERTY=TIMESERIES, $$ DIMENSION: Measures
DIMENSION=Measures, CAPTION='Measures', $
HIERARCHY=Measures, CAPTION='Measures Levels', HRY_DIMENSION=Measures,
HRY_STRUCTURE=STANDARD, $
FIELDNAME=MEASURES, ALIAS='Gen1,Measures', USAGE=A8, ACTUAL=A8,
WITHIN='*Measures', PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=GEN2_MEASURES, ALIAS='Gen2,Measures', USAGE=A9, ACTUAL=A9,
WITHIN=MEASURES, PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=GEN3_MEASURES, ALIAS='Gen3,Measures', USAGE=A17,
ACTUAL=A17, WITHIN=GEN2_MEASURES, PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=GEN4_MEASURES, ALIAS='Gen4,Measures', USAGE=A18,
ACTUAL=A18, WITHIN=GEN3_MEASURES, PROPERTY=UID, $ HIERARCHY=Measures2, CAPTION='Measures Parent-Child',
HRY_DIMENSION=Measures, HRY_STRUCTURE=RECURSIVE, $
FIELDNAME=MEASURES_MEMBER, ALIAS=Measures, USAGE=A17, ACTUAL=A17,
WITHIN='*Measures2', PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=MEASURES_CAPTION, USAGE=A18, ACTUAL=A18,
REFERENCE=MEASURES_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAPTION, $
FIELDNAME=MEASURES_PARENT, USAGE=A17, ACTUAL=A17,
REFERENCE=MEASURES_MEMBER, PROPERTY=PARENT_OF, $
FIELDNAME=MEASURES_PARENTCAP, USAGE=A18, ACTUAL=A18,
REFERENCE=MEASURES_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAP_PARENT, $
FIELDNAME=MEASURES_LVLNO, USAGE=I2L, ACTUAL=I4,MISSING=ON,
ACCESS_PROPERTY=(INTERNAL),TITLE='Measures_LVLNO LEVEL_NUMBER',
REFERENCE=MEASURES_MEMBER, PROPERTY=LEVEL_NUMBER, $$ DIMENSION: Product
DIMENSION=Product, CAPTION='Product', $
HIERARCHY=Product, CAPTION='Product Levels', HRY_DIMENSION=Product,
HRY_STRUCTURE=STANDARD, $
FIELDNAME=PRODUCT, ALIAS='Lev2,Product', USAGE=A7, ACTUAL=A7,
WITHIN='*Product',PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=FAMILY, ALIAS=Family, USAGE=A11, ACTUAL=A11,
WITHIN=PRODUCT,PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=SKU, ALIAS=SKU, USAGE=A18, ACTUAL=A18,
WITHIN=FAMILY,PROPERTY=UID, $ HIERARCHY=Product2, CAPTION='Product Parent-Child',
HRY_DIMENSION=Product, HRY_STRUCTURE=RECURSIVE, $
FIELDNAME=PRODUCT_MEMBER, ALIAS=Product, USAGE=A7, ACTUAL=A7,
WITHIN='*Product2',PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=PRODUCT_CAPTION, USAGE=A18, ACTUAL=A18,
REFERENCE=PRODUCT_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAPTION, $
FIELDNAME=PRODUCT_PARENT, USAGE=A7, ACTUAL=A7,
REFERENCE=PRODUCT_MEMBER, PROPERTY=PARENT_OF, $
FIELDNAME=PRODUCT_PARENTCAP, USAGE=A18, ACTUAL=A18,
REFERENCE=PRODUCT_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAP_PARENT, $
FIELDNAME=PRODUCT_LVLNO, USAGE=I2L, ACTUAL=I4,
MISSING=ON, ACCESS_PROPERTY=(INTERNAL),
TITLE='Product_LVLNO LEVEL_NUMBER',
REFERENCE=PRODUCT_MEMBER, PROPERTY=LEVEL_NUMBER, $$ DIMENSION: Market
DIMENSION=Market, CAPTION='Market', $
HIERARCHY=Market, CAPTION='Market Levels', HRY_DIMENSION=Market,
HRY_STRUCTURE=STANDARD, $
FIELDNAME=MARKET, ALIAS='Gen1,Market', USAGE=A6, ACTUAL=A6,
WITHIN='*Market', PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=REGION, ALIAS=Region, USAGE=A7, ACTUAL=A7,
