The output format of your content determines the type of file that is generated when that content is run. Different output types enable different levels of run-time interactivity, embedding behavior, and compatibility with outside programs, so you can change the output type depending on how you intend to use your content and who the intended audience is.
To change the output format of a report created in WebFOCUS Designer, click the Style tab ![]() , and select an option from the Output Format drop-down menu. The following options are available:
, and select an option from the Output Format drop-down menu. The following options are available:
- HTML
- AHTML
- PPTX
- XLSX
- Select at runtime
The HTML and AHTML options are browser-based formats, while PDF, PPTX, and XLSX output can be downloaded, distributed, and opened using standard office suite software. The Select at runtime option provides the ability to run a report using any of the other output formats. Users can select a format at runtime in which to run the report.
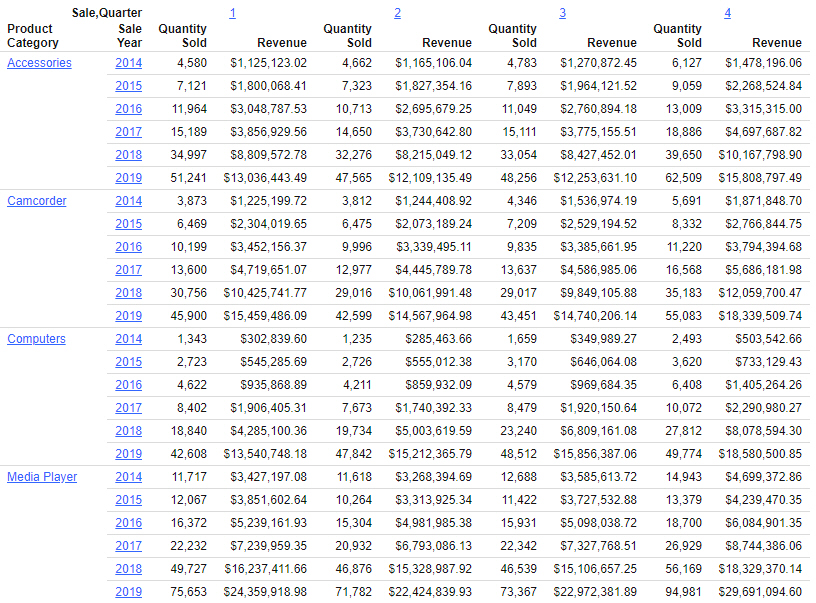
The HTML output format generates a basic report that can be run in a web browser. The simplicity of the HTML format makes it extremely flexible. Run-time interactivity is available in the form of hyperlinks, which can be used to drill into data hierarchies used in the report, known as Auto Drill, or connect to outside content through shared parameters associated with sort fields in the report, known as Auto Linking. An example of an HTML report with Auto Drill hyperlink behavior is shown in the following image.
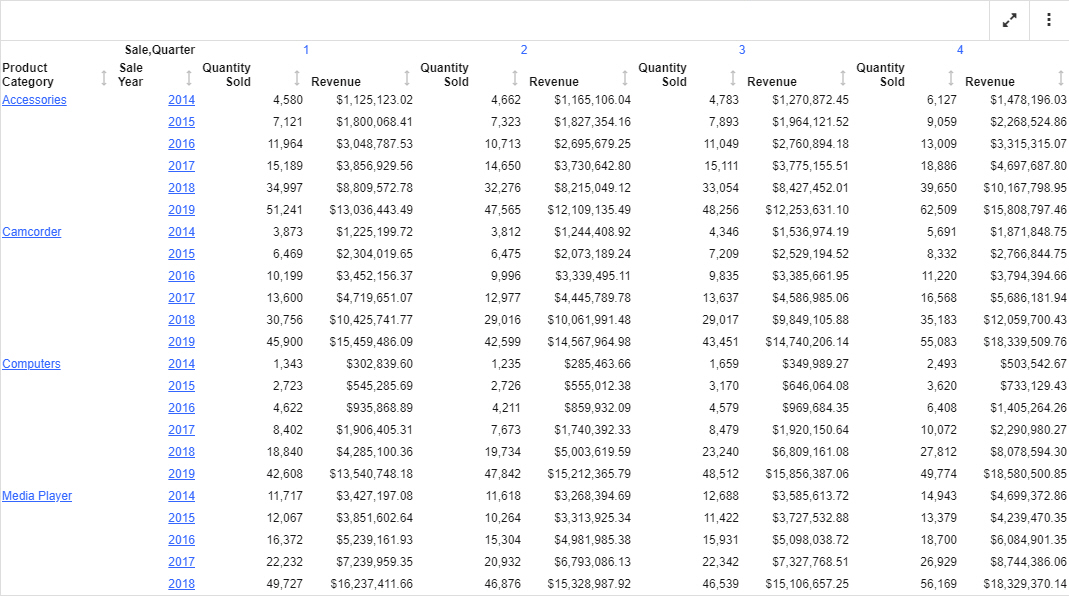
When you click a column header, another set of options appears, allowing you to explore and transform the report, as shown in the following image.
