Configuring the Adapter for Hadoop/Hive
Configuring the adapter consists of specifying connection and authentication information for each of the connections that you want to establish. The adapter supports Hiveserver2, which is available in Hive 0.11.0 and later. It is strongly recommended for improved throughput, functionality, and security.
Configure the Hadoop/Hive Adapter
You can configure the adapter from either the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface or the ibi Data Migrator desktop interface.
- Procedure
- From the
WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface Applications page,
click
Get
Data.
or
From the ibi Data Migrator desktop interface, expand the Adapters folder.
In the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface, the Get Data page opens showing your configured adapters. In the ibi Data Migrator desktop interface, the Adapters folder opens.
- In the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface, click the (+) button, and find the adapter on the page.
- In the ibi Data Migrator desktop interface, expand the appropriate group folder and the specific adapter folder. The group folder is described in the connection attributes reference.
- Right-click Apache Hive and click Configure.
- In the URL box, type the URL used to connect to your Hive server. For more information, see Hive Adapter Configuration Settings.
- In the Driver Name box, type the driver name from the following table:
Driver
JDBC Driver Name
Apache Hive
org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver
Cloudera/Simba
com.cloudera.hive.jdbc41.HS2Driver
- Select the security type. If you are using Explicit,
type your user ID and password.
The following image shows an example of the configuration settings used:
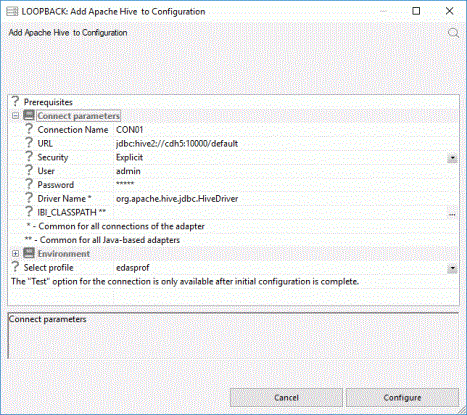
- Select edasprof from the Select profile dropdown menu to add this connection for all users, or select a user profile.
- Click Test. You should see a list of data sources on your server.
- Click Configure.
Hive Adapter Configuration Settings
The Adapter for Hadoop/Hive is under the SQL group folder.
Logical name used to identify this particular set of connection attributes. The default is CON01.
Is the URL to the location of the data source.
The URL used depends on what type of server you are connecting to. See the table below for examples. For more details, see the JDBC section in the online documentation for Apache Hive, or the Cloudera JDBC Driver for Apache Hive documentation, which is included with the JDBC driver download.
|
Server |
URL |
|---|---|
|
Hiveserver2 |
jdbc:hive2://server:10000/default |
|
Kerberos Hiveserver2 (static) |
jdbc:hive2://server:10000/default; principal=hive/server@REALM.COM |
|
Kerberos Hiveserver2 |
jdbc:hive2://server:10000/default;principal=hive/ server@REALM.COM; auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject |
|
Cloudera/Simba (no security) |
jdbc:hive2://server:10000;AuthMech=3;transportMode=binary
|
|
Kerberos Cloudera/Simba |
jdbc:hive2://server:10000;AuthMech=1;KrbRealm=REALM.COM; KrbHostFQDN=server.example.com;KrbServiceName=hive |
where:
Is the DNS name or IP address of the system where the Hive server is running. If it is on the same system, localhost can be used.
Is the name of the default database to connect to.
Is the default port number HiveServer2 is listening on if not specified when the Hive server is started.
For a Kerberos enabled Hive server, this is the name of your realm.
Is the name of the JDBC driver, for example, org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver or com.cloudera.hive.jdbc41.HS2Driver.
Defines the additional Java class directories or full-path jar names, which will be available for Java Services. Value may be set by editing the communications file or in the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface. Using the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface, you can enter one reference per line in the input field. When the file is saved, the entries are converted to a single string using colon (:) delimiters for all platforms. When editing the file manually, you must maintain the colon delimiter.
There are three methods by which a user can be authenticated when connecting to a database server:
- Explicit. The user ID and password are explicitly specified for each connection and passed to the database, at connection time, for authentication.
- Password Passthru. The user ID and password received from the client application are passed to the database, at connection time, for authentication.
- Trusted. The user ID is passed from a trusted source.
Primary authorization ID by which you are known to the data source.
Password associated with the primary authorization ID.
Select a profile from the dropdown menu to indicate the level of profile in which to store the CONNECTION_ATTRIBUTES command. The global profile, edasprof.prf, is the default.