WITHIN=MARKET, PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=STATE, ALIAS=State, USAGE=A13, ACTUAL=A13,
WITHIN=REGION, PROPERTY=UID, $ HIERARCHY=Market2, CAPTION='Market Parent-Child', HRY_DIMENSION=Market,
HRY_STRUCTURE=RECURSIVE, $
FIELDNAME=MARKET_MEMBER, ALIAS=Market, USAGE=A13, ACTUAL=A13,
WITHIN='*Market2', PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=MARKET_CAPTION, USAGE=A13, ACTUAL=A13,
REFERENCE=MARKET_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAPTION, $
FIELDNAME=MARKET_PARENT, USAGE=A13, ACTUAL=A13,
REFERENCE=MARKET_MEMBER, PROPERTY=PARENT_OF, $
FIELDNAME=MARKET_PARENTCAP, USAGE=A13, ACTUAL=A13,
REFERENCE=MARKET_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAP_PARENT, $
FIELDNAME=MARKET_LVLNO, USAGE=I2L, ACTUAL=I4, MISSING=ON,
ACCESS_PROPERTY=(INTERNAL), TITLE='Market_LVLNO LEVEL_NUMBER',
REFERENCE=MARKET_MEMBER, PROPERTY=LEVEL_NUMBER, $$ DIMENSION: Scenario
DIMENSION=Scenario, CAPTION='Scenario', $
HIERARCHY=Scenario, CAPTION='Scenario Levels', HRY_DIMENSION=Scenario,
HRY_STRUCTURE=STANDARD, $
FIELDNAME=SCENARIO, ALIAS='Gen1,Scenario', USAGE=A8, ACTUAL=A8,
WITHIN='*Scenario', PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=GEN2_SCENARIO, ALIAS='Gen2,Scenario', USAGE=A10,
ACTUAL=A10, WITHIN=SCENARIO, PROPERTY=UID, $ HIERARCHY=Scenario2, CAPTION='Scenario Parent-Child',
HRY_DIMENSION=Scenario, HRY_STRUCTURE=RECURSIVE, $
FIELDNAME=SCENARIO_MEMBER, ALIAS=Scenario, USAGE=A10, ACTUAL=A10,
WITHIN='*Scenario2', PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=SCENARIO_CAPTION, USAGE=A10, ACTUAL=A10,
REFERENCE=SCENARIO_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAPTION, $
FIELDNAME=SCENARIO_PARENT, USAGE=A10, ACTUAL=A10,
REFERENCE=SCENARIO_MEMBER, PROPERTY=PARENT_OF, $
FIELDNAME=SCENARIO_PARENTCAP, USAGE=A10, ACTUAL=A10,
REFERENCE=SCENARIO_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAP_PARENT, $
FIELDNAME=SCENARIO_LVLNO, USAGE=I2L, ACTUAL=I4,
MISSING=ON, ACCESS_PROPERTY=(INTERNAL),
TITLE='Scenario_LVLNO LEVEL_NUMBER',
REFERENCE=SCENARIO_MEMBER, PROPERTY=LEVEL_NUMBER, $$ DIMENSION: DATA
SEGMENT=DATA, SEGTYPE=U, PARENT=BASIC, $
FIELDNAME=DATA_VALUE, ALIAS=DATA_VALUE, USAGE=D20.2, ACTUAL=D8,
MISSING=ON, TITLE='DATA_VALUE', $$ DIMENSION: ATTR
SEGMENT=ATTR, SEGTYPE=U, PARENT=BASIC, $
FIELDNAME=CAFFEINATED, ALIAS=Caffeinated, USAGE=A17, ACTUAL=A17,
REFERENCE=SKU, PROPERTY=UDA, $
FIELDNAME=OUNCES, ALIAS=Ounces, USAGE=A9, ACTUAL=A9,
REFERENCE=SKU, PROPERTY=UDA, $
FIELDNAME=PKG_TYPE, ALIAS='Pkg Type', USAGE=A8, ACTUAL=A8,
REFERENCE=SKU, PROPERTY=UDA, $
FIELDNAME=POPULATION, ALIAS=Population, USAGE=A15, ACTUAL=A15,
REFERENCE=STATE, PROPERTY=UDA, $
FIELDNAME=INTRO_DATE, ALIAS='Intro Date', USAGE=A21, ACTUAL=A21,
REFERENCE=SKU, PROPERTY=UDA, $$ DIMENSION: UDA
SEGMENT=UDA, SEGTYPE=U, PARENT=BASIC, $
FIELDNAME=MARKET_UDA, ALIAS=Market, USAGE=A13, ACTUAL=A13,
REFERENCE=**Market, PROPERTY=UDA, $
Generated Access File
SEGNAME=BASIC, SERVER=EDASOL28, DBNAME=Basic, APPLNAME=Sample, $
TIMEDIM=YEAR, $
SHARE=300-30, PARENT=Diet, DIM=Product, $
SHARE=200-20, PARENT=Diet, DIM=Product, $
SHARE=100-20, PARENT=Diet, DIM=Product, $
Managing Synonyms
Once you have created a synonym, you can right-click the synonym name in the navigation pane of either the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface or the Data Management Console to access the available options.
For a list of options, see Synonym Management Options.
Using Default Field Names
The default field names that are used are taken from the generation names, if available, in the outline. Otherwise, they take the format:
FIELDNAME=generationnumber_dimensionname
where:
Is the generation number within the dimension (for example, GEN2).
Is the name of the dimension.
For example, if the outline has a SCENARIO dimension, the first field name would be FIELDNAME=Scenario to represent the highest generation, the second field name would be FIELDNAME=GEN2_SCENARIO, and so on down the dimension hierarchy. For an illustration, see Creating Synonyms.
Access File Keywords
|
Keyword |
Description |
|---|---|
SERVER |
Essbase Server name. |
DBNAME=database_name
|
Indicates access to the specified database within an application. |
APPLNAME=application_name
|
Indicates access to the specified application, which can contain one or more databases. |
Parent/Child Support
The parent/child view in the Master File enables you to make requests using a member without having to know the generation to which the member belongs. The fields that provide this functionality are:
Is the declaration for the field that contains the dimension members. It represents members of the product at all levels of the dimension.
Is the declaration for the field that contains the label displayed on reports for DIMENSION_MEMBER (this is the Essbase alias).
Is the declaration for the field that contains the parent of DIMENSION_MEMBER.
Is the declaration for the field that contains the label displayed on reports for DIMENSION_PARENT (this is the Essbase alias).
The following is a sample of the parent/child view in the Master File:
FIELDNAME=SCENARIO_MEMBER, ALIAS=Scenario, USAGE=A10, ACTUAL=A10,
WITHIN='*Scenario2',
PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=SCENARIO_CAPTION, USAGE=A10, ACTUAL=A10,
REFERENCE=SCENARIO_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAPTION, $
FIELDNAME=SCENARIO_PARENT, USAGE=A10, ACTUAL=A10,
REFERENCE=SCENARIO_MEMBER, PROPERTY=PARENT_OF, $
FIELDNAME=SCENARIO_PARENTCAP, USAGE=A10, ACTUAL=A10,
REFERENCE=SCENARIO_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAP_PARENT, $
Using the Parent/Child View in the Master File
In the first request, Actual is explicitly identified with the generation GEN2_SCENARIO:
TABLE FILE BASIC PRINT DATA_VALUE WHERE GEN2_SCENARIO EQ 'Actual' END
In the second request, which takes advantage of a parent/child view, Actual is represented as a member of the Scenario dimension. It is not necessary to know which generation it falls under.
