Functions of an Adapter
The server uses adapters to access data sources. The server can receive two types of requests from the client: SQL or WebFOCUS®.
When the server receives requests from the client, it passes them to the adapter in a standard format. The adapter takes the request, transforms it into the native data manipulation language (DML), and then issues calls to the data source using its API. In this way, the adapter insulates the server from details of the data source. An application can issue SQL statements, issue WebFOCUS® commands, or call stored procedures.
Adapters are available for many data sources. Every adapter is specifically designed for the data source that it accesses, and, as a result, is able to translate between SQL or WebFOCUS and the DML of the data source. Adapters provide solutions to product variations, including product differences in syntax, functionality, schema, data types, catalogs, data representations, message processing, and answer set retrieval.
Read/Write Considerations
If the adapter has read/write capabilities, it inserts the data from an application to the data source.
In order to do so, proper privileges must be granted to the application ID the adapter uses to connect to the data source. For most SQL data sources, the typical set of GRANTs that allow the adapter to write is accumulated in the CONNECT, RESOURCE roles. Always consult vendor documentation for the exact set of privileges.
How an Adapter Works
The adapter manages the communication between the data interface and the data source, passing data management requests to the data source and returning either answer sets or messages to the requestor.
To perform these functions, the adapter:
- Translates the request to the applicable DML.
- Attaches to the targeted data source, using standard attachment calls. The adapter then passes the request to the data source.
- The data source processes the request.
- The results or error conditions are returned to the client application for further processing.
Processing SQL Requests
A server can be configured to behave in different ways upon receipt of SQL requests from a client application. A server handles SQL requests for data in the following ways, as illustrated in the diagram:
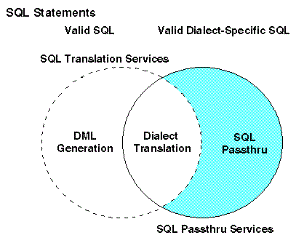
- Direct Passthru. When Direct Passthru is enabled, the server passes SQL requests directly to the specified RDBMS for processing. The name of the targeted RDBMS (the database engine) is supplied in the server profile or, in some cases, by the client application. A Full-Function or Hub Server can operate temporarily in Direct Passthru mode when invoked by a client application. The user is responsible for activating and deactivating Direct Passthru as needed.
- SQL Processing. When the database engine is not set in
the server profile or supplied by a client application, Direct Passthru
is not enabled. Instead, a Hub or Full-Function Server invokes its
default behavior: it accepts the incoming SQL request and verifies
that it is valid. Then the server determines if it can process the
incoming SQL request:
- If the request meets certain requirements, the server passes it directly to the RDBMS for processing. This is called Automatic Passthru.
- If the syntax of the request does not conform to the syntax of the RDBMS, the server translates the request into internal DML and passes it to the adapter. The adapter generates adapter-specific DML and passes the request to the RDBMS for processing. This is called SQL translation.
Processing ibi WebFOCUS Requests
When the server receives a WebFOCUS request, it passes it to the adapter. The adapter analyzes the request and generates DBMS-specific DML for those parts of the request that have DML equivalents. As WebFOCUS is a more robust language than DML, some parts of the request may not have such equivalents. The adapter then passes the generated DML to the DBMS for processing. When the answer set is returned by the DBMS, WebFOCUS processes those parts of the request that the adapter could not pass to the DBMS.
Throughout this manual there are descriptions of some useful features that are not supported by SQL syntax but are supported by WebFOCUS syntax.
For complete information about the WebFOCUS language, see the following manuals:
- Creating Reports With ibi™ WebFOCUS® Language
- Describing Data With ibi™ WebFOCUS® Language
- ibi™ WebFOCUS® Developing Reporting Applications
Relational and Non-Relational Adapters
Adapters can retrieve answer sets from both relational and non-relational data sources. Since the architectures of relational and non-relational data structures vary, the relational and non-relational adapters adjust for these differences. For example, relational adapters are designed to handle data sources that contain data in rows and columns in tables, while non-relational adapters are designed to accommodate the architecture of each distinct data source, for instance, a hierarchical or network data source, or a sequential or indexed file system.
The following table lists key features of relational and non-relational adapters:
|
Feature |
Relational Adapters |
Non-Relational Adapters |
|---|---|---|
|
DEFINE (virtual field) in Master File |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Access Control |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Transaction Management Commands |
Yes |
No |
Relational and non-relational adapters:
- Allow the data source to perform the work required to join, sort, and aggregate data. Therefore, the volume of data source-to-server communication is reduced, resulting in better response times for users. The adapter tries to optimize the queries as best it can.
- Communicate with the data source through DML statements. You
can view these DML statements with traces provided by the trace
facilities. These traces are helpful for debugging your procedure
or for adapter performance analysis. Note that traces:
- Are common for all relational adapters.
- Vary for non-relational adapters to accommodate the differences in data structures and DML calls.
- Support both DEFINE (virtual) fields and DBA.
- Relational adapters include a variety of COMMIT, connection, and thread control commands that enable Database Administrators to control the opening and closing of connections and choose when to commit or rollback transactions. This level of transaction control is not supported by non-relational adapters. In Full-Function Server mode, COMMIT/ROLLBACK will be propagated to all relational data sources local to the server. If the hub is active, a COMMIT will be issued against remote data servers as well. All PREPARE handles are cleared (this is a Broadcast COMMIT).
To address these similarities and differences, this manual contains:
- General components with information that is common to all adapters, as well as information that is common either to all relational or to all non-relational adapters.
- Customized components with information that applies to specific adapters.
Supported Adapters
For specific information about supported releases and platforms, see the following table, which summarizes this information:
* The underlying databases for these adapters do not necessarily run directly on the IBM i platform (formerly known as i5/OS). However, they may be configured and accessed.
Functionally Stabilized Adapters
The following adapters are functionally stabilized.
| Adapter | Windows | UNIX | z/OS |
IBM i (formerly i5/OS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1010data |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
| Adabas® |
|
Yes |
|
|
| Apache Kafka® |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| CA IDMS® /DB |
|
|
Yes |
|
| CA IDMS /SQL |
|
|
Yes |
|
| Caché® |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
| Couchbase | Yes | Yes | ||
| DATACOM®/DB |
|
|
Yes |
|
| ElasticSearch® |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| Essbase |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
| Informix CISAM |
|
Yes |
|
|
| JD Edwards® EnterpriseOne |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| JD Edwards World |
|
|
|
Yes |
| Lawson |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| Lotus Notes® |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| Model 204 |
|
|
Yes |
|
| MongoDB | Yes | Yes | ||
| PeopleSoft® |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
| Progress® |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
| RServe |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| RStat Complied Models |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| SAP ERP |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
| SAP® BW® |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
| Supra | Yes | |||
| TIBCO ModelOps | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |