Preparing the SAP Environment
The Server requires the SAP RFC SDK to communicate with the SAP Application Server. The location of the RFC SDK depends on the platform specific search path.
Platform dependent search path for shared libraries (RFC SDK):
- Windows:
Environment variable PATH.
- AIX:
Environment variable LIBPATH.
- z/OS:
Environment variable LIBPATH.
- All other UNIX platforms:
Environment variable LD_LIBRARY_PATH.
If the server does not start, and indicates that some NLS libraries cannot be found, try:
EXPORT NLSUI_7BIT_FALLBACK=YES
You will use SAP GUI to logon to SAP and prepare the environment.
A Developer Key is required for the SAP user ID of the administrator. (The system prompts for the Developer Key if it has not been entered previously.)
USER IDs are required for authorization, with variations in privilege assignments based on the nature of the users responsibilities. Basic privileges are assigned to users who only need to execute procedures (focexecs). Administrative privileges are assigned to users who need to perform a variety of administrative functions for the Adapter for SAP. For example, the Adapter for SAP generates ABAP/4 programs dynamically at run time. This is done using adapter components uploaded into the SAP system during the configuration of the adapter, a task that requires administrative privileges.
For related information, refer to the following lists of processing objects: List of Authorization Objects, Fields, and Required Values for USER and List of Authorization Objects for Background Processing.
List of Authorization Objects, Fields, and Required Values for USER
The following charts reflect any differences that apply for basic users and adapter administrators.
S_RFC: Authorization check for RFC access
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
|
ACTVT (Activity) |
16 (Execute) |
|
RFC_NAME (Name of RFC to be protected) |
For administrators: AQRC, SDTX, SLST, SUTL, SYST, Z*** For basic users: SYST, Z*** |
|
RFC_TYPE (Type of RFC object to be protected) |
FUGR (function group) |
S_TCODE: Authorization check for Transaction Start
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
|
TCD (Transaction code) |
For administrators: S001, SE09, SE11, SE11_OLD, SE13, SE37, SE38, SE80, SU53 For basic users: S001, SE37, SE38, SU53 |
S_ADMI_FCD: System Authorizations
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
|
S_ADMI_FCD (System administration functions) |
For administrators: MEMO |
S_C_FUNCT: C Calls in ABAP Programs
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
|
ACTVT (Activity) |
For administrators: 16 (Execute) |
|
CFUNCNAME (Name of a CALLable C routine) |
For administrators: SYSTEM |
|
PROGRAM (ABAP program name) |
For administrators: SAPLSTRF, SAPLSTRI |
S_DATASET: Authorization for File Access
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
|
ACTVT (Activity) |
For administrators: 33, 34, A6 |
|
FILENAME (Physical file name) |
For administrators: * |
|
PROGRAM (ABAP program name) |
For administrators: * |
S_TABU_DIS: Table Maintenance (via standard tools such as SM30)
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
|
ACTVT (Activity) |
For administrators: 03 |
|
DICBERCLS (Authorization group) |
For administrators: SS, &NC& |
S_DEVELOP: ABAP Workbench
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
|
ACTVT (Activity) |
For administrators: 01, 02, 03, 07, 16, 40 |
|
DEVCLASS: Development class for transport system |
For administrators: * |
|
OBJNAME: Object name |
For administrators: * |
|
OBJTYPE: Object type |
For administrators: DEVC, FUGR, PROG, TABL, TABT |
|
P_GROUP: Authorization group with ABAP programs |
For administrators: * |
S_TRANSPORT: Transport Organizer
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
|
ACTVT (Activity) |
For administrators: 01 |
|
TTYPE (Request type (Change and Transport System)) |
For administrators: DTRA, TASK |
List of Authorization Objects for Background Processing
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
|
S_BTCH_ADM |
N (unless you want the user to have administrative rights for Background jobs) |
|
S_BTCH_JOB |
RELE |
Preparing the SAP Environment for Adapter Components
The Adapter for SAP generates ABAP/4 programs dynamically at run time. This is done using adapter components uploaded into the SAP system during the configuration of the adapter. Prior to uploading the components, the SAP system has to be prepared.