TABLE FILE BASIC PRINT DATA_VALUE WHERE SCENARIO_MEMBER EQ 'Actual' END
Both requests yield the same output:
DATA_VALUE = 105,522.00
Support for User-Defined Attributes
A User-Defined Attribute (UDA) in Essbase enables you to select and report on data based on a common characteristic. You can include UDAs in report requests. For each dimension with UDAs in an Essbase outline, synonym creation generates a UDA field name under a segment called UDA in the Master File.
Reporting From a UDA Segment
The Sample Master File contains the following UDA segment:
$ DIMENSION: UDA
SEGMENT=UDA, SEGTYPE=U, PARENT=BASIC, $
FIELDNAME=MARKET_UDA, ALIAS=Market, USAGE=A13, ACTUAL=A13,
REFERENCE=**Market, PROPERTY=UDA, $
When referencing UDAs in a request, you must also reference a member of the dimension that contains the UDA. In this example, STATE is a member of the MARKET Dimension in the Master File.
TABLE FILE BASIC PRINT DATA_VALUE BY STATE WHERE MARKET_UDA EQ 'New Market' END
The output displays the values only for the states that have the UDA 'New Market' as a common characteristic:
STATE DATA_VALUE --------- ---------- Colorado 7,227.00 Louisiana 2,992.00 Nevada 4,039.00
Describing Attribute Dimensions in the Master File
An attribute dimension is identified by the word Attribute, which appears next to the Dimension name in the Essbase outline. Attribute dimensions are usually associated with standard Essbase dimensions. For example, in the following outline, Population is an Attribute dimension associated with the standard dimension Market.
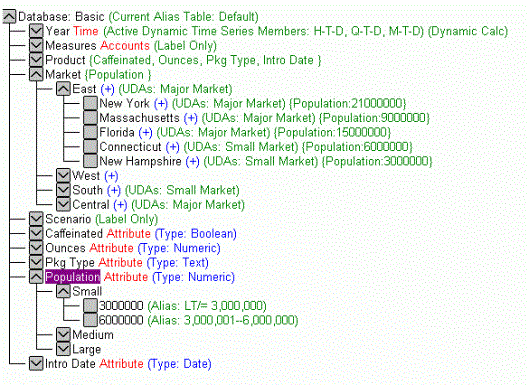
The standard dimension serves as the base dimension for the associated attribute dimensions.
Generating Attribute Dimensions
Synonym creation generates a Master File that contains an ATTR (attribute) segment, which defines attribute tagged dimensions.
The following is a portion of the Master File BASIC. Notice that Market is the base dimension with which the attribute dimension Population is associated.
FILENAME=SAMPLE, SUFFIX=ESSBASE ,$
SEGMENT=BASIC, SEGTYPE=S0, $
>.
>.
>.
$ DIMENSION: Market
DIMENSION=Market,CAPTION=Market, $
HIERARCHY=Market,CAPTION=Market Levels,
HRY_DIMENSION=Market,HRY_STRUCTURE=S, $
FIELDNAME=MARKET, ALIAS='Gen1,Market', USAGE=A6, ACTUAL=A6,
WITHIN='*Market', PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=REGION, ALIAS=Region, USAGE=A7, ACTUAL=A7,
WITHIN=MARKET,PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=STATE, ALIAS=State, USAGE=A13, ACTUAL=A13,
WITHIN=REGION,PROPERTY=UID, $
HIERARCHY=Market2,CAPTION=Market Parent-Child,
HRY_DIMENSION=Market,HRY_STRUCTURE=R, $
FIELDNAME=MARKET_MEMBER, ALIAS=Market, USAGE=A13, ACTUAL=A13,
WITHIN='*Market2', PROPERTY=UID, $
FIELDNAME=MARKET_CAPTION, USAGE=A13, ACTUAL=A13,
REFERENCE=MARKET_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAPTION, $
FIELDNAME=MARKET_PARENT, USAGE=A13, ACTUAL=A13,
REFERENCE=MARKET_MEMBER, PROPERTY=PARENT_OF, $
FIELDNAME=MARKET_PARENTCAP, USAGE=A13, ACTUAL=A13,
REFERENCE=MARKET_MEMBER, PROPERTY=CAP_PARENT, $
.
