LPAD: Left-Padding a Character String
LPAD uses a specified character and output length to return a character string padded on the left with that character.
Pad a Character String on the Left
LPAD(string, out_length, pad_character)
where:
string
Fixed length alphanumeric
Is a string to pad on the left side.
out_length
Integer
Is the length of the output string after padding.
pad_character
Fixed length alphanumeric
Is a single character to use for padding.
Left-Padding a String
In the following request against the WF_RETAIL data source, LPAD left-pads the PRODUCT_CATEGORY column with @ symbols:
DEFINE FILE WF_RETAIL LPAD1/A25 = LPAD(PRODUCT_CATEGORY,25,'@'); DIG1/A4 = DIGITS(ID_PRODUCT,4); END TABLE FILE WF_RETAIL SUM DIG1 LPAD1 BY PRODUCT_CATEGORY ON TABLE SET PAGE NOPAGE ON TABLE SET STYLE * TYPE=DATA,FONT=COURIER,SIZE=11,COLOR=BLUE,$ END
The output is:
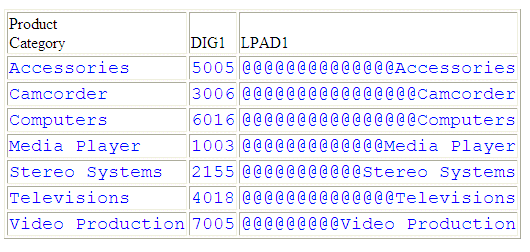
LPAD left-pads the PRODUCT_CATEGORY column with @ symbols:
LPAD(PRODUCT_CATEGORY,25,'@')
For Stereo Systems, the output is @@@@@@@@@@@Stereo Systems.
Usage Notes for LPAD
- To use the single quotation mark (') as the padding character, you must double it and enclose the two single quotation marks within single quotation marks (LPAD(COUNTRY, 20,''''). You can use an amper variable in quotation marks for this parameter, but you cannot use a field, virtual or real.
- Input can be fixed or variable length alphanumeric.
- Output, when optimized to SQL, will always be data type VARCHAR.
- If the output is specified as shorter than the original input, the original data will be truncated, leaving only the padding characters. The output length can be specified as a positive integer or an unquoted &variable (indicating a numeric).