To prepare the SAP environment for the adapter components, perform the following steps:
- Log on to SAP.
- Create the Development Class or Package.
- Create the Function Group.
- Activate the Function Group.
- Verify the Function Group.
Log on to SAP
- Procedure
- Launch SAP
logon. In a standard SAP GUI installation, the executable file resides
in \Program Files\SAP\FrontEnd\SAPgui\saplogon.exe. The SAP Logon
dialog opens.
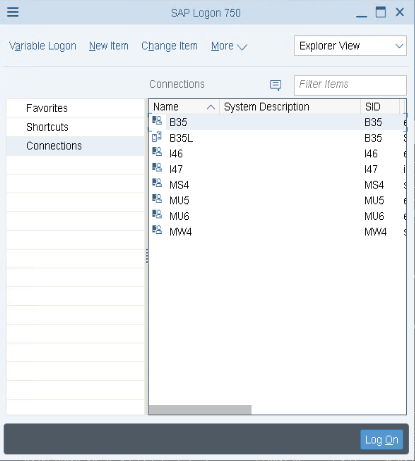
If the list is empty, create a new entry.
- Click New. The New Entry dialog
opens.
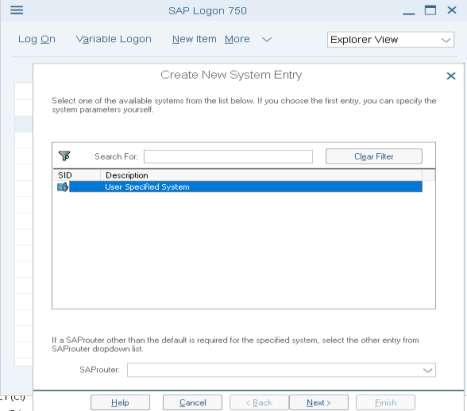
- Type the Description and Application Server, and select
the System Number. In most cases, the SAP Router String is not needed,
but check with your assigned SAP technical contact.
In the Application Server field, type either the SAP application server network name or IP address.
Click OK to create a new entry on the Logon list.
- Click New. The New Entry dialog
opens.
- Select the
entry on the list and click Logon.
A logon page prompting for a user ID and password appears. Logon to the system. Note that if the user ID is being used for the first time, the system will ask for the password to be changed.
Create a Development Class or Package
- Procedure
- Execute transaction SE80 to start the Object Navigator.
- Type the Development Class or Package name for the installation
of the Adapter for SAP (for example, ZIBI).
Note: The Development Class or Package name can be a maximum of 14 characters and must follow SAP naming conventions for customer objects.
- Click Display
 .
.
The system responds: Development Class or Package ZIBI does not exist.
- Click Yes to create the object.
- Type a short description for the Development Class or Package, for example, IBI-Created.
- Accept all
displayed defaults and click Create.
The system generates a unique Change and Transport System (CTS) request #.
- Save this CTS request # for deployment of the adapter to other SAP systems.
- Click Continue.
Create a Function Group
- Procedure
- Execute transaction SE80 to start the Object Navigator.
- From the pull-down menu, select Function Group.
- Type the same Development Class or Package name for the installation of the Adapter for SAP that you specified in Create a Development Class or Package (for example, ZIBI).
- Click Display.
The system responds: Function Group ZIBI does not exist.
- Click Yes to create the object.
- Enter a description for the Function Group.
- Accept all displayed defaults and click Save (unless otherwise directed by an SAP Basis Administrator).
- Under Create Object Directory Entry, type the same characters assigned to the Development Class and click Save.
- Under Prompt for transportable change request, type the CTS request # assigned during the creation of the Development Class or Package.
- Click Continue.
Deactivate the Unicode Checks
This procedure applies only to SAP Release 4.7.