.
.
DIMENSION: ATTR
SEGMENT=ATTR, SEGTYPE=U, PARENT=BASIC, $
FIELDNAME=CAFFEINATED, ALIAS=Product, USAGE=A17, ACTUAL=A17,
REFERENCE=SKU, PROPERTY=UDA, $
FIELDNAME=OUNCES, ALIAS=Product, USAGE=A9, ACTUAL=A9,
REFERENCE=SKU, PROPERTY=UDA, $
FIELDNAME=PKG_TYPE, ALIAS=Product, USAGE=A8, ACTUAL=A8,
REFERENCE=SKU, PROPERTY=UDA, $
FIELDNAME=POPULATION, ALIAS=Market, USAGE=A15, ACTUAL=A15,
REFERENCE=STATE, PROPERTY=UDA, $
FIELDNAME=INTRO_DATE, ALIAS=Product, USAGE=A21, ACTUAL=A21,
REFERENCE=SKU, PROPERTY=UDA, $
The corresponding Access File contains any two-pass calculated members, as well as members with the following consolidation properties: (-0, (/), (*), (%). In addition, it contains the names of any shared dimension members. For an illustration, see Reporting Against Attribute Tagged Dimensions.
SEGNAME=BASIC, SERVER=edasol29, DBNAME=Basic, APPLNAME=Sample, $ TIMEDIM=Year, $ MEASURE=Measures, $ MEMBER=COGS, AGGREGATE=NO, $ MEMBER=TOTAL_EXPENSES, AGGREGATE=NO, $ MEMBER=PROFIT_%, AGGREGATE=NO, $ MEMBER=PROFIT_PER_OUNCE, AGGREGATE=NO, $ SHARE=300-30, PARENT=Diet, DIM=Product, $ SHARE=200-20, PARENT=Diet, DIM=Product, $ SHARE=100-20, PARENT=Diet, DIM=Product, $
Reporting Against Attribute Tagged Dimensions
This example uses data defined in the sample Master and Access Files in Generating Attribute Dimensions.
Note that using an Attribute Dimension as a BY field in a request is only supported with the MDX adapter (ENGINE ESSBASE SET MDX ON).
The following request references the Population attribute dimension in the ATTR segment of the Master File. The request also references a member of the Population attribute dimension, 3000000. Market is the base dimension for the Population attribute dimension.
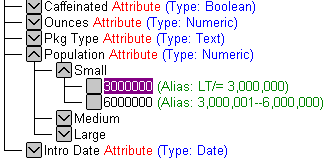
The BY phrase in the request references STATE, which falls within the 3rd Generation (GEN=3) of the Market dimension. This reference is consistent with the following image in the Essbase outline.

The outline names the Base dimension (Market) and identifies the generation (GEN3) that you must reference within that Base dimension when you create an Essbase request using the specified member (3000000) of the Population attribute dimension.
TABLE FILE BASIC PRINT DATA_VALUE BY STATE WHERE POPULATION EQ '3000000' END
The output is:
STATE DATA_VALUE ------------- ---------- Iowa 9,061.00 Nevada 4,039.00 New Hampshire 1,125.00 New Mexico 330.00 Utah 3,155.00
The next request generates a message because the generation of the referenced field, REGION, falls within the 2nd generation of the base dimension, Market, as shown in the previous outline.
TABLE FILE BASIC PRINT DATA_VALUE BY REGION WHERE POPULATION EQ '3000000' END
As a result, the request displays the following message:
(FOC43271) Small_3000000 is not an associated attribute of any requested column
Describing Measure Groups in the Master File
Measure groups in Essbase can be represented in two ways to the server: as normal dimensions or as pseudo accounts dimensions. If they are to be described as normal dimensions, the synonym creation process generates field descriptions for the dimension. If you wish to describe them as pseudo accounts to generate the measure group in place of the accounts dimension segment, use the SET SCENARIO command. You must issue the SET SCENARIO command before the synonym is created.