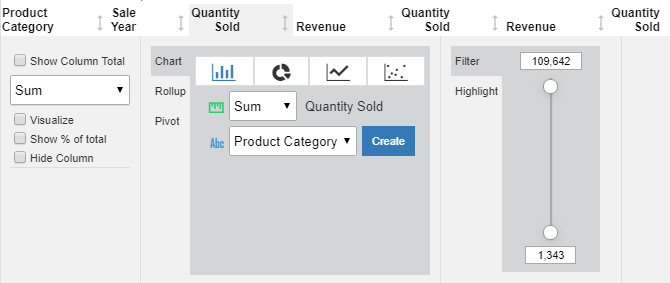
You can also make your report output available to common desktop tools by using the PDF, PPTX, or XLSX output formats.
When you run a report that uses PDF, PPTX, or XLSX as the output format, a file is created in a .pdf, .pptx, or .xlsx format, respectively. The file opens in a browser viewer for that file type or is downloaded in the browser. The file can be opened using a tool compatible with the output file type.
Certain features may not be available, depending on the file type. For example, the PDF, PPTX, and XLSX output formats do not support Auto Linking or Auto Drill, since a single, self-contained file is created.
Page breaks also behave differently, depending on the output file type. In PDF, a separate page is created for each page break, and in PPTX, a separate slide is created. In XLSX, however, separate pages of a report are output to the same worksheet, with a set of column headers for each section, similar to how page breaks work in the HTML output format.
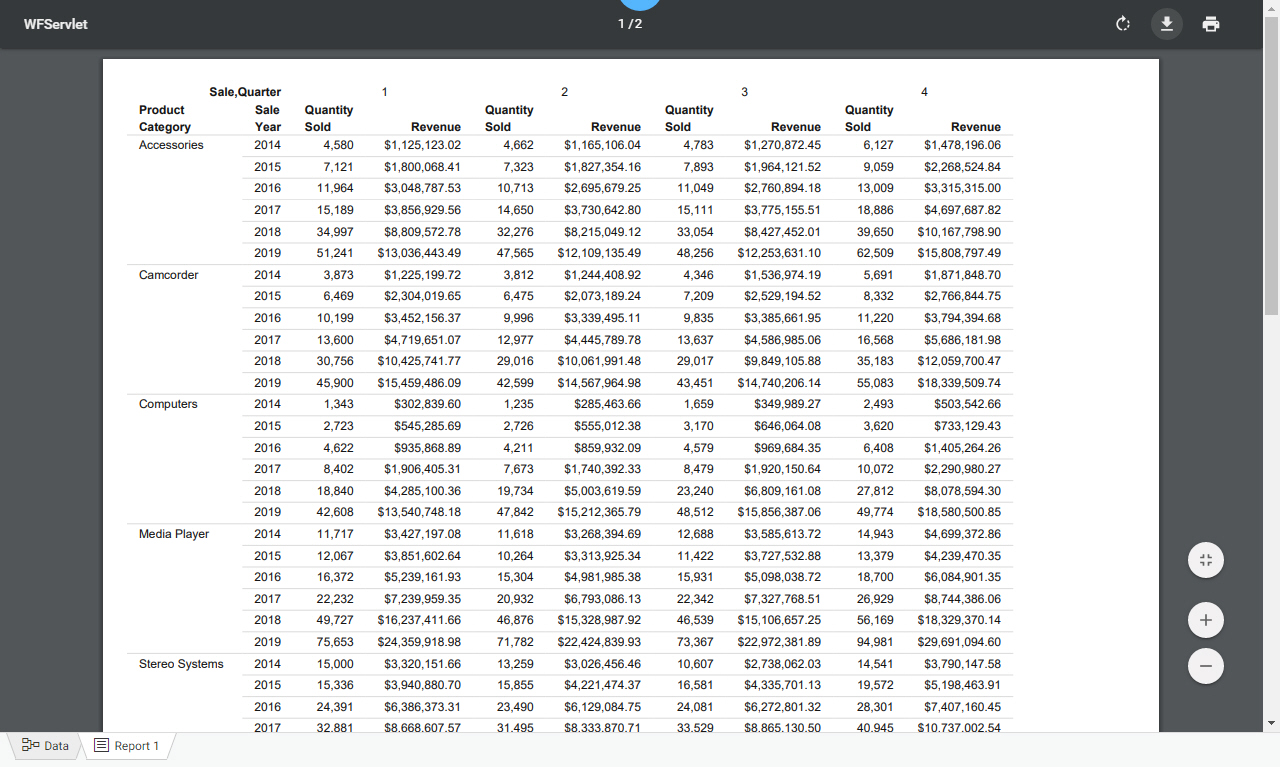
The following image shows an example of a report created using the PDF output format viewed in a web browser.
The following image shows an example of a report created using the PPTX output format viewed in Microsoft PowerPoint 2007.
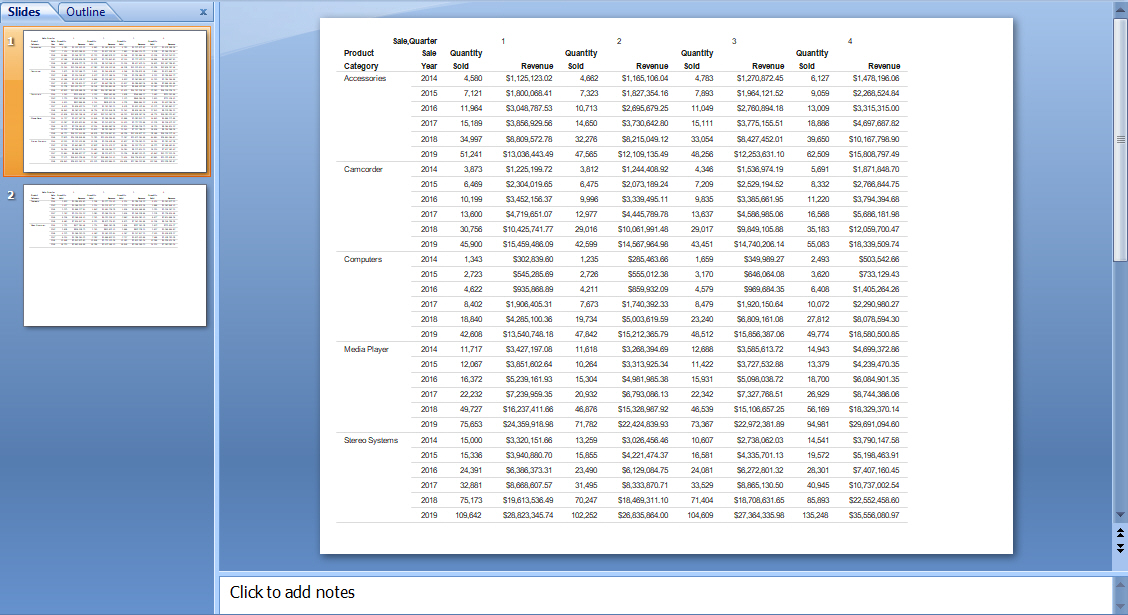
The following image shows an example of a report created using the XLSX output format viewed in Excel 2007.