- Procedure
- Execute transaction SE80 to start the Object Navigator.
- From the pull-down menu, select Function Group.
- For Function Group value, type the name of the function group you created (for example, ZIBI).
- Click Display.
The object window shows an open folder with the name of the function group and a closed folder named Includes.
- Right-click the function group name (for example, ZIBI)
and select Change from the pop-up menu.
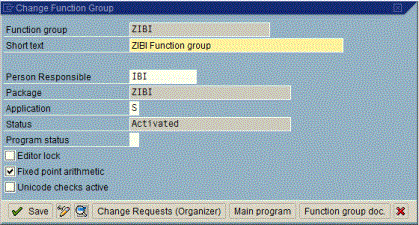
- Deselect the Unicode checks active checkbox and click Save.
Activate a Function Group
- Procedure
- Execute transaction SE80 to start the Object Navigator.
- From the pull-down menu, select Function Group.
- For Function Group value, type the name of the function group you created (for example, ZIBI).
- Click Display.
The object window shows an open folder with the name of the function group and a closed folder named Includes.
- Right-click the function group name (in this example,
ZTST) and select Activate from the pop-up
menu.
A new window lists all inactive objects. Note that the object name now begins with SAPL.
Make sure the object for the function group ZTST is selected.
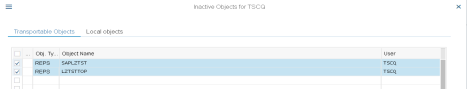
- Click Continue.
Verify a Function Group
- Procedure
- Execute transaction SE80 to start the Object Navigator.
- From the pull-down menu, select Function Group.
- For Function Group value, type the name of the function group you created (for example, ZIBI).
- Click Display.
- Right-click the ZTST folder and select Check - Extended Check.
- Select Perform
Check.
You should get a report similar to the following:
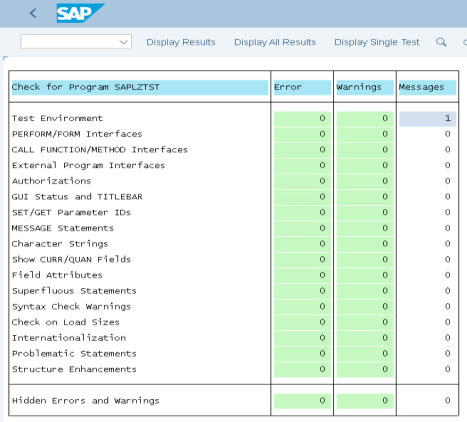 Note: If you encounter errors or warnings during this step, resolve them at the SAP layer before continuing with the installation of the Adapter for SAP.
Note: If you encounter errors or warnings during this step, resolve them at the SAP layer before continuing with the installation of the Adapter for SAP. - Double-click the error line for detailed information about the error.
The SAP environment is now prepared for the next step of function module upload from the WebFOCUS Reporting Server browser interface.
Customizing the Transport/Promotion of the ZXXX* Temporary Objects
During the installation of the SAP adapter, a set of function modules, including two temporary objects like ZXXXBTCH and ZXXXREPTS, are uploaded and registered in the SAP repository. In preparation for the transport from the QA to DEV to PROD application servers, the ZXXXBTCH object must be assigned to the ZXXX development class. Otherwise, ZXXXBTCH will be assigned to the development class $TMP or remain unassigned, either of which can cause the transport to fail.
Transport Control
SAP provides a transport control program (tp) to handle release upgrades and transports among SAP systems. The transport control program:
- Keeps track of transports.
- Exports and imports objects in the correct order.
- Ensures that imports into a target system are performed in the same order as the exports from the source system(s). (Processing of imports out of order can result in severe inconsistencies in the target system, which are difficult to diagnose.)
- Enables you to perform exports and imports separately.
During an export, the objects to be transported are extracted from the database of the source system and stored in files of the operating system.
During the import, the objects are added to the database of the target system (according to the transport function recorded in the task).