If you wish to create a new profile, either a user profile (user.prf) or a group profile if available on your platform (using the appropriate naming convention). Choose New Profile from the dropdown menu and enter a name in the Profile Name field (the extension is added automatically).
Store the connection attributes in the server profile (edasprof).
Configure Multiple Users for Bulk Load Using the SFTP Protocol
When you configure Bulk Load using SFTP, you create an auxiliary connection with its own user ID, for example, user1. If a user connects to the server with a different user ID, for example, user2, and wants to initiate bulk load using that same auxiliary connection, user2 must create a key file specific to user2 and attach that key to the user1 ID.
In the following procedure:
- The server is referred to as dmhost.
- The SFTP server is referred to as sftphost.
- The user connected to the server is referred to as userdm.
- The user configured in the connection to the SFTP server is referred to as usersftp.
Perform the following steps to configure userdm to be able to initiate bulk load using the SFTP auxiliary connection:
- Procedure
- On sftphost, issue the following commands to create the directory for the keys.
/home/usersftp/$ mkdir .ssh /home/usersftp/$ cd .ssh
Issue the following command to create a file named authorized_keys that will contain your authorized keys.
/home/usersftp/$ .ssh $ touch authorized_keys
- On dmhost, issue the following commands to enable usersftp to connect to sftphost from dmhost.
/home/userdm/$ sftp usersftp@sftphost sftp> exit
- On dmhost, optionally verify known_hosts to make sure that sftphost is listed there.
/home/userdm/$ cd .ssh /home/userdm/.ssh $ ls -ltr -a /home/userdm/.ssh $ cat known_hosts /home/userdm/.ssh $ cd
You should see the remote host name listed, in the first position in the file.
- Create keys on dmhost.
/home/userdm/$ ssh-keygen -t rs
- On dmhost, append the public key of userdm to the authorized_keys file on sftphost.
/home/userdm/$ append id_rsa.pub authorized_keys
or
/home/userdm/$ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub | ssh usersftp@sftphost "cat >> /home/usersftp/.ssh/authorized_keys"This will ensure that usersftp can connect to sftphost using the userdm ID.
- Use the following command to connect using SFTP on dmhost password-less to sftphost.
/home/userdm/$ sftp usersftp@sftphost sftp> ls sftp> exit
- Start the server on dmhost. Connect to the server on dmhost:
http://dmhost:8117
When connecting, use the OPSYS security provider and user ID userdm.
- Issue the following command from the server profile, edasprof.prf of dmhost to establish a connection for a fixed format file to sftphost.
ENGINE FIX SET CONNECTION_ATTRIBUTES conTest 'sftp://sftphost'/usersftp,:'mydir1' - Test the connection. The result should be:
User has read access to the FTP server directory User has write access to the FTP server directory. Successful test for the connection conTest.
Kerberos
Connections to a Hive server with Kerberos enabled can be run in several ways:
- Static. The same Kerberos credential is used
for all connections. You must obtain a Kerberos ticket before starting
the server. On expiration of the Kerberos ticket, a new one must be obtained and the server must be restarted. Use Trusted as the security type.
This mode is useful for testing, but is not recommended for production deployment.
- User. Each user connecting to the server connects to Hive using their own credentials from the Hive Adapter connection in the user profile. The server obtains a Kerberos ticket for the user. Use Explicit as the security type.
- Database. Users connect to the server using the Kerberos credentials, which are authenticated against a Hive server with Kerberos enabled. The server obtains a Kerberos ticket for the user. Use Password Passthru as the security type.
- Single Sign-on. Users log into Windows with their Kerberos or Active Directory credentials and Windows obtains a Kerberos ticket. That ticket is used when the user connects to the server and is passed to Hive. Use Trusted as the security type.
To setup connections to a Kerberos enabled Hive instance:
- The WebFOCUS Reporting Server has to be secured. The server can be configured with security providers PTH, LDAP, DBMS, OPSYS, or Custom, as well as multiple security providers environment,
Kerberos Static Ticket Requirements
In this configuration, all connections to Hive instance will be done with the same Kerberos user ID derived from the Kerberos ticket that is created before the server starts.
- Create Kerberos ticket using:
kinit kerbid01where:
kerbid01Is a Kerberos ID.
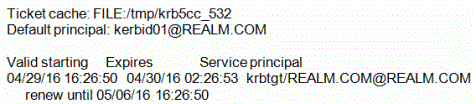
- Verify Kerberos ticket using klist. The following message
should be returned:
- Before configuring the Hive Adapter connection to a Kerberos-enabled instance, the connection should be tested. Log in to the system running Hive and use Beeline, the native tool, to test it.