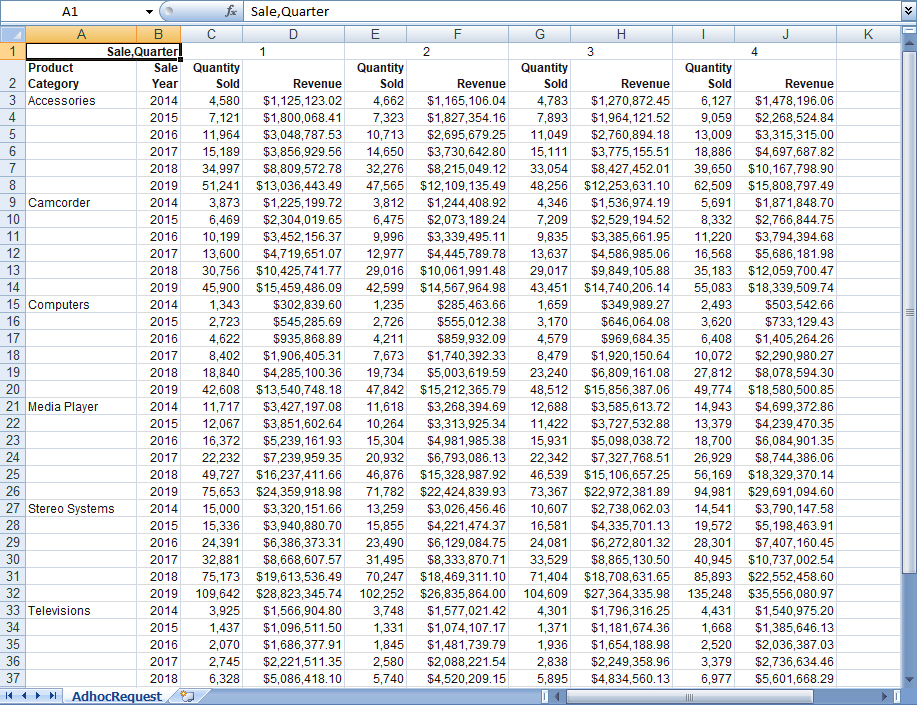
You can use the Select at runtime option to enable any of these output formats. When a report using the Select at runtime option is run, the Responsive Autoprompt page opens. You can select an output type from the drop-down menu, as shown in the following image.
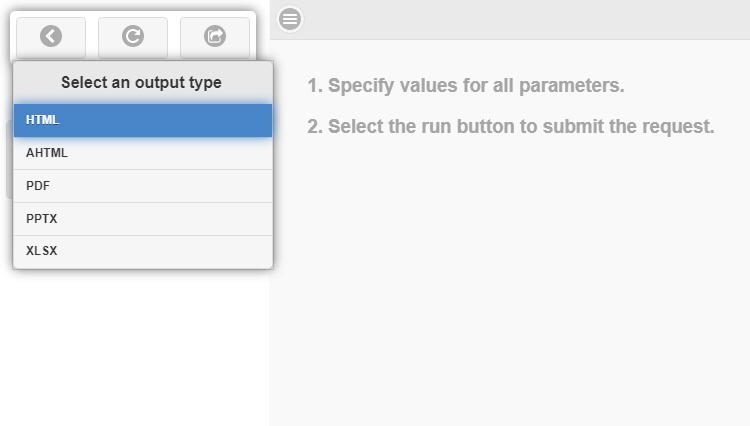
When you click the Run button  , the report runs in the selected output format.
, the report runs in the selected output format.