Generate a Measure Group
If you wish to generate the Scenario dimension to be used in place of the accounts dimension segment, issue:
ENGINE ESSBASE SET SCENARIO DIM dimension_name [member_name|ALL] FOR synonym
where:
Is the measure group name.
When used in the SET SCENARIO command, dimension_name is case-sensitive and must match the case in the Essbase outline.
Specifies a member name in the measure group to be used to generate a field for every measure intersection. When used in the SET SCENARIO command, member_name is case-sensitive and must match the case in the Essbase outline.
Indicates that all members of the measure group are used to generate the Master File. ALL is the default value.
Is the Master file name for one application.database combination.
For each Measure group/Accounts member intersection, a field is generated in the Master File. If this multiplicity effect causes the Master File that is generated to be invalid (due to the total length of the fields), synonym creation fails and displays the following message:
Total actual or usage exceeds 32768 To cut down,try SET SCENARIO
If you receive this message, you will need to issue fewer SET SCENARIO commands to limit the scope of the Master File with regard to the number of measure groups used.
Describing the Measures Dimension in the Master File
The SET MEASURE command enables you to set or change the Accounts tagged dimension without having to change the outline in the Essbase Database Server. With this setting, the adapter produces an actual field name for every member of the named dimension in the Master File rather than producing the dimension in terms of generations. You must issue the SET MEASURE command before the synonym is created.
Set or Change the Measures Dimension in the Master File
To set the Accounts tag for a dimension, issue:
ENGINE ESSBASE SET MEASURE dimension_name FOR synonym
where:
Is the name of the dimension to be interpreted as an Accounts tagged dimension when generating a synonym.
Generates a Master File in which the Accounts Tagged dimension is represented as generations.
Is the Master file name for one application.database combination.
Using the SET MEASURE Command
The following command displays the actual member names of the measure group (for ACTUAL, BUDGET, or VARIANCE), rather than displaying fields like SCENARIO or GEN2_SCENARIO, in the Master file.
ENGINE ESSBASE SET MEASURE Scenario FOR SAMPLE
Limiting the Number of Fields in a Master File
SET MEASURE can be set to NONE. With this setting, all of the dimensions are interpreted as non-Accounts dimensions in the Master File and represented as generations.
In addition, a segment called DATA is added to the Master File. This segment contains a field called DATA_VALUE, which enables you to display the values of the Measures dimension although the actual member names are not present in the Master File.
Limit the Number of Fields in a Master File
ENGINE ESSBASE SET MEASURE NONE FOR SAMPLE
where:
Generates a Master File in which the Accounts tagged dimension is represented as generations.
Reporting Against a Master File With a Limited Number of Fields
If SET MEASURE has been set to NONE, you can display the values of the Measures dimension although the actual member names are not present in the Master File. The following is a sample DATA segment, which includes the field DATA_VALUE, against which you can report.
$ DIMENSION: DATA
SEGMENT=DATA, SEGTYPE=U, PARENT=BASIC, $
FIELDNAME=DATA_VALUE, ALIAS=DATA_VALUE, USAGE=D20.2, ACTUAL=D8,
MISSING=ON, TITLE='DATA_VALUE', $
TABLE FILE BASIC
PRINT DATA_VALUE
BY PRODUCT
END
The output is:
PRODUCT DATA_VALUE $ ------------- ------------------- Product 105,522.00
Changing the Default Usage Format of the Accounts Dimension
All dimension descriptions in the Master File, except for the accounts dimension, have the USAGE format of alphanumeric. The default format of the accounts dimension is D20.2. You can change this default using the SET CONVERSION command.
Change the Default Usage Format of the Accounts Dimension
ESSBASE SET CONVERSION format PRECISION n m
where:
Possible values are:
FLOAT which
indicates that the command applies only to double precision floating
point columns.
DECIMAL which
indicates that the command applies only to decimal columns.
Is the precision. It must be a valid number representing the maximum value for precision for the data type.
Is a valid number representing the maximum value for scale for the data type.
If you do not specify a value for scale, the current scale setting remains in effect. If the scale is not required, you must set m to 0 (zero).