- Start the server in the same Linux session where the Kerberos ticket was created. Log in to the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface and click the Adapters tab.
- Right-click Apache Hive.
Use the following parameters to configure the adapter:
URLEnter the same URL that you use to connect to the Hive Instance using Beeline. For example:
jdbc:hive2://server:10000/default;principal=hive/server@REALM.COM
SecuritySet to Trusted.
- In the Select profile dropdown menu, select the edasprof server profile.
- Click Configure.
- Next, configure Java services. Click the Workspace tab and expand the Java Services folder.
- Right-click DEFAULT and select Properties.
- Expand the JVM Settings section. In the
JVM options box, add the following:
-Djavax.security.auth.useSubjectCredsOnly=false
- Restart Java services.
Once these steps are completed, the adapter can be used to access a Kerberos-enabled Hive instance.
Kerberos User Ticket Requirements
In this configuration, each connected user has a Hive Adapter connection with Kerberos credentials in the user profile.
- Enable multi-user connection processing for Kerberos by
adding the following line to your profile (edasprof.prf):
ENGINE SQLHIV SET ENABLE_KERBEROS ON
- Kerberos looks for the default realm in /etc/krb5.conf, or on Windows krb5.ini. Make sure that this file contains the information for your Kerberos server, and not the sample file.
If you are running the server on a Windows system, under the Local System account, specify your realm name and Kerberos Key Distribution Center. To do so:
- Expand the Workspace folder.
- Expand the Java Services folder, right-click DEFAULT, and click Properties.
- Expand the JVM settings section and add the following in the JVM Options box:
-Djava.security.krb5.realm=REALM.COM -Djava.security.krb5.kdc=kdc.realm.com
where:
REALM.COMIs the realm name of your organization.
kdc.realm.comIs the Key Distribution Center of your organization.
- Configure the Hive Adapter Connection in the user profile using
the following values:
URL
Is the URL to the location of the data source.
Server
URL
Kerberos Hiveserver2 (User)
jdbc:hive2://server:10000/default;principal=hive/server@REALM.COM; auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject
Kerberos Cloudera/Simba
jdbc:hive2://server:10000;AuthMech=1;KrbRealm=REALM.COM; KrbHostFQDN=server.example.com;KrbServiceName=hive
SecuritySet to Explicit.
User and PasswordEnter your Kerberos user ID and password. The server will use those credentials to create a Kerberos ticket and connect to a Kerberos-enabled Hive instance.
Note: The user ID that you use to connect to the server does not have to be the same as the Kerberos ID you use to connect to a Kerberos-enabled Hive instance.Select ProfileSelect your profile or enter a new profile name consisting of the security provider, an underscore, and the user ID. For example, ldap01_pgmxxx.
- Click Configure.
Kerberos Password Passthru Requirements
This procedure shows you how to create a connection to a Kerberos enabled Hadoop cluster using the Adapter for Apache Hive with security Password Passthru.
- Configure the connection to Hive using
the following values:
URL
Is the URL to the location of the data source.
jdbc:hive2://server1:10000/default;principal=hive/server1@REALM.COM; auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject
where:
server1Is the name of a node on your Hadoop cluster where a Hive2 server is running.
SecuritySet to Password Passthru.
Select ProfileSelect the server profile, edasprof.
Driver NameIs the name of the JDBC driver, for example, org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver.
IBI_CLASSPATHDefines the additional Java class directories or full-path jar names, which will be available for Java Services (if not included in your system CLASSPATH).
/path/to/hive-jdbc-<version>standalone.jar - Click Configure.
You also need to configure Hive as a DBMS Security Provider.
- From the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface, click Access Control.
- Under Security Providers, right-click DBMS and click New.
The DBMS Security Provider Configuration page opens.
- Enter the following values:DBMS Provider
Enter the provider, as desired. For example, hive.
Security DBMSSelect SQLHIV - Apache Hive.
security_connectionThe connection name you specified, for example, server.
- Click Save.
The DBMS Security Provider Configuration page opens.
- Select the line DBMS - hive , where hive is the name you used.
- From the Status dropdown menu, select Primary or Secondary, as desired.
Kerberos Single Sign-On Requirements
The following sections show you how to configure a server for access to Hadoop through Hive with Kerberos enabled Hadoop cluster using the Adapter for Apache Hive with Single Sign-on from the desktop to the browser using Hive.
- Configure the connection to Hive using
the following values:
URL
Is the URL to the location of the data source.
jdbc:hive2://server1:10000/default;principal=hive/server1@IBI.COM; auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject
where:
server1Is the name of a node on your Hadoop cluster where a Hive2 server is running.
SecuritySet to Trusted.
Select ProfileSelect the server profile, edasprof.
Driver NameIs the name of the JDBC driver, for example, org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver.
IBI_CLASSPATHDefines the additional Java Class directories or full-path jar names, which will be available for Java Services (if not included in your system CLASSPATH).
/path/to/hive-jdbc-<version>standalone.jar - You also need to configure the server for inbound Kerberos.
- Click Configure.
Configuring the ibi WebFOCUS Reporting Server for Inbound Kerberos
A server started with security provider OPSYS can be configured for Kerberos connections.
To implement the single sign-on Kerberos security:
- On the Access Control page, right-click the OPSYS provider,
and select Properties from the context menu.
The OPSYS Security Configuration page opens.
- In the krb5_srv_principal * field, enter your server principal used for Kerberos security.
- Click Save.
The edaserve.cfg file is updated with this attribute.
- On the Workspace page, expand the Special Services and Listeners folder, right-click TCP/HTTP, and select Properties of TCP.
- Check SECURITY=KERBEROS.
- Click Save and Restart Listener.
The odin.cfg file is updated with this attribute.
When the server is started, a user can connect to the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface from Internet Explorer without a prompt for user ID and password. The Login Info shows connection type Kerberos. The connection is done using the Kerberos ticket from the browser. The connected user ID is derived from this ticket.
Connection to the server requires that there is a local OPSYS user ID with the same name as the Kerberos user ID on the operating system running the server. This user ID is used for tscom3 process impersonation.
If a user signs off from the Kerberos connection, the user can make explicit connections with the local Unix user ID and password. Connection with another Kerberos user ID as an explicit connection will not work.
Configuring Java Authentication and Authorization Services
Once you configure a server for access to Hadoop through Hive, you must also configure Java to use the HTTP service principal.
- Using the name of the HTTP service principal for your server that you specified when configuring the server for inbound Kerberos, store the credentials for this principal in a keytab. Enter the following line:
$ klist -k /etc/krb5.keytabConfirm the credentials are stored correctly, as follows:
Keytab name: FILE:/etc/krb5.keytab KVNO Principal ---- -------------------------------------- 1 HTTP/server.example.com@REALM.COM - Create a jaas.conf file in the location of your choice, using your preferred text editor, for example, /ibi/srv82/wfs/etc/jaas.conf. The example code also shows sample values for the keyTab and principal parameters.
jconnection { com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required debug=false doNotPrompt=true useKeyTab=true keyTab="/etc/krb5.keytab" storeKey=true isInitiator=false principal="HTTP/server.example.com@REALM.COM";; }; com.sun.security.jgss.accept { com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required debug=false doNotPrompt=true useKeyTab=true keyTab="/etc/krb5.keytab" storeKey=true isInitiator=false principal="HTTP/server.example.com@REALM.COM";; }; - From the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface, click the Workspace folder.
- Expand the Java Services folder, right-click DEFAULT, and click Properties. The Java Services Configuration window opens.
- Expand the JVM section. In the JVM_Options box, enter the location where you saved the jaas.conf file. For example:
-Djava.security.auth.login.config=/ibi/srv82/wfs/etc/jaas.conf - Click Save and Restart Java Services.
Troubleshooting
Here are some of the errors that you may see when attempting to connect to a Hadoop cluster. These error messages will be prefixed by FOC1500.
Java listener may be down
ERROR: ncjInit failed. Java listener may be down - see edaprint.log.
This is a Java specific issue. Confirm that your Java version meets your system requirements for bit size (32 bit vs 64 bit), and that the value for JAVA_HOME is pointing to the correct Java version.
No suitable driver found for jdbc: ...
(-1) [00000] JDBFOC>> makeConnection(): conn is NULLjava.sql.
SQLException: No suitable driver found for jdbc:hive1://server:10000/default
The name of the JDBC driver in the URL is incorrect. For example, in the above URL, the driver is hive1.
ClassNotFoundException
(-1) [00000] JDBFOC>> connectx(): java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver
One of the jar files that comprises the Hive JDBC driver is not found in the CLASSPATH, or the driver name is incorrect. In the above example, the driver name is org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver.
Required field 'client_protocol' is unset!
(-1) [00000] JDBFOC>> makeConnection(): conn is NULLjava.sql. SQLException: Could not establish connection to jdbc:hive2://server:10000/default;principal=hive/server@REALM. COM;auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject: Required field 'client_protocol' is unset! Struct:TOpenSessionReq(client_protocol:null, configuration:{use:database=default})
This is due to a Java version mismatch. The version of Java on the client is newer than the one on the server. To resolve this error, update Java on the system where you are running our server.
Could not open client transport with JDBC Uri:
-1) [00000] JDBFOC>> makeConnection(): conn is NULLjava.sql. SQLException: Could not open client transport with JDBC Uri: jdbc:hive2://server:10000/default;principal=hive/server@REALM. COM;auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject: ...
This is a generic error, and could be due to any kind of error in the URL or configuration. For more details, read the rest of the message.
Unsupported mechanism type PLAIN
(-1) [00000] JDBFOC>> makeConnection(): conn is NULLjava.sql.
SQLException: Could not open client transport with JDBC Uri:
jdbc:hive2://server:10000/default: Peer indicated failure: Unsupported
mechanism type PLAIN
The cluster has Kerberos enabled and a Kerberos principal to authenticate against is not specified. To resolve this error, add the following to the end of the URL using your cluster and REALM name:
;principal=hive/server@REALM.COM
UnknownHostException: server
(-1) [00000] JDBFOC>> makeConnection(): conn is NULLjava.sql. SQLException: Could not open client transport with JDBC Uri: jdbc:hive2://server:10000/default;principal=hive/server@REALM. COM;auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject: java.net. UnknownHostException: name
The server you specified could not be reached. Either the system is down or the name is invalid.
Could not open client transport with JDBC Uri:... Connection refused
(-1) [00000] JDBFOC>> makeConnection(): conn is NULLjava.sql. SQLException: Could not open client transport with JDBC Uri: jdbc:hive2://server:10000/default;principal=hive/server@REALM. COM;auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject: java.net. ConnectException: Connection refused: connect
The hostname could be reached, but there is no Hive Thrift server running at the hostname and port number you specified.
Client not found in Kerberos database
(-1) [00000] JDBFOC>> makeConnection(): javax.security.auth.login. LoginException: Client not found in Kerberos database (6)
The user ID (User Principal Name) specified is not a valid Kerberos user ID.
Pre-authentication information was invalid
-1) [00000] JDBFOC>> makeConnection(): javax.security.auth.login.LoginException: Pre-authentication information was invalid (24)
The user ID (User Principal Name) specified was found, but the password is missing or invalid.
GSS initiate failed
(-1) [00000] JDBFOC>> makeConnection(): conn is NULLjava.sql. SQLException: Could not open client transport with JDBC Uri: jdbc:hive2://server:10000/default;principal=hive/server@domain. COM; GSS initiate failed Caused by: org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransportException:
Kerberos was unable to authenticate against the specified Service Principal Name.
This occurs if you are using static credentials that were obtained by kinit before the server starts, and did not specify the option to allow that. To resolve this issue, from the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface:
- Click Workspace in the side bar.
- Expand the Java Services folder.
- Right-click DEFAULT.
- Click Properties.
- Expand the JVM Settings section.
- Enter the following in the JVM_OPTIONS box:
-Djava.security.auth.useSubjectCredsOnly=false
This also occurs if you are using subject credentials with explicit or password pass through security, but did not specify that you are doing so. Add the following to the end of the URL:
;auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject
Could not create secure connection to ... Failed to open client transport
(0) [ 08S0] Could not create secure connection to jdbc:hive2://server:10000/default;principal=hive/server@REALM. COM;auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject: Failed to open client transportjava.sql.SQLException: Could not create secure connection to jdbc:hive2://server:10000/default;principal=hive/server@REALM. COM;auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject: Failed to open client transport
The client was not able to use Kerberos to connect. You did not enable Kerberos and are using subject credentials. To resolve this issue, add the following to the server profile:
ENGINE SQLHIV SET ENABLE_KERBEROS ON
Cannot locate default realm
(-1) [00000] JDBFOC>> makeConnection(): javax.security.auth.login. LoginException: KrbException: Cannot locate default realm
Kerberos looks for the default realm in /etc/krb5.conf, or on Windows krb5.ini, and it either cannot find or read the file or the default realm is not specified.
For a server running as a service on a Windows machine, you must explicitly specify the realm for the organization and the KDC. Review the file to make sure that the default realm is specified and correct. To resolve this issue, from the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface:
- Click Workspace in the side bar.
- Expand the Java Services folder.
- Right-click DEFAULT.
- Click Properties.
- Expand the JVM Settings section.
- Using the name of your realm and Key Distribution Center (KDC), enter the following in the JVM_OPTIONS box:
-Djava.security.krb5.realm=REALM.COM -Djava.security.krb5.kdc=kdc.domain.com
- Click Save and Restart Java Services.